Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews043
Download as PDF
Open to 21 July 2021. The consultation document notes that the 2019 evaluation of the 1991 UWWTD concluded that it is largely fit for purpose, but some aspects need to be improved, and updates should align with Green Deal environment and climate objectives. The consultation is a general public questionnaire, plus additional questions for experts and operators – you do not have to answer all questions. General questions ask what you see as important risks from municipal wastewater, key mitigation actions, priorities for action (nutrients are one of seven proposed priorities), how to improve protection of nutrient “Sensitive Areas”, addressing micropollutants, circularity (proposals include recovery obligations for phosphorus and other materials).
In particular, the question (p32 of the questionnaire in PDF) “How appropriate are the following proposed measures for building a more circular waste water treatment sector?” offers the option “Setting minimum levels for recovering phosphorous and other materials” (please NOTE: ‘5’ = important). ESPP will propose, under comments to this question, to Include materials from wastewater as a priority stream for development of EU End-of-Waste criteria under the Circular Economy Action Plan.
“Water pollution – EU rules on urban wastewater treatment”, Eu public consultation open to 21 July 2021.
The 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference (ESPC4) is postponed (because of Covid). New dates are 20-22 June 2022 in Vienna.
Updates: see www.phosphorusplatform.eu and https://phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews054
Download as PDF
4th Phosphorus in Europe Research Meeting (PERM)
Registration now open!
Events
AquaEnviro Wastewater Resource Recovery Conference: 18 May 2021
SYSTEMIC: nutrients from biowaste, 27 May 2021
4th Phosphorus in Europe Research Meeting (PERM): 2 June 2021
IFA plant nutrition innovation conference: 8-10 June 2021
Nutrients, aquatic methane emissions and climate change: 22-27 June 2021
New dates for ESPC4: 20-22 June 2022
Policy
EU consultation on Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive (UWWT)
Joint action for End-of-Waste status for materials recycled from wastewaters
“Environmental Hazard Potential” of the CRM “Phosphate Rock”
Sewage Sludge Directive revision workshop
Safe recycling of nutrients to animal feed
European Parliament on Circular Economy
Fertilising Products Regulations
Digestate and compost in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation
France proposes “half waste” status for sewage sludge composts
Manure and Animal By Products in “STRUBIAS”
ESPP proposals for “CMC-WW”
Industry
Florida: state of emergency for disused phosphogypsum pond
New phosphate production planned in Sweden
Irish Water and Ostara to produce 14 t/day of struvite
Benefits of struvite
CRU Phosphates Conference 2021
Global phosphate market outlook
New EU Fertilising Products Regulation (FRP)
Fertiliser market trends in Europe
How EU policies will influence phosphorus use
EasyMining phosphorus recycling
Glatt PHOS4green
Phosphoric acid from low-grade phosphate rock
P4: outlook for a Critical Raw Material
Recycled nutrients in Organic Farming
RELACS: recycled nutrients in Organic Farming
Environment and health
Perspectives for acceptance of recycled nutrients in Organic Farming
Research
Eutrophication significantly increases greenhouse emissions
Biochar pyrolysis removes antibiotic resistance genes
Differing positions on sewage sludge use in agriculture
Phosphate fertiliser value of dairy processing sludges
Stay informed
ESPP members
4th Phosphorus in Europe Research Meeting (PERM)
Registration now open!
Online, 2nd June 2021
Event web page: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/PERM4
Registration: https://us02web.zoom.us/meeting/register/tZ0qcOmrrjouEtRlibbtiMrcZVSKb4MEvYyc

Events
AquaEnviro Wastewater Resource Recovery Conference: 18 May 2021
One day conference on resource recovery from wastewaters and biosolids, covering nutrient recovery, hydrogen and other materials: experience from pilot and full scale plants; market pull, user confidence and business models, regulatory framework, links to net zero carbon 2030 agenda for the UK wastewater industry.
“The Art of the Possible: Resource Recovery from Wastewater and Bioresources”, May 18th 2021 online https://conferences.aquaenviro.co.uk/events/conferences/resource-recovery-from-wastewater/
SYSTEMIC: nutrients from biowaste, 27 May 2021
Webinar “Enabling a Circular Economy: How to encourage a viable agricultural market for nutrients recovered from biowaste”, with William Neale, Advisor, European Commission DG Environment, Jan Huitema, Member of the European Parliament, Ludwig Hermann, Proman and ESPP President, Oscar Schoumans, Wageningen University and Research, Annabelle Williams, European Landowners Association.
SYSTEMIC (Horizon 2020 project) webinar, Thursday 27th May: 13h30-15h30 CEST Registration
4th Phosphorus in Europe Research Meeting (PERM): 2 June 2021
This meeting, co-organised by ESPP, Biorefine Cluster Europe and ETA Renewable Energies, will link science, industry, agriculture and policy makers. EU-funded projects on nutrient sustainability and phosphorus recycling (Horizon2020, Interreg, LIFE…) and national and company nutrient projects will present, enabling dialogue and synergies. PERM will address how to improve uptake of project recommendations by policy makers and users, through to market, and identify perspectives for research and policy, and implementation gaps.
In parallel to PERM, ESPP is updating our online ‘inventory’ of nutrient-related R&D projects here.
PERM4 – online – 2nd June 2021: event website: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/PERM4
Registration: https://us02web.zoom.us/meeting/register/tZ0qcOmrrjouEtRlibbtiMrcZVSKb4MEvYyc
Proposals are welcome for presentations of studies into what factors in nutrient R&D projects improve uptake of conclusions by policy makers, industry and users.
If you wish your project to be included in the programme and/or added to the inventory of nutrient R&D projects, please contact
IFA plant nutrition innovation conference: 8-10 June 2021
The global fertiliser industry (International Fertilizer Association) “Smart & Green” conference will bring together scientists, industry and start-up technologies around controlled-release and stabilised fertilisers, biostimulants, incentivising and funding fertiliser innovation, digital fertiliser management, organic fertilisers and nutrient recycling.
IFA Smart & Green “where tech meets plant nutrition”, 8-10 June, online here.
Nutrients, aquatic methane emissions and climate change: 22-27 June 2021
ASLO (Association for the Sciences of Limnology and Oceanography) Special Session (SS06) on Methane Accumulation in Oxic Aquatic Environments: Sources, Sinks and Subsequent Fluxes to The Atmosphere. Within the 2021 Aquatic Sciences Meeting (online, 22-27 June 2021). In partnership with the Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries (IGB) and ASLO, ESPP and SPA will follow-up with a webinar to exchange between science, water stakeholders and policy makers on implications of aquatic methane emissions for nutrient management. Proposals for input are welcome.
ASLO special session on methane in oxic aquatic environments: https://www.aslo.org/2021-virtual-meeting/session-list/
Contact Mina Bizic
To contribute to the ESPP- SPA- IGB webinar: contact
New dates for ESPC4: 20-22 June 2022
The 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference (ESPC4) is postponed (because of Covid). New dates are 20-22 June 2022 in Vienna. PERM, the European Phosphorus Research Meeting will be held virtually 2nd June 2021, see below.
Updates: see www.phosphorusplatform.eu and https://phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
Policy
EU consultation on Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive (UWWT)
Open to 21 July 2021. The consultation document notes that the 2019 evaluation of the 1991 UWWTD concluded that it is largely fit for purpose, but some aspects need to be improved, and updates should align with Green Deal environment and climate objectives. The consultation is a general public questionnaire, plus additional questions for experts and operators – you do not have to answer all questions. General questions ask what you see as important risks from municipal wastewater, key mitigation actions, priorities for action (nutrients are one of seven proposed priorities), how to improve protection of nutrient “Sensitive Areas”, addressing micropollutants, circularity (proposals include recovery obligations for phosphorus and other materials).
In particular, the question (p32 of the questionnaire in PDF) “How appropriate are the following proposed measures for building a more circular waste water treatment sector?” offers the option “Setting minimum levels for recovering phosphorous and other materials” (please NOTE: ‘5’ = important). ESPP will propose, under comments to this question, to Include materials from wastewater as a priority stream for development of EU End-of-Waste criteria under the Circular Economy Action Plan.
“Water pollution – EU rules on urban wastewater treatment”, Eu public consultation open to 21 July 2021.
Joint action for End-of-Waste status for materials recycled from wastewaters
Over 120 (to date) industry and public water operator federations, companies and research institutes, have signed a joint letter to the European Commission requesting that materials recovered from wastewaters be included in the priority streams for development of EU End-of-Waste criteria, currently being defined under the EU Circular Economy Action Plan. Further organisations are still welcome to join this initiative and sign the letter (see below).
Recycled materials suggested include algae or plant biomass grown using wastewater; fibres, fatty acids, proteins, gums, fats and oils; phosphates and other chemicals or minerals for industrial applications (the route to EU End-of-Waste status for fertiliser applications already exists via the EU Fertilising Products Regulation); CO2; grit and sand. The request was initiated by ESPP and signatories to date include Eureau (European Federation of National Associations of Water Services), Aqua Publica Europea (European Association of Public Water Operators), EABA (European Algae Biomass Association), Biorefine Cluster Europe, Water Alliance Netherlands, AquaMinerals BV, ACR+ (Association of Cities and Regions for sustainable Resource management) …
Further signatory organisations are welcome: contact
The joint letter can be consulted here: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/regulatory
“Environmental Hazard Potential” of the CRM “Phosphate Rock”
The final report (Task 2) to the European Commission for preparation of the new working plan for the Ecodesign Directive proposes as a new horizontal Ecodesign initiative “Scarce materials and critical raw materials”, because “very relevant in relation to the circular economy action plan and also in relation to the individual product’s lifecycle”.
Phosphate Rock, which is on the EU Critical Raw Materials list, is identified to have “High EHP” (Environmental Hazard Potentials). This is based on Dehoust et al. 2020 (UBA report).
Dehoust classifies Phosphate Rock as medium concern for governance, but high impact for global material and energy flow and for aggregated Environmental Hazard Potentials. The latter is based on suggested medium EHP for heavy metals, accidental hazards due to landslides etc, water stress and deserts, protected areas and governance, but high for association with radioactivity, surface mining and use of chemicals in processing (acids, flotation). This seems to indicate in some cases misinformation, for example acid used in processing phosphate rock is systematically a by-product. The report concludes that Phosphate Rock is “environmentally critical”.
The EU Critical Raw Material “Phosphorus”, that is P4, is not considered in the Ecodesign report, which is inappropriate in that P4 and P4-derivatives are essential for e.g. electronics manufacture and plastics fire safety, both of which are necessary for many energy using products addressed by EU Ecodesign criteria. This may be because “Phosphorus” (P4) is not considered in the Dehoust / UBA document.
Task 2 “Identification of product groups and horizontal measures”, final draft, March 2021.
Task 3 “Preliminary analysis of product groups and horizontal initiatives”, “Scarce and environmentally critical raw materials”, draft, February 2021.
https://www.ecodesignworkingplan20-24.eu/
“Environmental Criticality of Raw Materials, An assessment of environmental hazard potentials of raw materials from mining and recommendations for an ecological raw materials policy”, G. Dehoust et al., UBA TEXTE 80/2020 https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/sites/default/files/medien/1410/publikationen/2020-06-17_texte_80-2020_oekoressii_environmentalcriticality-report_.pdf
Sewage Sludge Directive revision workshop
A stakeholder workshop organised for the European Commission (20-21 April, online, over 270 participants) addressed the revision of the EU Sewage Sludge Directive (SSD) 86/278/EEC. The European Commission, DG Environment, explained that the objectives of this Directive, in the 1980’s, were to encourage the recycling of sewage sludge to agriculture and to ensure safety. The 2014 evaluation of the SSD here concluded that it is effective in returning carbon to soil, but inadequate for promoting the Circular Economy, or for controlling pollutants other than heavy metals, and that a number of Member States have today stricter rules. The 2019 evaluation of the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive concluded that better account should be taken of energy use and greenhouse emissions related to wastewater treatment, and that materials recovery and safe use should be promoted by the SSD. The revision of the SSD should also take into account the EU soil and pharmaceuticals strategies.
Workshop presentations included:
- Alberto Pistocchi, European Commission JRC, modelling toxicity risks of sewage sludge to surface waters and soil and concentrations of micropollutants in soil, crops and humans;
- Rachel Hurley, NIVA, microplastics in sewage sludge and in soils, and trnasfer to surface waters;
- Aoife Kyne, Irish Water and Anders Finnson, Swedish Water Association, quality standards systems for sewage biosolids and actions to reduce pollutants at source;
- Christian Kabbe, EasyMining, different routes for phosphorus recovery;
- Bertrand Vallet, Eureau, valorisation of sewage biosolids beyond agriculture, such as greening of disused mines or ski slopes;
- Dries Huyguens, JRC, direct and indirect greenhouse emissions from sewage treatment: energy use, NOx emissions, chemicals use, on-site renewable energy, displaced emissions from nutrient or materials recovery;
- Jóannes Jørgen Gaard, consultant to the Denmark Environment Ministry, significance of NOx emissions in sewage treatment and opportunities for reducing these.
Workshop conclusions, after breakout sessions, suggested that safe reuse of sewage biosolids in agriculture and recovery of secondary raw materials remain Circular Economy priorities, conform to Green Deal objectives, with possibilities also for biosolids reuse in land reclamation, for which standards should be defined. A priority is reduction of contaminants at source. There is a high potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in wastewater treatment, with questions on how and where to define greenhouse emissions objectives.
Possible policy measures proposed include permitting of emissions to sewers of sectors such as car-washes or hair salons, tracking contaminants to source, chemicals and product policies to avoid pollution at source, minimum recovery requirements for phosphorus and for other materials, and water reuse.
European Commission Sewage Sludge Directive web page and evaluation web page.
Safe recycling of nutrients to animal feed
The EU Animal Feed Regulation 767/2009 (art. 6(1) and annex II $1 and $5) excludes materials derived from wastewaters or manures irrespective of treatment or processing. Interpretation of this could pose problems for several recycling routes. For example, if phosphoric acid is recovered from sewage sludge incineration ash, it could be considered that this should not be placed on the commodity chemicals market or only with traceability indicating “not to be used in production of animal feed”.
ESPP has consulted operators and identified three relevant recycling routes, and has proposed to the European Commission to address these appropriately in order to lift potential obstacles to the Circular Economy:
- Phosphate chemicals recovered from ashes after incineration of sewage sludge or manure. Such chemicals can be used directly as animal feed (e.g. calcium phosphates) or sold as commodity chemicals (e.g. phosphoric acid). In that this is via ash, there should be no safety risk (incineration will eliminate pathogens).
- Nitrogen chemicals from ammonium gas stripping of sewage, manure or digestates, placed on the market as commodity chemicals. Evidence may need to be gathered to prove that pathogens are not transferred through the gas stripping and chemical processing.
- Algae or other biomass using wastewater or manure as growth medium: case specific safety assessment may be necessary.
ESPP’s letter is supported by a table detailing relevant processes, uses of recovered products, status of implementation and safety questions. Comments and input are welcome.
ESPP letter to the European Commission (DG SANTE), 7th May 2021, and supporting table: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/regulatory
European Parliament on Circular Economy
The European Parliament has voted a resolution on the new EU Circular Economy Action Plan. Parliament calls for binding EU targets to reduce material and consumption footprints and harmonised circularity indicators. Parliament calls for investigation of the sources, fate and effects of micro-plastics in wastewater treatment and for equipping new washing machines with microfibre filters. For the Key Product Value Chain “Food, Water and Nutrients”, Parliament calls for action to reduce food waste, separate collection of bio-waste, increased replacement of fossil materials with renewable bio-based materials, measures to close the agricultural nutrient loop, reduction of EU dependency on imported vegetable protein for animal feed and increased recycling of animal manure and other organic nutrients. Parliament calls for a circular approach in waste water treatment and “highlights that resources can be recovered from wastewater, ranging from cellulose via bioplastics to nutrients, energy and water”.
European Parliament, 10th February 2021, resolution P9_TA(2021)0040 on the New Circular Economy Action Plan https://www.europarl.europa.eu/doceo/document/TA-9-2021-02-10_EN.html
Fertilising Products Regulations
Digestate and compost in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation
Some 280 participants took part in the EBA – ECN webinar on 28th April.
David Wilken, German Biogas Association, presented conclusions of the EBA – ECN European survey on perspectives for CE-marking of compost and biogas under the EU Fertilising Products Regulation (FPR), when it enters into implementation in July 2022. The survey received over 100 answers from 21 countries. A large majority of respondents considered that the future CE-mark will be relevant for composts and digestates, in particular as a route to obtaining End-of-Waste status and better marketability, although many do not expect it to bring higher sales revenue and most expect it to involve significant administrative burdens and costs (in particular for conformity assessment). Most respondents consider that digestate will need some process of upgrading to achieve FPR criteria (CMC5), e.g. composting of digestate, drying, liquid/solid separation. Manure is seen as a very relevant input material, as well as sewage sludge (which is however excluded from EU FPR composts and digestates), as well as a wide range of other materials.
Theodora Nikolakopoulou, DG GROW, addressed a range of questions concerning application of the FPR to composts and digestates : manures and animal-by products as inputs – do they have to be pasteurised upstream of composting/digestion?; multiplication of conformity assessments if one compost producer supplies several fertiliser producers; definition of “sludge”; additives used upstream of the digestion process (e.g. flocculation agents) – must be declared as a distinct CMC; demonstrating conformity to PAH limits – does not necessarily mean testing …
Digestate valorisation under the EU Fertilising Products Regulation, webinar, 28 April 2021 here. Links to slides and conference report.
ESPP proposals for “CMC-WW”
As indicated I ESPP eNews n°53, the European Commission has proposed a new Component Material Category for the EU Fertilising Products Regulation, “CMC-WW”, open to any by-product coming from a “production process” or from a gas processing / gas emissions control process” which offers “high purity” and does not contain specified contaminants. ESPP has input proposals suggesting that:
- CMC-WW should be extended to “and derivates”, that is authorise use of such by-products as precursors for producing fertilising materials (not only use directly as such). E.g. by-product sulphuric acid used in phosphate fertiliser production, but not used itself in fertilisers.
- Not require testing for a contaminant if there is no reason for it to be present
- Replace the concept of “high purity” by safety requirements
ESPP submitted list of possible candidate materials for CMC-WW, collated from stakeholders, including: ammonium and sulphur compounds from gas cleaning, sulphur from oil refining, wax by-products, spent acids, ammonium salts from fire extinguisher refurbishment, mineral salts from waste incinerator ashes, by-products from drinking water production, PHBV from fatty acid fermentation, vivianite, nutrient residues from wood bioethanol production …
ESPP proposals to the European Commission on CMC-WW for by-products in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation www.phosphorusplatform.eu/regulatory
France proposes “half waste” status for sewage sludge composts
The French Government seems to be proposing a new legal status for composts and digestates containing sewage biosolids, manure, biowaste, etc. fulfilling the AFNOR NFU 44 095 standard (that is recognition as a French ‘national’ fertiliser product). These organic fertilisers would have “Waste” (not “Product”) status, but could be placed on the market and would NOT be subject to a spreading plan (the producer is responsible “until they are used by the farmer”).
The proposed decree would establish three categories A1 (“Product”), A2 = all composts and digestates containing sewage sludge, manure, food waste, etc (“Waste”, but not subject to waste spreading plan) and B (“Waste”, subject to spreading plan).
The official Opinion of the French national agency for health, food, environment etc. (ANSES) states that “the concept of these three categories is not intuitive and their appropriation is not immediate and the whole decree has to be read to understand the distinction” (20 pages!).
It is unclear to ESPP whether this “half-waste” status (waste, but not subject to waste management plan) is conform to European regulation (Waste Framework Directive). Also, if the producer responsibility stops when the A2 materials are spread on a field, given that they are spread as a “waste”, presumably the legal responsibility is transferred to each farmer, which is unlikely to be welcome.
Manure and Animal By Products in “STRUBIAS”
After consultation of stakeholders and operators, ESPP has written to the European Commission (SANTE and GROW) proposing approaches to the currently outstanding question of use of manure or other Animal By Products (ABPs) in “STRUBIAS” materials under the EU Fertilising Products Regulation (FPR), that is struvite and precipitated phosphates, ash-derived materials, pyrolysis and biochars.
The technically-finalised “STRUBIAS” criteria authorise the use of certain ABPs (inc. manure) as inputs for the three STRUBIAS categories, but only if ABP End Point “has been determined”. In order to move this forward, ESPP proposes:
- For ashes and ash-derived materials: ABP ash is already today widely used as fertiliser (e.g. poultry litter ash) so determining this ABP End Point should be a priority. In that the incineration combustion conditions defined in the STRUBIAS ash criteria are those recognised in the ABP Regulations as ensuring safety, this should be rapidly possible without requiring any data collection or risk assessment.
- For precipitated phosphates: there appears to be only one installation recovering struvite or precipitated phosphates (of STRUBIAS quality) from manure or ABPs in Europe (NuTriSep Geltz, Germany). Most manure struvite projects recover from digestate, where the digestor can already ensure the ABP End Point. ESPP therefore proposes no further action for this STRUBIAS category at present.
- For biochars: ESPP notes that the JRC report concluded that the pyrolysis conditions defined under STRUBIAS will ensure elimination of pathogens. ESPP requests that EFSA be mandated to define an ABP End Point for STRUBIAS biochars and pyrolysis materials.
ESPP letter to the European Commission on “Animal By Product End Points for EU Fertilising Products Regulation STRUBIAS materials”, 16th April 2021 www.phosphorusplatform.eu/regulatory
STRUBIAS criteria, as published for the public consultation February 2021
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12136-Pyrolysis-and-gasification-materials-in-EU-fertilising-products
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12162-Thermal-oxidation-materials-and-derivates-in-EU-fertilising-products
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12163-Precipitated-phosphate-salts-and-derivates-in-EU-fertilising-products
Industry
Florida: state of emergency for disused phosphogypsum pond
Up to 1.8 billion litres of polluted water are being released from a disused phosphate fertiliser factory’s 31 ha phosphogypsum pond, at Piney Point, near Tampa, Florida. The State Governor has declared a state of emergency and evacuated 300 households because the pond walls risk collapse, after starting to leak. The fertiliser factory was operated from 1966 to 1999. Media reports suggest that problems with the pond walls have been known for nearly 20 years. The water released from the pond contains phosphorus and nitrogen which will contribute to eutrophication of Tampa Bay and environmental NGOs have warned of risks of red tide algal blooms. The phosphogypsum in the pond also contains radioactive elements, but the Florida authorities say that levels in released water meet quality standards.
The Guardian UK, 4th April 2021, and other media online.
New phosphate production planned in Sweden
Two significant projects to “mine” phosphate from secondary resources in Sweden were presented at the Nordic Circular Materials Conference: 21-22 April 2021. In both cases, the projects will extract phosphate from apatite minerals (phosphate rock family) present in tailings of from iron ore mining, either from operating iron production sites or from stocked tailings from closed mines. The apatite is mainly rare earth element substituted fluorapatite, e.g. monazite, low in cadmium and arsenic, and the extraction of the rare earths with the phosphate will enable economic viability.
Ulrika Håkansson, LKAB, presented the company’s project treating ore tailings from iron mines in Kiruna and Malmberget. LKAB’s objective is to be operational by 2027, producing c. 50 000 tP/year (five times Sweden’s mineral P fertiliser consumption), as apatite concentrate, and c. 30% of EU rare earth needs.
Christer Lindqvist presented the Grängesberg Apatite Recovery Project, which aims to recover apatite from stocked tailings of the Grangesberg iron mine (John Matts dam), which was the world’s biggest iron ore producer in the nineteenth century. The following rare earth elements will be produced: Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Tb, Eu. Production will be around 13 000 tP/y, with the aim of starting within 3-4 years. The stocked tailings will support around seven years production, and this may be extended with a project to re-open the iron ore mine
Slides from Nordic Circular Materials Conference
LKAB secondary P-mining project: www.ree-map.com
Grängesberg Exploration Holding AB https://grangesbergexploration.se/
Irish Water and Ostara to produce 14 t/day of struvite
Murphy Ireland and Ostara have announced construction of a new Ostara Pearl® struvite recovery installation, with WASSTRIP®, as part of the upgrade of Irish Water’s Ringsend waste water treatment plant to 2.4 million p.e. capacity and conversion to biological phosphorus removal. Struvite production should start in 2023. Ringsend treats around 40% of Ireland’s wastewater and discharges into the nutrient Sensitive Area, Lower Liffey Estuary and Dublin Bay.
“Ostara and Murphy Partner to deliver part of Ringsend Wastewater Treatment Plant Upgrade Project for Irish Water”, 28th April 2021 press release.
Benefits of struvite
An article by Ostara in World Fertilizer provides an accessible summary of different benefits of recycling phosphorus from sewage as struvite, as operational with 22 commercial Ostara reactors running worldwide. The paper outlines the Planetary Boundary challenge for phosphorus and summarises environmental footprint study data comparing recovered struvite to production of mineral phosphate fertiliser (“emergy” approach, see ESPP eNews 35). Agronomic benefits of struvite are also outlined. Because struvite is crop-available (soluble in weak organic acids) but it is not water soluble, there is no risk of burning germinating crops, lower osmotic stress on soil micro-organisms, and reduced risks of phosphorus run-off to surface waters. Trials have shown that a combination of struvite and mineral fertiliser can increase yield and crop quality in potatoes, above standard fertiliser practice.
“Greener Cycle”, R. Leatherwood & R. van Springelen, Ostara, World Fertilizer, March 2021 http://bit.ly/3vf9ZFG
CRU Phosphates Conference 2021
“Phosphates 2021”, the only annual global event for the phosphate mining, processing, phosphorus chemicals and phosphate fertiliser industries, brought together some 560 delegates, online, 23-25 March 2021. The online format increased attendance by +50% compared to previous physical conferences.
https://www.phosphates2021.com/
Global phosphate market outlook
Chris Lawson and Glen Kurokawa of CRU outlined current world market trends for phosphates. After falling from around 2012 to end 2019, prices have risen rapidly since 2020, and are back to their 2012 levels (but still less than half the peak prices reached in 2008-2009). This recent increase mirrors increases in agricultural crop prices, and is driven by high world phosphorus demand (including in China, despite a long-term trend to better P efficiency here), low stocks, Covid supply disruption and specific impacts of new import tariffs for the USA.
CRU consider however that the current price level will not be sustained because increases in production (e.g. in China) will bring prices down somewhat in the coming year.
Over the next five years, significant increases in capacity will come online, e.g. in Morocco. Nonetheless prices are expected to remain high over this period because of continuing global demand and increasing costs of raw materials, wages, and (in China) environmental restoration measures.
Over coming decades, the phosphate market is expected to be impacted by long-term trends including continuing growth in agricultural demand, and circular economy initiatives (especially in Europe) to develop recycled products.
New EU Fertilising Products Regulation (FRP)
Johanna Bernsel, European Commission DG GROW, explained that the new regulation is very ambitious, widening to cover many different products related to nutrient use in agriculture, including biostimulants which can improve fertiliser nutrient use efficiency. The regulation has Circular Economy objectives, opening the European market for both recycled nutrient materials and recycling technology providers. It will also bring new protection to EU consumers, because for the first time contaminant limits are introduced for CE fertilisers, including for cadmium.
It is important to note that when the new Regulation enters into implementation in June 2022, producers will no longer be able to market under the old regulation 2003/2003, but will have the choice of using the new regulation (CE-Mark) and/or selling under national fertiliser regulations, which will remain in force in each Member State (“Optional Harmonisation”).
Producers should refer to the Frequently Asked Questions and to the Labelling Guidance, both of which documents provide important clarifications on implementation of the new regulation.
In questions from conference participants, it was clarified that the new regulation will limit cadmium to 60 mgCd/kgP2O5 in all CE-Mark mineral phosphate fertilisers from June 2022, as well as limits on certain other heavy metals, and that producers have the option to label “Low Cadmium” when below 20. However, the Commission is mandated by the regulation to review the cadmium limit by 2026, and also to assess a possible uranium limit. Johanna Bernsel also underlined that possible action is also envisaged on contaminants in all fertilisers (organic and mineral, CE-Mark or national fertilisers) with a study underway (see ESPP eNews n°52.
European Commission FRP “Frequently Asked Questions” here
European Commission FRP labelling guidance document C(2021)726 (18/2/2021) and Annex here
Fertiliser market trends in Europe
Konstantin Golambek, Fertilizers Europe, presented latest conclusions from the federation’s annual analysis of European fertiliser markets and estimates for trends for the coming decade. Phosphorus consumption in mineral fertilisers has fallen by around half in Europe since the 1980’s and has been fairly stable since the late 2000’s. Fertilizers Europe estimates that P use in mineral fertilisers in Europe will fall very slightly, maybe c. 2%, over the next ten years, and N by maybe -5 to -6%. However, there are major regional differences in mineral P fertiliser use across Europe, partly related to differences in density of livestock production (and so manure availability and use).
Fertiliser use will be influenced by crop choice, by climate and by the global agri-food commodity market, by innovation in agriculture, by regulation and also in the long term by a move towards more plant-based diets and by the need for the EU to replace imported animal feedstuffs, such as soy. Farmers in Europe are under high pressure because of labour costs, food industry purchasing and regulation.
Fertilizers Europe sees as key to responding to these challenges: balancing all nutrients and use of both mineral and organic fertilisers, adapting to different regional contexts, increasing knowledge per hectare, Circular Economy and high-efficiency fertilisers. The aim is to improve Nutrient Use Efficiency and maintain soil fertility. Nutrient Management Plans in the Common Agricultural Policy will be critical for this.
How EU policies will influence phosphorus use
Chris Thornton, ESPP, summarised European policies and regulations which will significantly impact phosphorus use in Europe in coming years. The Green Deal Farm-to-Fork and Biodiversity Strategy target to reduce nutrient losses by 50% by 2030 should considerably impact use of mineral fertilisers, organic fertilisers and livestock manure. This is driven by the ongoing problem of eutrophication, likely to be accentuated by climate change, with phosphorus the main (non-morphological) cause of failure to achieve Water Framework Directive quality status requirements in surface waters. Farm-to-Fork also announces actions to promote a shift towards healthy and sustainable diets, with more plant-based foods and less red meat. However, these objectives require clear requirements on balanced nutrient management in the European Common Agricultural Policy (CAP), and this is not yet defined. Other EU policies which significantly impact phosphorus use include the confirmed inclusion of both phosphate rock and P4 on the EU Critical Raw Materials List, the EFSA safe limit (ADI) for phosphorus in food (2019) and Circular Economy policies.
ESPP presentation slides here: https://www.slideshare.net/NutrientPlatform
EasyMining phosphorus recycling
Yariv Cohen, Sara Stiernström and Christian Kabbe presented the EasyMining (a subsidiary of Ragn-Sells) Ash2Phos process for recovering phosphorus in a purified form from sewage sludge incineration ash. The process uses acid then lime to extract phosphorus from ash and separate off the inert silica (as a sand, useable in the construction industry). The phosphorus is purified (>96% removal of impurities including heavy metals) to produce a precipitated calcium phosphorus (PCP) which is for example 80% soluble in NAC (conform to the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation requirement of >75%) or can be converted to di-calcium phosphate (DCP, 100% NAC soluble). Iron and aluminium can be recovered and recycled as coagulants for sewage treatment. Because of the purity of the recovered PCP, this is currently being trialled for use in animal feed (see ESPP eNews n°52). Easymining today have a 30 000 t-ash/year plant currently in the permitting process in Helsingborg, Sweden, a second 30 000 t-ash/y plant under planning near Berlin Germany and aim to have a third 300 000 t-ash/year capacity in Germany within a decade.
http://easymining.se/ and ESPP – DPP – NNP P-recovery Technology Catalogue
http://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/p-recovery-technology-inventory
Glatt PHOS4green
Jan Kirchhof, Glatt Ingenieurtechnik GmbH, presented this process which is based on suspension and granulation technologies. Ash is mixed with phosphoric or other acid or additives in a batch reactor, then buffered, then goes to a continuous spray granulation process. The processing is flexible, and other acids or solid or liquid raw materials can be used. At present, the process transfers all contaminants, inert materials such a silica, and iron and aluminium, present in the ash, into the final product. This means that at present only ashes which themselves fulfil fertiliser regulation requirements can be used. Glatt indicate that they are currently at the design phase for a process for heavy metal removal. A first full-scale plant is currently under commissioning in Haldensleben, Germany, with capacity to intake c. 30 000 t-ash per year and produce c. 60 000 t/y fertiliser.
https://phos4green.glatt.com/ and ESPP – DPP – NNP P-recovery Technology Catalogue
http://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/p-recovery-technology-inventory
Phosphoric acid from low-grade phosphate rock
Marc Sonveaux and Hadrien Leruth, Prayon, presented Prayon’s phosphoric acid production processes, including from low-grade phosphate rock and for phosphorus recycling. The Ecophos / Technophos process produces feed grade DCP (di calcium phosphate) from low-grade phosphate rock with high magnesium content (P content ≥ 5%P) using hydrochloric acid. After acid digestion of the rock, calcium carbonate is added to precipitate impurities (fluoride, silicates (>95% removal), clays, iron and aluminium (>90% removal) and heavy metals), generating 0.3 - 0.45 tDM residue cake per tonne of rock input (depending on the rock composition). After processing to DCP, fluoride is well below 2000 ppm, cadmium below detection limit, arsenic < 3 ppm, etc. The DCP is di-hydrate, offering high biodigestibility. A 5 t/day rock input pilot has been tested for up to 10 days continuous (24/24) operation in Varna, Bulgaria (see ESPP SCOPE Newsletter n°120). Prayon today has a portfolio of five conventional processes to produce phosphoric acid from phosphate rock using sulphuric acid, as well as the Ecophos/Technophos process, and the GetMoreP process. Currently technologies including H2SO4/HCl based and phosphoric acid based processes from Ecophos, aiming to recover phosphorus from sewage sludge incineration ash and other waste ashes, are at the pilot stage phase (see ESPP SCOPE Newsletter n°138)
Roy Movsowitz, Tenova Bateman Technologies, presented the TAT PPA process to produce phosphoric acid from low-grade phosphate rock (as low as 10% P) using hydrochloric acid (excess from the ChlorAlkali process). Two solvent extraction circuits, both with several stages, are required to removal calcium, sulphate and some iron, then to remove further iron and heavy metals, followed by post-treatment to remove organics, reduce fluorine and finally concentrate the phosphoric acid. Further challenges are treatment of liquid effluent (after lime neutralisation) and solid waste. A 21 000 tP2O5/y output plant is being commissioned in India and a second of the same capacity is in the construction stage.
P4: outlook for a Critical Raw Material
Willem Schipper summarised uses and perspectives for P4 and its derivatives, which represent around 2% of world phosphate rock consumption (of which around half in the herbicide glyphosate). Although this is a relatively small quantity, many uses of P4 are critical and non-substitutable, including in lithium-ion batteries, fire safety, matches and pyrotechnics, catalysis, lubricants … as well as thermal phosphoric acid for electronics applications requiring very high purity. Today there are around forty P4 furnaces operating worldwide, mostly in China (maybe 30 plants, c. 70% of world production), Vietnam (8 plants, c. 10%), USA (1 plant, c. 10%) and Kazakhstan (1 Plant, c. 10%). Prices were stable in 2020, with no large new applications foreseen, and a significant part of China’s production of P4 still going to uses such as detergents or food phosphates where P4 derivatives can today be replaced by chemicals from purified “wet acid” route phosphoric acid. The market outlook is mixed, with on the one hand a new P4 production plant coming onstream shortly in Malaysia and expansions in capacity of “wet acid” purification also underway, but on the other hand growth in uses. For more information on P4 and P4 derivates, see ESPP SCOPE Newsletter n°136.
Willem Schipper also provided an overview of phosphorus recycling technologies and their development, underlining that regulation drives technology development (e.g. Germany and Switzerland P-recycling obligations). In particular, technologies are today available for phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge incineration ash and animal by-product ash, with a number of full-scale plants at the construction or commissioning stage. The successful processes will probably be those which are economic, accept different input materials and produce products adapted to market needs.
Recycled nutrients in Organic Farming
RELACS: recycled nutrients in Organic Farming
The final two RELACS webinars on potential and risks of use of recycled nutrient products in Organic Farming considered contaminants, recycling routes and Life Cycle Analysis (following on from the first three webinars already summarised in ESPP eNews n°53) and concluded with discussion of how use of recycled nutrients is considered in the EU Organic Farming Regulation and perspectives for using recycled nutrients as Organic Farming inputs in the future.
Environment and health
Robin Harder, SLU (Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences), presented possibilities of recycling nutrients from human faeces and urine and from municipal sewage. When excreta are collected separately at the source (to date only marginal in Europe), this can provide nutrients in a more concentrated form and with less contaminants than in municipal sewage, though pharmaceuticals and hormones are still potentially present. Technically, it should be possible to obtain clean and safe recycling fertilisers from both source-separated urine and faeces and from municipal sewage. In case of recovery from municipal sewage, the focus is often on phosphorus, whereas with recovery from source-separated excreta, a broader focus on more nutrient elements is more common.
Kristian Koefoed Brandt, University of Copenhagen, summarised knowledge on antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in organic waste streams and in soils. Farmland application of organic fertilizers typically leads to a transient increase in abundance and diversity of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). Metals such as copper and zinc may constitute persistent selection pressures for antibiotic resistance (co-selection) in some agricultural soils, whereas antibiotic residues tend to be quickly biodegraded or inactivated in soil (Song et al., 2017). Results from a recent Swedish agricultural field trial indicated that 40 years of sewage sludge application did not have any clear effects on ARGs most likely due to competitive exclusion of sludge-derived bacteria (Rutgersson et al., 2020).
Lukas Egle, Vienna Municipality, presented the City’s objective to recover phosphorus from ash from mono-incineration of sewage sludge, and maybe in the future, also animal by-products. The incineration route ensures elimination of organic contaminants and microplastics, and heavy metals are removed in the ash processing. In Austria, sewage contains around 1 kgP/person per year, and phosphorus in animal by-products is a further 0.5 – 0.6 kgP/person/year. If this were fully recovered, it would represent nearly half of Austria’s mineral phosphate fertiliser use.
Ludwig Hermann, Proman and ESPP President, summarised conclusions of LCA comparisons between mineral fertilisers and recycled nutrient products under the Phorwärts (see ESPP eNews n°28), Systemic and Lex4Bio projects. Greenhouse gas emissions from mineral phosphate fertiliser production are relatively limited, 1 – 1.5 kgCO2-eq./kgP2O5, compared to 9 -11 kgCO2-eq./kgN for mineral nitrogen fertilisers. Environmental impacts of most recycled P-fertilisers are lower than those of mineral P-fertilisers, particularly if heavy metals are removed. However, the lower impact is not guaranteed due to high chemicals consumption for some recovery processes or relevant heavy metal concentrations (Zn, Cu, Pb, Cr) compensating the advantage of lower cadmium concentrations. LCA analysis suggests that the most important environmental impacts are freshwater eutrophication (in the use phase), cadmium toxicity (depending on the source of rock used) and risk of accidental pollution from phosphogypsum waste stocks (generally around historic production sites, see article on Tampa, Florida, below). Difficulties are that various different LCA methodologies are not compatible, results depend very strongly on definition of boundaries and allocation of impacts to different outputs, non-coverage of accidental pollution risks in LCAs and need for probabilistic risk assessment for pollutants.
Perspectives for acceptance of recycled nutrients in Organic Farming
Bernhard Speiser, FiBL, outlined key points of the EU Organic Farming Regulation relevant to use of secondary nutrient materials. A material can only be used as an input (e.g. fertiliser) in Organic Farming if it is specifically listed in the Regulation annex. At present, a number of secondary nutrient materials are listed (with various specific conditions, in particular “not from factory farming”): manure, dejecta of insects and worms, composted/digested household biowaste, biogas digestate, mushroom culture waste, slaughterhouse wastes, alcohol industry stillage, mollusc waste, egg shells, industrial lime from sugar or salt production. The Regulation also fixes some general principles: input materials must be from plants, algae, animals, microbes or minerals (i.e. not chemically processed) unless such materials are not available in sufficient quantity or quality. Also (art. 5) mineral fertilisers must be “low solubility”.
Frank Oudshoorn, SEGES Denmark and member of EGTOP (the EU expert group on Organic Farming) explained that this group examines proposals to add additional input materials to the Regulation annex, when a dossier is submitted with support of a Member State. EGTOP examines whether the proposed material is needed for Organic Farming, safety, and assesses conformity to the overall principles of Organic Farming: natural or Organic origins of the material, low solubility, principle for fertilisers of feeding the soil not the plant. However, Member States may sometimes interpret differently. For example, Denmark has, in advance, accepted use in Organic Farming of ammonium sulphate recovered from digestate by combining stripped ammonia with stripped sulphur – because it was considered the production process was a “mechanical” concentration of digestate. The process has however not been used yet.
Anne-Kristin Løes, NORSØK (Norwegian Centre for Organic Agriculture), underlined the need for a scientific approach to defining terminology used in the Organic Farming Regulation, such as “natural”, “low solubility”, “physical processing”. This is explored in Løes and Adler, 2019 which discusses the dilemmas between “natural” and sustainability and recycling; between “low solubility” and clean, low contaminant products, between “non-chemical processing” and efficient use of natural resources. The concept of “natural” in Organic Farming is explored in Verhoog 2003 and 2007.
Jakob Magid, University of Copenhagen, summarised a study underway in Denmark on opinions of committed Organic consumers on the use of recycled materials as inputs to Organic production. This suggests that there are two types of committed Organic consumers, at present of similar proportions: those who see Organic products as “pure and clean” and find abhorrent recycling of wastes to Organic farming, and those who favour “sustainability” and consider recycling as an important path towards a more sustainable food system.
In discussions with webinar participants and from the presentations at the five webinars, the following possible conclusions were proposed and will be elaborated in a synthesis document:
- Many contaminants have decreased in both sewage sludge and manure
- Organic contaminants in sewage are not a significant risk, but do generate fear and uncertainty
- Sustainability and recycling are core objectives of Organic Farming
- Multi-criteria assessments of recycling options are needed, including sustainability aspects
- Work is needed on defining terms used in the Organic Farming Regulation, such as “low solubility” or “processing.
- In particular, a definition of “factory farming” is needed (the European Commission has started discussions on this).
- The Organic Farming movement should have a voice on societal questions such as livestock production localisation, separative sewage collection
RELACS (Improving Inputs for Organic Farming), Horizon 2020 https://relacs-project.eu/
Research
Eutrophication significantly increases greenhouse emissions
A review of around 100 scientific publications concludes that eutrophication significantly increases greenhouse gas emissions from freshwaters (CO2, methane, N2O). An increase of 5 µg/l of chlorophyll-a in lakes and reservoirs worldwide would result in an increase of GHG emissions equivalent to >6% of fossil fuel CO2.
The current GHG emissions from freshwaters worldwide are estimated to be equivalent to >30% of global fossil fuel CO2 emissions (56% from freshwater CO2 release, 40% from methane, 4% from N2O).
Eutrophic shallow lakes are estimated to emit nearly 50% more methane than comparable non-eutrophic lakes. Eutrophication increases organic matter production in fresh waters, but it is unclear whether the resulting net CO2 uptake will compensate for increased methane production, because the organic matter produced is readily degradable. Increased nitrogen loading to surface waters can cause them to shift from being N2O sinks to net N2O emitters. Eutrophication also increases freshwater GHG emissions indirectly, for example, by shifting from vegetation dominated by macrophytes to algae, whereas macrophyte roots tend to reduce methane production by moving oxygen to sediments. Also, cyanobacteria readily produce methane even in the oxic water zone, both at day and at night.
The review also shows that climate change is expected to significantly increase freshwater GHG emissions and eutrophication (see also ESPP SCOPE Newsletter n°137 on climate change and eutrophication), with positive feedback loops. Increasing temperatures will increase release of nutrients from sediments (accelerated mineralisation), as will extreme climate events (remobilisation of sediments). Both will also lead to increased nutrient losses from land to freshwaters. Increased temperatures may also favour methane production in freshwaters, rather than methane consumption.
This review confirms that policy makers need to further reduce nutrient inputs to surface waters, both because climate change will increase eutrophication risks, and because freshwater eutrophication contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
“The role of freshwater eutrophication in greenhouse gas emissions: A review”, Y. Li et al., Science of the Total Environment 768 (2021) 144582 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144582
Biochar pyrolysis removes antibiotic resistance genes
Pot trials in China using pakchoi (Brassica chinensis) suggest that pyrolysis at 400 – 450°C for 30 minutes reduces ARGs (antibiotic resistance genes) to levels comparable to those in control soil. The tests compared composted pig manure (“high temperature” composting for several weeks) from two different farms to control soil (collected from farmland) and to pyrolysed composted manures (biochar). Compost was added to the pots at 4% dw/dw, and the biochar at 1.2% (equivalent because biochar yield was c. 30% of compost input dw/dw). The pots to which compost was added showed much higher levels of ARGs and of MGEs (mobile genetic elements) on the day of application than the control and biochar pots, between which there was no significant different in number of ARGs. Levels of ARGs were still higher in the compost pots after 40 days. The authors conclude that pyrolysis to produce biochar mitigates ARGs in manure.
In a paper cited, H. Liao et al. compared impacts of two composting systems, large scale (c. 20 tonnes), on levels of ARGs in sewage sludge: hyperthermophilic composting (total time 25 days, of which 15 days > 70°C), conventional composting (total time 45 days, 5 days > 55°C). The hyperthermophilic composting showed significantly better reduction of ARGs and MGEs, and shorter half-lives, compared to conventional composting. Hyperthermophilic composting reduced resistance to different antibiotics by 60 – 85 %, whereas conventional composting reduced resistance by 30 – 40%.
“Turning pig manure into biochar can effectively mitigate antibiotic resistance genes as organic fertilizer”, X. Zhou et al., Science of the Total Environment 649 (2019) 902–908 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.368
Differing positions on sewage sludge use in agriculture
A paper based on literature and 17 stakeholder interviews concludes that attitudes to agricultural use of sewage sludge in Sweden (after treatment such as composting or anaerobic digestion) are highly polarised. Fear of contamination, in particular “unknown or unfamiliar” risks, and “feelings of disgust” are obstacles to acceptance, despite the benefits of recycling nutrients and organic matter. Stakeholders interviewed were 5 famers or farmers’ cooperatives, one food retailer, one NGO, sewage works operators, regulators and consultants. An identified need is better monitoring and risk assessment of emerging contaminants such as PFAS or microplastics. The study concludes that use of sewage sludge in agriculture brings important benefits but that the priority should be better understanding and control of risks.
“Resources and Risks: Perceptions on the Application of Sewage Sludge on Agricultural Land in Sweden, a Case Study”, N. Ekane et al., Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 5:647780, https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2021.647780
Phosphate fertiliser value of dairy processing sludges
Dairy industry wastewater phosphate removal sludges, resulting from use of aluminium or calcium to precipitate phosphate to sludge, were compared to superphosphate for P-fertiliser effectiveness, on grassland in a field trial in Ireland on P-deficient soil. The P was applied on 12th April and grass was harvested on 24th May, 17th July, 26th September and 6th February of the following year. Differences in grass biomass yield were not significant compared to control, neither for the superphosphate nor for the dairy sludges. Differences in grass P concentration were not significant compared to control for any treatment in the second and third harvest, but were significantly higher with superphosphate in the first harvest, and significantly higher with both of the dairy sludges in the fourth harvest. The authors calculate that the fertiliser replacement value for the first harvest was 50% for the aluminium sludge and only 16% for the calcium sludge, but increasing to around 100% over time (one year, fourth harvest) for the aluminium sludge. They conclude that P fertiliser replacement value of dairy sludges varies significantly depending on the P-removal process and that appropriate information should be supplied to farmer to enable appropriate P management.
“Differing Phosphorus Crop Availability of Aluminium and Calcium Precipitated Dairy Processing Sludge Potential Recycled Alternatives to Mineral Phosphorus Fertiliser”, S. Ashekuzzaman, Fertiliser. Agronomy 2021, 11, 427 https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030427
Stay informed
SCOPE newsletter: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/SCOPEnewsletter eNews newsletter: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNewshome
If you do not already receive SCOPE and eNews (same emailing list), subscribe at www.phosphorusplatform.eu/subscribe
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/european-sustainable-phosphorus-platform/ Twitter: @phosphorusfacts
Slideshare presentations: www.slideshare.net/NutrientPlatform
ESPP members

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews053
Download as PDF
Events
Nutrients, aquatic methane emissions and climate change: 22-27 June 2021
New dates for ESPC4: 20-22 June 2022
4th Phosphorus in Europe Research Meeting (PERM): 2 June 2021
P-efficiency in poultry farming: 22 April 2021
Nordic Circular Materials Conference: 21-22 April
Digestates in the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation: 28 April
AquaEnviro Wastewater Resource Recovery Conference
Policy
ESPP webinar on waste-grown algae
End-of-Waste status for secondary materials from waste waters
EU integrated nutrient management action plan
EU Fertilising Products Regulation
STRUBIAS criteria finalised
Fertiliser additives and REACH
Possible new approach for by-products
Technical adjustments and clarifications
EBIC ECOFI position on Animal By-Products
Organic Farming
Public consultation on authorised inputs for Organic Farming
EU Action Plan for Organic farming and aquaculture
RELACS Organic Farming & recycled nutrients webinars
RELACS setting the scene
Organic contaminants and other risks
Digestates, composts, nutrient recycling
Research
Farmer survey on preferences for bio-based fertilisers
Why Phosphorus Use Efficiency in aquaculture needs to improve
Eutrophication drives lake CO2 emissions or uptake
ESPP members
Events
Nutrients, aquatic methane emissions and climate change: 22-27 June 2021
ASLO (Association for the Sciences of Limnology and Oceanography) Special Session (SS06) on Methane Accumulation in Oxic Aquatic Environments: Sources, Sinks and Subsequent Fluxes to The Atmosphere. Within the 2021 Aquatic Sciences Meeting (online, 22-27 June 2021). In partnership with the Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries (IGB) and ASLO, ESPP and SPA will follow-up with a webinar to exchange between science, water stakeholders and policy makers on implications of aquatic methane emissions for nutrient management. Proposals for input are welcome.
ASLO special session on methane in oxic aquatic environments: https://www.aslo.org/2021-virtual-meeting/session-list/
Contact Mina Bizic
To contribute to the ESPP- SPA- IGB webinar: contact
New dates for ESPC4: 20-22 June 2022
The 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference (ESPC4) is postponed (because of Covid). New dates are 20-22 June 2022 in Vienna. PERM, the European Phosphorus Research Meeting will be held virtually 2nd June 2021, see below.
Updates: see www.phosphorusplatform.eu and https://phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
4th Phosphorus in Europe Research Meeting (PERM): 2 June 2021
This meeting, co-organised by ESPP, Biorefine Cluster Europe and ETA Renewable Energies, will link science, industry, agriculture and policy makers. EU-funded projects on nutrient sustainability and phosphorus recycling (Horizon2020, Interreg, LIFE…) and national and company nutrient projects will present, enabling dialogue and synergies. PERM will address how to improve uptake of project recommendations by policy makers and users, through to market, and identify perspectives for research and policy, and implementation gaps.
In parallel to PERM, ESPP is updating our online ‘inventory’ of nutrient-related R&D projects here.
PERM4 – online – 2nd June 2021: event website: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/PERM4
Proposals are welcome for presentations of studies into what factors in nutrient R&D projects improve uptake of conclusions by policy makers, industry and users.
If you wish your project to be included in the programme and/or added to the inventory of projects, please contact
P-efficiency in poultry farming: 22 April 2021
A stakeholder webinar will present and discuss the results of the PeGaSus (ERA-NET) research project (Phosphorus efficiency in the chicken Gallus gallus and pig Sus scrofa) 22nd April 2021, 15h-17h CEST Topics will cover feeding strategies, animal physiology and genetics, soil agro-ecosystems, phosphorus re-use and recycling options, measures of farmers’ economic performance, legislative aspects on manure management, and governance & policy instruments.
Programme and registration: http://pegasus.fbn-dummerstorf.de/stakeholder_workshop.html
Nordic Circular Materials Conference: 21-22 April
This two day virtual conference (270 Euros registration) includes a session on phosphorus, 22nd April, 13h – 14h30 CEST, with EasyMining, LKAB, RISE, Grängesberg apetite mining project, University of Boras, Technical University of Denmark DTU.
https://www.circularmaterialsconference.se/
Digestates in the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation: 28 April
Presentation of an evaluation by EBA (European Biogas Association) and ECN (European Compost Network) of the interest to place compost or digestate organic fertilisers on the market under the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation and discussion with the European Commission
“Digestate valorisation under the Eu Fertilising Products Regulation”, 28 April 201, 10h-12h CEST online https://attendee.gotowebinar.com/register/1601772252033859597
AquaEnviro Wastewater Resource Recovery Conference: 13 May 2021
One day conference 13 May 2021 on resource recovery from wastewaters and biosolids, covering nutrient recovery, hydrogen and other materials: experience from pilot and full scale plants; market pull, user confidence and business models, regulatory framework, links to net zero carbon 2030 agenda for the UK wastewater industry.
“The Art of the Possible: Resource Recovery from Wastewater and Bioresources”, May 13th 2021 online https://conferences.aquaenviro.co.uk/events/conferences/resource-recovery-from-wastewater/
Policy
ESPP webinar on waste-grown algae
The webinar organised by ESPP with EABA (European Algae Biomass Association, 22nd March 2021, brought together over 400 participants online (from 700 registrants, all of whom have access to meeting networking) including the European Commission (ENV, GROW, MARE, SANTE, RTD, EASME, JRC). Presentations identified and illustrated regulatory questions around valorisation of algae and plants grown using secondary resources in a range of sectors (municipal wastewater, green waste, eutrophication remediation, cement industry (CO2 capture), aquaculture, manure digestate, dairy processing ...) with active discussion in the chat. Questions raised included waste status of algae, contaminants and safety, use in animal feed or fish feed, use in Organic Farming, human food, biofuels … ESPP will now develop a summary of this webinar, including a list of regulatory questions and opportunities, and work on proposals to take these forward (see below a first action on End-of-Waste status for secondary materials from waste waters).
Event webpage: slides, Chat transcript: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/algae2021
Full recording of webinar can be seen on ESPP’s YouTube channel
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCMid-39AIMT-3pzjoY58qiQ
End-of-Waste status for secondary materials from waste waters
The European Commission is currently defining a list of secondary material streams for “scoping of development of EU End-of-Waste and By-Product criteria”, as specified in the EU Circular Economy Action Plan (11th March 2020, ESPP eNews n°42). This Action Plan cites “Food, water and nutrients” as one of seven identified Key Product Value Chains. As an action from ESPP’s webinar on regulatory status of waste-grown algae (see above), ESPP is preparing with a number of companies and stakeholders, a joint letter requesting that specific recovered material streams from municipal wastewater (and biomass-derived wastewaters) should be considered for EU End-of-Waste status: algae and biomass grown in waste waters, fibres & polymers etc., nitrogen stripping, phosphate salts for industrial applications. The draft letter is available here and companies and organisations interested to co-sign are invited to contact ESPP.
Contact:
EU integrated nutrient management action plan
The European Commission has announced that it will prepare in 2021 an Integrated Nutrient Management Action Plan (INMAP), as announced in the Farm-to-Fork Strategy and in the new EU Circular Economy Action Plan. After wide consultation of our members and network of stakeholders, ESPP has prepared and submitted to the European Commission proposals for the objectives, content and implementation tools of such an Action Plan. ESPP’s input presents a proposed ambitious EU strategy on nutrients, across all relevant policy areas, and a comprehensive set of concrete policy actions and tools. ESPP is open for further comments and input on this document, in that the development of the EU INMAP Action Plan is expected in 2021 to include consultations enabling to make further input.
ESPP input to INMAP 27/3/2021 www.phosphorusplatform.eu/regulatory
EU Farm-to-Fork Strategy, COM(2020)381, 20th May 2020 here
EU new Circular Economy Action Plan, COM(2020)98, 11th March 2020 here
EU Fertilising Products Regulation
Good progress was noted on several dossiers at the EU Fertilisers Expert Group 18-19 March 2021. The meeting also received updates on the European Commission (DG Environment) study underway into contaminants and possible risks of organic-containing and of mineral fertilisers (see detail and call for data in ESPP eNews n°52), ECHA work underway towards restrictions on microplastics under REACH, and on the update of the EU Organic Farming regulation annexe listing fertilising materials authorised for use in Organic Farming. It was noted that the principle of inclusion of sewage-recovered struvite and calcined phosphates in Organic Farming was approved by the EU scientific committee (EGTOP) in 2016. ESPP requested that, as the STRUBIAS criteria are now finalised (subject to formal adoption and publication, see below), the Commission should now engage discussions to define the conditions and legal wording for inclusion of these two materials into the next update of the Organic Farming regulation annexes.
EU Fertilising Products Regulation 2019/1009 https://ec.europa.eu/growth/sectors/chemicals/specific-chemicals_en
EU Fertilisers Expert Group documents (CIRCAB): https://circabc.europa.eu/ui/group/36ec94c7-575b-44dc-a6e9-4ace02907f2f
STRUBIAS criteria finalised
This meeting technically validated the finalised texts of the “STRUBIAS” criteria to add struvite and phosphate salts, ash / ash derived materials and pyrolysis materials (inc. HTC, biochars) as component materials in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation. Except some minor tidying of legal wording, the criteria remain as published for the public consultation (see ESPP eNews n°51). Hopefully, the finalised criteria will now be published in coming months, in time for the entry into implementation of the new Fertilising Products Regulation itself in June 2022.
STRUBIAS criteria, as published for the public consultation February 2021)
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12136-Pyrolysis-and-gasification-materials-in-EU-fertilising-products
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12162-Thermal-oxidation-materials-and-derivates-in-EU-fertilising-products
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12163-Precipitated-phosphate-salts-and-derivates-in-EU-fertilising-products
Fertiliser additives and REACH
Following the Joint Letter coordinated by ESPP and signed by a number of industry federations and companies (mineral fertilisers, organic fertilisers, biostimulants, see ESPP eNews n°51), the European Commission provided answers on several points in a proposed update to the “Frequently Asked Questions” document, which is published and regularly extended and updated on the Commission website, and which provides guidance on interpretation and implementation of the Regulation.
The proposed additional FAQs clarify that:
- Additives used in fertilisers must be REACH registered for use “in” fertilising products (not “as”), coherent with Recital 26 of the Regulation. This is important, in that e.g. a granulation agent does not have as its function to be a fertilising product, but its safety for use in a fertilising product should be verified.
- For recovered products, art. 2(7)(d) of REACH can be used (Registration is not necessary, but appropriate information must be available)
- Detectable traces of unreacted agents or processing agents in final fertiliser products
- Substances which evolve over time or react when in contact with soil.
- Further clarifications concerning the definition of “precursors” of CMCs (chemicals which react together to produce a CMC)
European Commission “FAQ” for the Fertilising Products Regulation here (current version online = 21/12/2020).
Joint industry letter and European Commission reply here.
Possible new approach for by-products
The European Commission presented progress of work on criteria for use of by-products as component materials (CMC11) in CE-mark fertilising products.
It is now under consideration to specify not only a short, limitative list of certain by-products, with specific contaminant and other criteria for each one, but also to add a category “CMC-WW” which could cover any by-product coming from a “production process or gas processing / gas emissions control process” which is reach registered, relevant for trade, has agronomic value, offers “high purity” and does not contain specified contaminants (to be defined). Questions raised are: will this concern organic materials or only mineral chemical by-products? Will it concern by-products from waste treatment processes or waste recycling processes?
To date, only four categories of by-product were proposed for inclusion in the short list for CMC11, from: fossil fuel refining (possibly widened to some chemical industry by-products, such as ammonium from caprolactum …), refining of minerals, ores and metals (but phosphogypsum seems to be not included), some gas cleaning systems (but not from waste or manure treatment, see below), processing of biomass, water, food, drink, biorefineries, including from the pulp and paper industries.
“Technical proposals for by-products as component materials for EU Fertilising Products” (2nd report), European Commission JRC, 27th November 2020 here. Comments must be submitted via a member of the EU Fertilising Products Expert Group. ESPP is a member, so you can send comment to and we will forward them.
JRC proposals for CMC-WW see document “2021.03.18 CMC 11 CRITERIA_JRC STUDY PROGRESS.PDF” at the Fertilising Products Expert Group CIRCAB site https://circabc.europa.eu/ui/group/36ec94c7-575b-44dc-a6e9-4ace02907f2f
Technical adjustments and clarifications
The meeting also validated in principle a number of technical modifications to the Annexes of the EU Fertilising Products Regulation concerning traces of substances subject to limits for food and feed (limit values, labelling), clarifications concerning fertilising products which also have a plant protection effect, typologies of micronutrient fertilisers, contaminants in certain growing media, acceptance of natural, biodegradable and soluble polymers (e.g. in processing and handling additives), chelating agents, tolerance rules for labelling, fiberised plant materials, category 2 & 3 animal by products (including manures) in composts and digestates.
Draft document “Fertilising products - technical update”
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12135-Technical-amendments-to-the-annexes-to-the-Fertilising-Products-Regulation
EBIC ECOFI position on Animal By-Products
The industry associations EBIC -biostimulants) and ECOFI (organic fertilisers) have published a detailed 30-page position paper on Animal By-Products (ABPs) in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation (FPR). The paper underlines that there is a long history of safe use for a range of Animal By-Products (many of which have significant nutrient content), for example in over 62 000 controls in Italy, only nine cases required further investigation for pathogens, and all nine were finally determined to be negative for contamination. EBIC and ECOFI raise six questions about the process for establishing the ABP End-Points necessary for their use in EU fertilising products in the FPR. The paper provides detailed information on the transformation, legal status, FPR relevance, risks and management for 20 different ABPs today used in fertilising products. The document reminds that art. 46(4) of the FPR obliges the European Commission to engage an assessment to establish whether certain ABPs already widely used in Europe in fertilising products can be included in FPR CE-mark fertilisers and questions why some materials in this list are not in the terms of reference of the mandate given to EFSA in May 2020 (2020-0088 here, see ESPP eNews n°50): meat and bone meal, hydrolysed proteins Cat3, processed manure, glycerine etc from biofuels, derived products from blood, hoofs and horns. EBIC and EFSA also question why existing End Points in the Animal By-Product Regulation 142/2011 seem to be opened to question, but not others. The question is also raised as to why the mandate to EFSA does not take into account that the FPR will ensure certain safety levels through the limits to contamination and pathogens fixed in the PFCs.
EBIC & ECOFI joint position “End points for animal by-products used in EU Fertilising Products should recognise the history of safe use of many common materials”, European Biostimulants Industry Council (EBIC) and the European Consortium of the Organic-Based Fertilizer Industry (ECOFI), March 2021 here.
Organic Farming
Public consultation on authorised inputs for Organic Farming
The European Commission has opened a public consultation (to 23 April 2021) on a proposed update to the annex of the EU Organic Farming Regulation 2018/848 which specifies which substances can be used in Organic Farming in Europe, in particular as fertilisers, soil conditioners, pesticides and disinfectants.
Iron(III) phosphate (ferric phosphate) and diammonium phosphate (only in traps) are authorised as pesticides and phosphoric acid for cleaning/disinfection.
Authorised P-containing secondary nutrient sources containing phosphorus include (subject generally to specific conditions or criteria): materials of plant origin, manures (“factory farming origin forbidden”), source-separated household organic waste, biogas digestate, some animal by-products, algae, sawdust and wood ash (“not chemically treated after felling”), soft ground rock phosphate (subject to EU Fertilising Products Regulation contaminant limits), aluminium-calcium phosphate, Thomas phosphate slag, mollusc waste and crustacean chitin (from sustainable fisheries or Organic aquaculture), certain anoxic organic-rich freshwater sediment, biochars from plant materials.
Authorised P-containing animal feeds include a number of phosphate chemicals “of mineral origin” and fishmeal/oils/etc from sustainable fisheries (with specific conditions).
Monocalcium phosphate is authorised in Organic bakery products (raising agent) and diammonium phosphate in Organic alcoholic beverages.
ESPP will input to the public consultation underlining that Organic farms often have negative phosphorus, potassium and sulphur balances, and that increasing use of recycled phosphorus materials is needed to maintain Organic Farming productivity and soil health and to achieve the Farm-to-Fork target of 25% Organic Farming in Europe. ESPP underlines also that Regulation 2018/848 art.5(c) specifies as a “general principle” of Organic Farming “the recycling of wastes and by-products of plant and animal origin as input in plant and livestock production”. ESPP will request that the positive EGTOP Opinion of 2/2/2016 on acceptance of struvite and calcined phosphates from municipal wastewater should be implemented, and that other recycled phosphate materials should be assessed for acceptance into Organic Farming.
Public consultation to 23 April 2021: “Organic farming - list of products & substances authorised in organic production (update)” here.
EU Action Plan for Organic farming and aquaculture
The European Commission has published an “Action Plan for the Development of Organic Production”, aiming to increase Organic production in the context of the Green Deal target of 25% of EU agricultural land by 2030 (compared to 8.5% in 2019, and an estimate of 15-18% by 2030 if no action is taken beyond current policies). Member States are asked to fix national targets to achieve together this EU total. The Action Plan has three axes (23 actions): promote Organic food and products ensure consumer trust (including public purchasing), conversion from conventional to Organic agriculture and improving the contribution of Organic Farming to sustainability, and an emphasis on supportive R&D. Action 16 includes developing animal feeds based on algae, aquaculture wastes and insects. Action 23 aims at more efficient use of resources and (alongside biodegradable and compostable plastics) will “promote … the reduction of nutrient release”. The Action Plan however fails to mention recycling (except one mention of plastics) and does not address how increased Organic production can be achieved without new sources of nutrient input, in particular – for sustainability objectives – recycled nutrients.
European Commission Communication “on an Action Plan for the Development of Organic Production”, 25th March 2021, COM(2021)141 - SWD(2021)65 here and annex
RELACS Organic Farming & recycled nutrients webinars
FiBL and RELACS are organising five 2-hour webinars to exchange between researchers and Organic farming stakeholders to gather knowledge on potential risks of use of recycled fertilisers.
To date, this webinar series has some 140 registrants (including nearly 20 speakers), with around 70 researchers and over 30 Organic Farming organisations and a range of other stakeholders.
Remaining webinars:
- How to recycle nutrients from human excreta, 12 April 2021, 14h – 16h Paris summer time (CEST)
- Socioeconomic aspects and final discussion , 22 April 2021, 10h – 12h Paris summer time (CEST)
To register, contact:
RELACS setting the scene
The first webinar (3 March 2021) set the scene. A survey of over 70 Organic farms by RELACS shows concern about contaminants, especially in composts and digestates, particularly from household wastes.
Marie Reimer, Hohenheim University summarised data on European Organic farm nutrient balances. The balance is often positive for nitrogen but negative for phosphorus and potassium, especially in specialist arable Organic farms (without livestock). Farms which rely largely on BNF (biological nitrogen fixation) have more negative P and K balances (see further information in ESPP eNews n°49).
Jakob Magid, Copenhagen University, presented field trials in Denmark (CRUCIAL study) over nearly twenty years, applying sewage sludge to levels equivalent to two centuries normal application. So far no unwanted effects (except nutrient loss) have been found on soil and crops caused by recycling of societal wastes in accelerated amounts. Heavy metals in sewage sludge have fallen considerably over recent years. Copper and zinc need to be reduced in animal feeds, to reduce levels in manure. Also, a risk assessment concluded that the risk associated with agricultural use of Danish sewage sludge is comparable to that of animal slurry, once the EU limits for Zn and Cu addition to pig feed have been fully implemented, which should be the case from 2022.
Erik Smolders, KU Leuven, explained that copper and zinc, mainly from manures, and cadmium, mainly from mineral phosphate fertilisers, are the main concerns in agriculture. However, plant availability of metals is more important than loads, and this depends on soil type.
Discussion concluded that Organic farming needs to increase nutrient use efficiency in order to improve productivity and sustainability, and to increase nutrient inputs in some Organic systems such as arable and vegetables. Organic farmers in Denmark tend to consider that it would be preferable to use recycled nutrients from societal wastes, including in the longer term from municipal sewage, over using conventional manure. Questions were raised on whether easily soluble recycled fertilisers could be acceptable.
Organic contaminants and other risks
The second webinar (11 March 2021) discussed the scientific data on the risks of organic chemicals, microplastics and pathogens in manure and sewage sludge.
Stephen Smith, Imperial College London, explained that contaminants in sewage sludge have been considerably reduced over the last few decades. Most toxic chemicals are adsorbed in soil, so have low biological activity, and negligible crop uptake, so that use on cropland seems to not be a concern. Transfer to diet via livestock does however require attention but studies spiking cattle feed with sewage sludge showed very low and temporary, or non-detectable, transfer to milk (see ESPP Scope Newsletter n°126). There are over 23 000 chemicals registered under REACH in the EU, of over 100 000 on the chemicals inventory. Many enter secondary resource streams and can pose risks in recycling. Problematic chemicals today are brominated dioxins (resulting from brominated flame retardants), chlorinated alkanes (restricted under POP regulations, but still present in secondary resources) and PFAS/PFOS (perfluorinated chemicals, for which EU further restrictions are now being discussed). QSAR (modelling) analysis of new brominated flame retardants introduced to replace banned substances suggests that these will also prove problematic in the future. Overall, halogenated chemicals are problematic, and the solution is to stop producing and using these. Another problem is the illegal presence of restricted substances in imported articles.
Moritz Bigalke, University of Bern, presented current understanding on microplastics. Significant levels can be present in sewage sludge or composts. The main inputs to soils seem to generally be vehicle tire dust, sewage sludge, compost and agricultural films. While most studies show ecotoxicological impact only at high concentrations of microplastics, one study (Rodriguez-Seijo et al. 2017) suggest that microplastics may impact earthworms at environmentally relevant levels. Microplastics are mobile in soils, can modify soil properties and impact plants (see ESPP eNews n°38). A major difficulty is the absence of standard methods for analysing microplastics in soils and their impacts on soil organisms.
Annika Nordin, SLU (Swedish Agricultural University), presented pathogens in sewage sludge and manures. Treatments such as composting, anaerobic digestion or ammonia sanitisation reduce pathogens to low and safe levels, while storage or alkaline treatment are not efficient against helminth eggs (which are a big problem e.g. in Africa). The EU Sewage Sludge Directive today still allows spreading of untreated sewage sludge if ploughed in within 24 hours.
Discussion concluded that more research is needed into microplastics and into the fate and risk assessment of organic chemical contaminants in soil-plant systems. Input should perhaps be made to the European Commission to propose that the current revision of the Sewage Sludge Directive should ban the spreading of untreated sewage sludge.
Digestates, composts, nutrient recycling
The third RELACS webinar (17 March 2021) saw several presentations on recycled nutrient materials.
Kurt Möller, Hohenheim University, presented studies on composts and digestates, showing considerably preferable LCA for anaerobic digestion compared to composting, and also much lower nitrogen losses during processing, but a higher N loss risk for digestates after field application. The long-term fertiliser efficiency of P and K in organic fertilizers is nearly 100 %, but the long term N efficiency varies in a wide range, for compost it is only 20-40%, whereas it can be nearly 70 to 80% for digestates. Both, N losses during storage and after field applications, and low efficiencies in the field affect the stoichiometry of nutrients in organic manures, mainly the N/P- and the N/K-ratio. Therefore, the use of composts (e.g. from food waste) to provide N to crops can result in nutrient imbalances in the soil, leading over time to e.g. phosphorus accumulation. Any treatment approach should emphasize on reduction of any kind of nutrient losses.
Elke Bloem, Julius Kühn Institute and PROMISE (Baltic Bonus project), summarised a study looking at mesophilic anaerobic digesters treating over 40 different input materials including sewage sludge, pig, cattle and poultry manure and maize (as a reference). Eight antibiotics were measured in input materials and in digestate (sulfonamids, tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones). At least one antibiotic was detected in 70-90% of input manures and 100% of sewage samples, with similar detection levels in digestate. Anaerobic digestion reduced median antibiotic levels by around 50%, but high levels were still present e.g. in poultry manure digestates. For comparison, literature data suggests reduction levels of 30% - 100% in composting, very variable even for the same substance in different composting systems (depending on time, temperature, pH, aeration …). The PROMISE study also carried out ecotox tests using Sinapsis alba (white mustard), showing effect concentrations of the order of 1 000 x higher than worst case calculated soil concentrations. However, the tests also showed that effects of several antibiotics are more than cumulative (synergistic) and should be considered. Also, some literature studies suggest that antibiotics may stimulate antibiotic resistant genes (AGRs) at significantly lower concentrations.
Anne-Kristin Løes, NORSØK, summarised studies on use of hydrolysed fish processing and seaweed processing wastes as fertilisers. Ground fish waste treated in formic acid (pH4) showed to be a very effective nitrogen and phosphorus fertiliser (hydrolysed proteins) in a field trial with rye grass, producing as much biomass as the reference treatment with the same N dose supplied as poultry manure, but with a much more rapid growth response. In the trial, this material was also tested with fibre residue from processing of rockweed (seaweed), from the company ALGEA (Syngenta), rich in K, S, Mg. Both of these residues are currently generally incinerated. Fish processing residues from caught wild fish are currently authorised for use in Organic Farming, whereas this is not clear for fish residues from aquaculture (category 2 waste not accepted; fish excrements not accepted). For further information, see Ahuja et al. review on fish waste based fertilisers.
Erik Meers, Gent University, presented a number of projects working on different routes for processing digestates to generate fertiliser materials, as a solution to transfer excess nutrients from intensive livestock regions to regions needing nutrients for arable production.
Participants discussed manures from digestate, questioning that such processing may only necessary or economic (as opposed to local use of the digestate) in intensive and concentrated livestock production, which is against the principles of Organic Farming.
Research
Farmer survey on preferences for bio-based fertilisers
The Horizon2020 R&D project, Fertimanure (ESPP member, see ESPP eNews n°41 Innovative nutrient recovery from secondary sources: production of high-added value FERTilisers from animal MANURE) has opened a survey of fertiliser users (in Europe, Argentina, Chile). Forty-seven questions ask about farm type and size, soil sampling, farm fertiliser management plan, fertiliser application costs, readiness to switch to Organic Farming or to bio-based fertilisers, familiarity with regulations, qualities considered important for bio-based fertilisers, materials considered acceptable in bio-based fertilisers, etc.
Fertiliser user questionnaire: https://www.fertimanure.eu/en/news/consult/26
Why Phosphorus Use Efficiency in aquaculture needs to improve
An overview of global phosphorus flows in fish production (capture and aquaculture) shows that the net P flow has changed from positive + c. 0.5 MtP/y (more P in harvested fish, both captured and cultured) in the 1960’s – 1970’s to negative – c. 1 MtP/y (more P used in aquaculture than harvested). P in harvested fish is an order of magnitude larger than other P pathways from water to land (migratory fish, seabirds, deposition). P input to aquatic systems from aquaculture globally is estimated at c. 2 MtP/y (2016), rising rapidly since the 1990’s with the expansion of aquaculture. This compares to estimates of losses from croplands and manure of 4 - 5 MtP/y (not including losses related to land use change) and of total river P discharge to oceans of 4 – 22 MtP/y. ESPP note: these numbers are coherent with global phosphate rock mining of 17 – 24 MtP/y (ESPP Factsheet). The authors estimate that c. 0.3 MtP/y of mineral phosphate is used in aquaculture feed. The authors estimate that global average Phosphorus Use Efficiency (PUE) in aquaculture is c. 20%, higher for finfish than for crustaceans. China represents nearly 60% of global aquaculture P input. In China, upper values for PUE are 44% for finfish and 24% for crustaceans. PRE (Phosphorus Retention Efficiency), that is % of input P retained in fish biomass in feeding experiments, can be higher, e.g. 44% median PRE for carp, which represents c. 40% of world aquaculture production. The authors estimate that an increase of global aquaculture PUE to 48% would be necessary to achieve “net zero” flows in fish capture and production, which would be very demanding. The authors note that aquaculture shows net P use (input – harvest) / protein of c. 0.3 g/g compared to 0.03 – 0.14 g/g calculated for crop-livestock systems.
Huang et al. 2021 “The shift of phosphorus transfers in global fisheries and aquaculture” https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14242-7
Eutrophication drives lake CO2 emissions or uptake
Net influx and efflux of CO2 was calculated for 15 eutrophic, shallow lakes (< 7m) in Iowa, USA (mostly manmade lakes), for which long term water chemistry survey data was available 2000 to 2010. Additionally, dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) was isotope tested, and dissolved organic matter (DOM was analysed. Without eutrophication, lakes are generally net sources of CO2 to the atmosphere (efflux). In this study of eutrophic lakes, five lakes showed net CO2 influx (sink) of c. -50 to -1800 mmolCO2/m2/day (average during the ice free season = c. 8 months), whereas ten showed net efflux (emission) of c. 320 – 11 800 mmolCO2/m2/day, showing values significantly higher than previously reported in literature. For the lake with the highest net efflux (Badger Lake, 0.17 km2) this represents around 21 000 tCO2/year (based on 8 months). The carbon analysis showed that in all fifteen lakes, the DIC was derived from degradation of lake carbon (e.g. from sediment), mineral dissolution and atmospheric uptake, and not from degradation of land runoff organic carbon. CO2 efflux from the lakes was correlated to total nitrogen and to watershed wetlands. Conclusions are that although algal blooms resulting from eutrophication can cause lakes to uptake CO2 from the atmosphere for periods of months, eutrophication can cause wide changes in CO2 influx or efflux, including in some cases high CO2 emissions. The large effluxes are hypothesised to possibly be related to photodegradation of nitrate and nitrite, related to high nitrogen inputs to the lakes.
Morales-Williams et al. 2021 “Eutrophication Drives Extreme Seasonal CO2 Flux in Lake Ecosystems” Ecosystems (2021) 24: 434–450
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-020-00527-2
ESPP members

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews052
Download as PDF
Events
Nutrients, aquatic methane emissions and climate change
Algae for nutrient removal and recycling: regulatory questions
P-efficiency in poultry farming
CRU Phosphates 2021: “the” phosphate industry event
AquaEnviro Wastewater Resource Recovery Conference
Call for data
Contaminants in mineral and organic fertilisers
ESPP member news
ESPP new member: HTCycle AG
EasyMining, Lantmännen & SLU to test recovered phosphate as animal feed
Industry news
DSM and livestock nutrient sustainability
New network of fertiliser regulatory experts
Baltic manure management recommendations
SuMaNu (1) report on manure management
SuMaNu (2) report on manure processing
SuMaNu (3) report: impact gap for manure nutrient projects
SuMaNu (4): draft policy recommendations
Research
Climate change and Circular Economy
Lakes as climate sinks and emitters
Organic contaminants eliminated in sewage sludge biochar
P-fertiliser effectiveness of organic residues
Stay informed
ESPP relaunches social media
ESPP members
Events
Nutrients, aquatic methane emissions and climate change
Freshwater emissions of methane are of the same order as methane released by wetlands, and a significant contributor to climate change. Nutrient losses to surface waters and eutrophication will impact methane emissions. ESPP and the US Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance summarised recent knowledge in SCOPE Newsletter n° 135 (July 2020).
ASLO (Association for the Sciences of Limnology and Oceanography) is organising, as part of the 2021 Aquatic Sciences Meeting (online, 22-27 June 2021), a Special Session (SS06) on Methane Accumulation in Oxic Aquatic Environments: Sources, Sinks and Subsequent Fluxes to The Atmosphere.
Deadline for abstract submission is 12th March (05:59 GMT, 1600 characters)
In partnership with the Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries (IGB) and ASLO, ESPP and SPA will follow-up the ASLO session with a webinar to exchange between science, water stakeholders and policy makers on implications of aquatic methane emissions for nutrient management. Both the ASLO session and this webinar will be summarised, with an update on recent science, in a further SCOPE Newsletter special edition.
ASLO special session on methane in oxic aquatic environments: https://www.aslo.org/2021-virtual-meeting/session-list/
Contact Mina Bizic
Abstract submission deadline 12 March 2021 (05:59 GMT)
To contribute to the ESPP- SPA- IGB webinar: contact
Algae for nutrient removal and recycling: regulatory questions
ESPP is organising a webinar workshop, with participation of the European Commission (DGs ENVI, GROW MARE, JRC) on Monday 22nd March, 9h-13h (Paris time, CET). The webinar aims to identify regulatory questions impacting valorisation of algae grown in wastewaters, or “fed” with other waste streams (e.g. CO2 capture), or for materials left after extracting materials such as biofuels or cosmetics from algae. Algae can be valorised to fertilisers (recycling nutrients and organic carbon to soil), animal feed, bioenergy or to many other applications. Use of nutrients from algae grown using waste inputs raise specific questions under EU fertilisers and animal feed regulations, as well as contaminant and safety questions.
Registration (free): https://algae2021.eventbrite.co.uk
Event webpage, updated programme www.phosphorusplatform.eu/algae2021
P-efficiency in poultry farming
A stakeholder webinar will present and discuss the results of the PeGaSus (ERA-NET) research project (Phosphorus efficiency in the chicken Gallus gallus and pig Sus scrofa) 22nd April 2021, 15h-17h CEST Topics will cover feeding strategies, animal physiology and genetics, soil agro-ecosystems, phosphorus re-use and recycling options, measures of farmers’ economic performance, legislative aspects on manure management, and governance & policy instruments.
Programme and registration: http://pegasus.fbn-dummerstorf.de/stakeholder_workshop.html
CRU Phosphates 2021: “the” phosphate industry event
 Members of ESPP benefit from a 10% reduction for registration to “Phosphates 2021”, online 23-25 March 2021. This is the only major global event for the phosphate mining, processing, phosphorus chemicals and phosphate fertiliser industries, and brings together over 400 industry participants every year. This year’s Phosphates conference is online, with virtual exhibition and networking centre, interactive discussion groups, conference presentations with Q&A. Registration prices are considerably lower than usual.
Members of ESPP benefit from a 10% reduction for registration to “Phosphates 2021”, online 23-25 March 2021. This is the only major global event for the phosphate mining, processing, phosphorus chemicals and phosphate fertiliser industries, and brings together over 400 industry participants every year. This year’s Phosphates conference is online, with virtual exhibition and networking centre, interactive discussion groups, conference presentations with Q&A. Registration prices are considerably lower than usual.
https://events.crugroup.com/phosphates/register
AquaEnviro Wastewater Resource Recovery Conference
One day conference on resource recovery from wastewaters and biosolids: nutrient recovery, hydrogen and other materials: experience from pilot and full scale plants; market pull, user confidence and business models, regulatory framework, links to net zero carbon 2030 agenda for the UK wastewater industry. Abstract submission deadline: Friday 12th March (200 words).
“The Art of the Possible: Resource Recovery from Wastewater and Bioresources”, May 13th 2020 online.
Abstract submission deadline 12th March https://conferences.aquaenviro.co.uk/events/conferences/resource-recovery-from-wastewater/
Call for data
Contaminants in mineral and organic fertilisers
The European Commission (DG Environment) has contracted to Arcadis and Arcadia International a study into contaminants in fertilisers (organic and inorganic fertilisers, sold as fertilisers under EU or under national regulations). The declared objective is to identify contaminants, fertiliser additives or fertiliser components or their decomposition products, which pose possible risks for the environment, for crops, for consumers (via crops) or for farmers. ESPP participated in a stakeholder workshop online organised by Arcadis 4th March 2021 (ESPP circulated the invitation to members), with nearly one hundred participants from different concerned companies and sectors. DG ENVI suggested that the study underway could lead to modifications of the EU Fertilising Products Regulation and to “Restrictions” under REACH. A shortlist of substances (mainly contaminants) to be studied has been defined: pyrazoles, dioxins, PCBs, PFAS (perfluorinated alkyls), pharmaceuticals (e.g. diclofenac), cadmium, chromium, mercury, vanadium and fluoride. A preliminary risk scoping will be carried out on these substances by mid-2021, including defining fertilisers concerned, risks, possible risk management measures (e.g. restrictions / limit levels in fertilisers). If potential risks are identified, these will be submitted to ECHA (European Chemical Agency) for additional data collection, risk assessment and then public consultation before possible “Restrictions” under REACH. Companies and stakeholders having data, studies on any of the above listed contaminants in fertilisers are invited to transmit these to Arcadia before end March 2020 (data on levels of these contaminants in fertilisers or in recycled nutrient materials, risk assessments for these contaminants in fertilisers or in soil).
Arcadia study contact
ESPP member news
ESPP new member: HTCycle AG
 Based in North-East of Germany, HTCycle AG uses biogenic waste as raw material to produce high quality end products, which are like active carbon and can be used for the 4th cleaning step in wastewater treatment plants, as well as ammonium sulphates and struvite for the agricultural sector.
Based in North-East of Germany, HTCycle AG uses biogenic waste as raw material to produce high quality end products, which are like active carbon and can be used for the 4th cleaning step in wastewater treatment plants, as well as ammonium sulphates and struvite for the agricultural sector.
HTCycle AG was established in 2009 and is part of the IPI group (International Power Invest AG), specialised in renewable energy solutions and environmental technologies. The patented HTCycle process is based on hydrothermal carbonisation technology and uses steam as the reaction medium at around 220°C, 24 bars for 3-5 hours. Focusing on sewage sludge with 25-30% dry matter content as raw material, the activated carbon produced from the sewage sludge can be used in the water cleaning process to remove micro plastic, hormones and pharmaceutical residues. Phosphorus can be leached from the HTCycle coal using sulphuric acid, to produce phosphoric acid. Ammonia stripped from offgases can be either reacted with the phosphorus to produce struvite and/or used to produce ammonium sulphate. The process thus complies with the German phosphorus recovery obligation (Sewage Sludge Ordinance of 2017). To date HTCycle AG has more than 10 years of experience operating pilot plants with 8.000 and 16.000 tons of capacity per year and is currently planning to build several full-scale 24/7 operating industrial-plants in Germany together with a European Infrastructure Fund. The first plant will be built in Wolgast, North East Germany, with a capacity of 16.000 tons per year of sewage sludge wet weight. HTCycle AG joins the ESPP because it aims to bring the economic and environmental benefits of hydrothermal carbonization, combined with efficient phosphorus recycling, to the attention of the general and professional public.
https://htcycle.ag/
EasyMining, Lantmännen & SLU to test recovered phosphate as animal feed
EasyMining (Ragn-Sells group), an ESPP member, the Swedish University of Agricultural Services (SLU) and Lantmännen Research Foundation (Swedish agricultural cooperative of 20 000 farmers) have launched a project to test calcium phosphate recovered from sewage sludge incineration ash as a phosphorus source in animal feed for poultry and pigs.
The PCP (precipitated calcium phosphate) is produced by the EasyMining Ash2Phos process from sewage sludge incineration ash (see ESPP P-recovery technology catalogue), 600 kg/day pilot operational in Helsingborg, two full scale plants in permitting. It offers high P content, the same P solubility as commercial MCP (mono calcium phosphate) today used in animal feed (90% in citric acid) and low fluorine. The planned trials, to run for two years, will assess the digestibility of the PCP, in order to enable optimal use in animal feed and to minimise losses to manure.
EasyMining underline the need to clarify EU regulation concerning use of products recovered from sewage sludge in animal feeds. ESPP has engaged discussions with the European Commission on this question.
“New project to test recovered phosphorus as feed phosphate” 15/2/2021 https://www.easymining.se/newsroom/articles-news/feed-project/
Industry news
DSM and livestock nutrient sustainability
Royal DSM has launched “Reducing emissions from livestock”, a sustainability platform addressing climate emissions and nutrient stewardship. DSM is a global science-based company in nutrition, health and sustainable living. DSM solutions for livestock include feed additives which improve nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) in poultry and in pigs, and so reducing N losses, improve phosphorus and amino acid digestibility, reduce methane emissions in ruminants and increase overall animal feed use efficiency. Ivo Lansbergen, President, DSM Animal Nutrition & Health: “Amidst global climate change, the need to reduce carbon emissions from animal livestock is increasingly important. It is not a question of whether we need to shift to a more sustainable business model, it is more a question of how fast and with what impact. We need to shift to a model where farmers are getting a fair price for the animal proteins produced, where people across the world have access to affordable proteins, and last but not least, where animal farming reduces its impact on the environment (emissions, water quality through manure measurement, bio-diversity) significantly”.
“Royal DSM N : DSM launches its sustainability platform ‘Reducing emissions from livestock' as part of We Make It Possible”, 21 January 2021 http://www.publicnow.com/view/572B40F4251CEEE2628E2D2033D1295A89DF2425
New network of fertiliser regulatory experts
The Fertiliser Consultants Network (FCN) www.fertcon.net is the first European network of regulatory consultancies for the fertiliser sector. The network can provide expertise across Europe as well as North Africa, South America, Russia and China. Members can provide consultancy on both national and European regulation including implementation of the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation 2019/1009 and of the new Regulation on Mutual Recognition 2019/515, biostimulants, fertiliser additives, organic and mineral fertilisers, Organic Farming. Founding members are Artemisa, Openagri, SILC Fertilizzanti, SUN Chemicals Services, Vox Gaia.
Fertiliser Consultants Network (FCN) www.fertcon.net
Baltic manure management recommendations
SuMaNu (1) report on manure management
The SuMaNu platform (Sustainable Nutrient and Manure Management for reduction of nutrient loss in the Baltic Sea Region) has published a report (by RISE) bringing together recommendations for manure management from seven Baltic manure projects (list below). These projects addressed different aspects of manure management, and this report aims to develop recommendations covering all aspects o sustainable manure use (nutrient utilisation, ammonia emissions, greenhouse gas emissions, nutrient runoff and leaching, manure nutrient recycling, odours, pathogens and contaminants) over the whole livestock production chain (feed, animal housing, manure storage, manure application and manure processing). Costs of manure management, economic and regulatory instruments are discussed. The report concludes that baseline obligatory standards for manure handling and use should be tightened, information of farmers should be increased and economic incentives implemented to help finance sustainable technologies and practices.
Project recommendations summarised in this report: Manure Standards, Baltic Slurry Acidification, GreenAgri, BONUS PROMISE, Baltic Manure, Baltic Deal, and Baltic Compass. “Technologies and management practices for sustainable manure use in the Baltic Sea Region”, E. Sindhöj et al., RISE Report 2020:77, SuMaNu http://ri.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1476430/FULLTEXT01.pdf
SuMaNu (2) report on manure processing
A second report from SuMaNu summarises different manure processing technologies and the resulting recycled nutrient fertiliser products. Regional manure nutrient misbalances in Finland, Sweden, Germany and Poland are assessed. Technologies summarised are: mechanical separation, slurry acidification, compositing, anaerobic digestion, thermal drying, pelletising, pyrolysis, HTC, combustion, gasification, ammonia stripping, membrane separation, struvite precipitation and vacuum evaporation. Fate of contaminants and pathogens are discussed. The report concludes that concentration of livestock production in certain regions generates nutrient surpluses: processing and recycling can enable transport of nutrients to crop-growing regions where they are needed, but manure processing is economically challenging. Incentives are needed to support the high investment costs for processing and to develop markets for recycled nutrient products. These often differ from conventional mineral fertilisers and services to facilitate transfer to their use should be supported.
“Manure processing as a pathway to enhanced nutrient recycling”, S. Luostarinen et al., 2020, SuMaNu https://jukuri.luke.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/546254/luke_luobio_62_2020.pdf
SuMaNu (3) report: impact gap for manure nutrient projects
A third report from SuMaNu analyses pitfalls between envisaged and realised impacts of manure nutrient projects, that is whether project recommendations were taken up by policy makers or implemented by farmers. The projects analysed are the Baltic manure projects listed in (1) above. The only project recommendation to achieve high policy maker and farmer uptake was the Baltic COMPASS recommendation to develop manure phosphorus management information, such as P-norms and standard P-indices for manures. Slurry acidification achieved medium policy integration and manure-based biogas production achieved medium policy integration and user uptake. Conclusions are that projects should explicitly define recommendations and make efforts to make these clear and accessible, and that project activities should correspond to objectives. Recommendations are more likely to be implemented if they are well communicated, in line with farmers’ needs, and if representatives of policy makers and farmers are involved in the project.
“Typical pitfalls leading to gaps between envisaged and realised impacts of manure and nutrient related projects - a gap analysis”, H. Lyngsø Foged et al., Organe Institute, June 2020, SuMaNu https://www.organe.dk/docs/SuMaNu_Report_2-3_Gap_analysis_Organe_Report.pdf
SuMaNu (4): draft policy recommendations
SuMaNu has also published six draft policy recommendation sheets, each 2-3 pages. These cover
- Fertilisation planning: in particular recommending obligatory farm gate nutrient balancing for N and P (comparison on nutrient inputs to offtakes, enabling calculation of nutrient efficiency)
- Fertilisation planning measures: development of Baltic region P fertiliser norms, a soil P-index model and tools for manure fertilisation planning, based on manure standards
- Handling and storage of manure: definition of BAT (Best Available Technologies) to reduce ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions, minimum manure storage capacities, spreading in Spring and Summer, application rates based on manure standards
- Regional nutrient reallocation: strategy and measures to support production and use of recycled nutrients from manure, with biofuel production / renewable transport
- Safe manure recycling: reduction of trace elements and pharmaceuticals in feed (then found in manure), improving hygiene of manure processing (avoid recontamination), avoid mixing manure and sewage sludge in processing
- Knowledge transfer between research, regulators and farmers, including via agricultural and environmental advisory services
SuMaNu draft policy recommendations: https://balticsumanu.eu/national-stakeholders-have-their-say-regarding-sumanu-policy-recommendations/
Research
Climate change and Circular Economy
A report from the Ellen Macarthur Foundation (EMF) and Institute for European Environmental Policy (IEEP) concludes that moving to circularity for steel, aluminium, plastics, cement and food could reduce by nearly half these sectors’ climate emissions, so reducing total world greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) by around 20%. Agriculture and food are estimated to contribute 17% of EU GHG. Over 20% of food is wasted in the EU. Combined with methane emissions from waste, global food waste is estimated to contribute 8% of anthropogenic GHG. EMF suggest that circularity in the agri-food system, including “regenerative agriculture” (~36%), reducing food waste (~12%) and recycling food waste back to soil (~2%) could reduce agri-food system GHG by nearly 50%, but most of this suggested reduction depends on “regenerative agriculture” (defined as “crop and livestock production approaches that enhance the health of the surrounding natural ecosystem”).
EMF states that policies needed include a reform of the CAP (EU Common Agricultural Policy), active policies to reduce food waste, separate collection of biowaste (as required by the Waste Framework Directive by 2024) and creating markets for composts and digestates. EMF also notes the need for fiscal reforms to support circularity, including for nutrients.
“A low-carbon and circular industry for Europe”, Ellen Macarthur Foundation and Institute for European Environmental Policy, 2021 https://think2030.eu/publications/a-low-carbon-and-circular-industry-for-europe/
“Completing the picture. How the circular economy tackles climate change”, Ellen Macarthur Foundation, 2019 https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/our-work/activities/climate-change
Lakes as climate sinks and emitters
In a 20-minute webinar online here, in the US Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance “Science Now” series, Adam Heathcote presents recent work estimating annual carbon capture in freshwater lakes (see paper by Anderson et al. summarised p.16 of SCOPE Newsletter n° 137). Based on a newly collated data set, covering 500 lakes and reservoirs worldwide, in different biomes, they conclude that lakes are a significant global carbon sink, with increasing nutrient losses increasing carbon sequestration to sediments. However, lakes remain a net carbon emitter, with net carbon releases into the atmosphere around twice burial rates. The largest cause of carbon burial is soil erosion, which takes organic carbon to sediments. Also, increasing carbon sequestration in lakes is maybe 15 to 25 times lower (greenhouse equivalent) than possible expected increases in aquatic methane emissions related to eutrophication (see SCOPE Newsletter n°135).
US Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance YouTube channel https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCNFDQTfeT7mGsMY_YOgMonA and Science Now “Nutrients Increase Global Freshwater Carbon Sink” https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L_IlFjiIfqE
Organic contaminants eliminated in sewage sludge biochar
Tests with sewage sludge show that pyrolysis at 400°C (2 hours) remove pharmaceuticals to below detection limits. Pyrolysis at 700°C (2 hours) also eliminated 99% of PVBs, PAHs and EDC/Hs*. The sewage sludge was from a 500 000 p.e. municipal sewage works in the Czech Republic operating chemical P-removal, after mesophilic anaerobic digestion, centrifuge dewatering and then dried in a paddle dryer (100°C, 3 hours). Pyrolysis was carried out in the laboratory on 100g samples of dried sludge, particle size 0.5 - 2 mm, in a quartz fixed-bed reactor, and was tested at 400°C, 500°C, 600°C, 700°C and 800°C in oxygen-free conditions (under helium). The sludge H/C-org ratio was 1.75 and this was reduced to H/C-org <0.7 in >= 500°C biochars, that is conform to the EU Fertilising Products Regulation (draft) STRUBIAS criteria.
Removal of PCBs may not be relevant in that total PCBs in the sewage sludge were < 300 ng/g: levels were reduced to < 30 ng/g in the biochars. Pyrolysis at >= 500°C reduced levels of PAH from 36 µg/g in the dried sludge to around 1 µg/g, that is significantly lower than the 6 µg/g limit proposed in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation (draft) STRUBIAS criteria. Only three EDC/Hs were found in the sludge: bisphenol A, oestradiol, triclosan. Of these, only bisphenol was detectable in any of the biochars, and was reduced from > 1 000 ng/g in the dried sludge to c. 10 ng/g event with >= 500°C pyrolysis. Nine of the twenty-seven pharmaceuticals tested were found in the dried sewage sludge (concentrations 0.1 - 50 ng/g) and all were non-detectable in all of the biochars.
The authors suggest that pyrolysis at >= 400°C for 2 hours is sufficient to ensure complete elimination of the studied pharmaceuticals from sewage sludge biochars. Based on fact that 700°C (2 hours) was sufficient to remove 99.8% of the other organic contaminants tested, the authors suggest the sewage sludge pyrolysis at temperatures higher than 600°C with sufficient residence time (> 30 min) should ensure efficient organic pollution removal. However, this is based on the limited number of different pharmaceuticals found in this sludge and on a limited number of other organic molecules. Also, the study did not assess whether the pyrolysis may have decomposed the pharmaceuticals or other organic contaminants into breakdown products, nor whether microplastics were eliminated. Therefore, further investigations into these questions are recommended.
* PCB = polychlorinated biphenyl. PAH = polyaromatic hydrocarbon. EDC/H = endocrine disrupting chemical or hormone.
“Effect of pyrolysis temperature on removal of organic pollutants present in anaerobically stabilized sewage sludge”, J. Mosko et al., Chemosphere 265 (2021) 129082 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129082
P-fertiliser effectiveness of organic residues
The RAE (Relative Agronomic Efficiency) for phosphorus of nineteen organic secondary nutrient materials was tested in three independent pot trials (each pot with four replicates, total of 152 pots over three years) with barley, for approx. 12 weeks (to maturity and grain harvest) and compared to single superphosphate fertiliser (SSP). Soil used was sandy, low P (13 mg/kg OlsenP), with pH 5.5 or limed to 5.8 or 6.5. Other nutrients (N, K, Mg, Ca, Fe, Zn, Mn, Cu, B, Mo, S) were applied sufficiently. The organic materials tested were manures/slurries from cattle, pig and fur fox, pig slurry mixed with food industry wastes (raw, composted or digested), sewage sludges (from 3 sewage works using iron salts for P-removal to different extents), pyrolysed and HTC sewage sludges.
The RAE (Relative Agronomic Efficiency) was calculated as the amount of P in SSP needed to produce the same yield as for the organic residue, divided by the total P applied in the organic residue.
At low P application rates, pig slurry, cattle slurry and composted cattle manure showed RAE above 100% (up to 189%). These materials were tested at application rates of 40 mgP/kg soil, whereas the sewage sludge derived products were tested at 150 mgP/kg soil, this being the highest P application rate at which SSP was tested. The manures, applied at only 40 mgP/kg, gave barley yields of yields of 47 – 61 g barley grains per pot, compared to the yield of 76 g grain/pot for SSP at 150 mgP/kg soil (3-13 g/pot only for control with no P addition).
On the other hand, digestate of pig slurry + food and enzyme industry wastes tested at a P application rate of 150 mgP/kg soil showed a calculated RAE of only 35% (yield 49 g/pot).
The authors suggest that the RAEs higher than 100% for manures may be because organic molecules may block P adsorption sites in soil so that P remains better available for crops and indicate that this hypothesis is supported by unpublished results of soil incubation experiments testing pig and cattle manures.
All the sewage sludges and sludge pyrolysis/HTC materials showed low RAEs (when tested at 150 gP/kg). Calculated RAEs were 6 – 68% for the sewage sludges, with yields of 17 – 66 g/pot. Calculated RAEs were 1 – 6% for the sludge or manure pyrolysis/HTC materials, with yields of 5 – 17 g/pot at 150 gP/kg.
The authors identify that the combined iron and aluminium content of the organic materials, i.e. molar ratio (Fe+Al):P, is a very good predictor of RAE for organic residues, correlating negatively to barley grain yield in these pot trials. Calcium was not a good predictor, as were also not phosphorus solubility/extraction methods (formic acid, citric acid, NAC, water, NaHCO3).
“Predicting relative agronomic efficiency of phosphorus-rich organic residues”, K. Ylivainio et al., Science of the Total Environment 773 (2021) 145618, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145618
Stay informed
ESPP relaunches social media
After a period of dormancy due to organisation changes, ESPP is relaunching our social media channels: LinkedIn and Twitter. ESPP is now working for communications with ETA – Florence Renewable Energies, a company with over 25 years’ experience promoting green innovation, especially for events, platforms and industry associations in the bioenergy sector.
Subscribe ESPP’s social media channels LinkedIn and Twitter to get up-to-date news on nutrients.
Link us on your own channels. Send us information to disseminate.
ESPP members
Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews051
Download as PDF
Events
Postponement ESPC4 and PERM to 2022
CRU Phosphates 2021: “the” phosphate industry event
Webinar series: recycled nutrients in Organic Agriculture
EIP-Agri “Healthy Soils” event
EU policy
Call for input: manure and animal by-products in EU fertilisers
Call for input: recycling nutrients into animal feeds
EU policy for algae
Recycled nutrients in Organic Farming
EU consultation on Soil Strategy
Nutrient stewardship and farmers
EU consultation: Zero Pollution Ambition
EU consultation: industrial and agricultural emissions
Public and specialist consultations: Sewage Sludge Use in Farming
Phosphogypsum
IFA aiming for 100% use of phosphogypsum
Prayon: near 100% phosphogypsum recycling
Phosagro: phosphogypsum valorisation in road building
EU Fertilising Products Regulation
Public consultation on STRUBIAS (Fertilising Products Regulation)
Technical adjustments of the EU Fertilising Products Regulation
Industry joint letter on additives and REACH
Research
Phos4You videos on P-recovery
Science reviews on algae for wastewater treatment
Sustainable diets are good for health
Crab shell waste tested for P-removal from sewage effluent
Calcined fish bones as fertiliser
Possible significance of phosphine in global P cycles
Study suggests healthier diets increases dietary P intake
Organic Farming can only feed the world with food system changes
Calcium phosphate citrate nanoparticles effective in targeting cancer tumours
How not to do Life Cycle Analysis
Stricter nutrient thresholds needed for rivers
Urban nitrogen budgets overview
ESPP members
Events
Postponement ESPC4 and PERM to 2022
Given the ongoing international corona virus situation, it is decided to postpone ESPC4 and PERM (4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference and European Phosphorus Research Meeting) to 2022, Vienna, as a physical conference (previous planned dates, now cancelled, Vienna 31st May – 2nd June 2021). New 2020 dates will be announced shortly, in Vienna, probably June 2020.
https://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
CRU Phosphates 2021: “the” phosphate industry event
 Members of ESPP benefit from a 10% reduction for registration to “Phosphates 2021”, online 23-25 March 2021. This is the only major global event for the phosphate mining, processing, phosphorus chemicals and phosphate fertiliser industries, and brings together over 400 industry participants every year. This year’s Phosphates conference is online, with virtual exhibition and networking centre, interactive discussion groups, conference presentations with Q&A. Registration prices are considerably lower than usual.
Members of ESPP benefit from a 10% reduction for registration to “Phosphates 2021”, online 23-25 March 2021. This is the only major global event for the phosphate mining, processing, phosphorus chemicals and phosphate fertiliser industries, and brings together over 400 industry participants every year. This year’s Phosphates conference is online, with virtual exhibition and networking centre, interactive discussion groups, conference presentations with Q&A. Registration prices are considerably lower than usual.
https://events.crugroup.com/phosphates/register
Webinar series: recycled nutrients in Organic Agriculture
FiBL and RELACS are organising five 2-hour webinars to exchange between researchers and Organic Farming stakeholders to gather knowledge on potential risks of use of recycled fertilisers, e.g. organic contaminants, pathogens and microplastics.
Introduction – 3 March 2021, 14h-16h Paris time (CET)
Organic contaminants and other risks, - 11 March 2021, 10h -12h Paris time (CET)
How to recycle nutrients from household wastes and the food industry, 17 March 2021, 14h – 16h Paris time (CET)
How to recycle nutrients from human excreta, 12 April 2021, 14h – 16h Paris summer time (CEST)
Socioeconomic aspects and final discussion , 22 April 2021, 10h – 12h Paris summer time (CEST)
To register, contact:
EIP-Agri “Healthy Soils” event
The call for participants is open to 14th February for the EU R&D EIP-AGRI seminar on healthy soils, 13-14 April 2021. The aim is to share knowledge, experience and innovation concerning on-farm actions to improve soil health, related to productivity, nutrient cycling, water, carbon sequestration and climate change.
Call for expression of interest to 14th February 2021 here.
EU policy
Call for input: manure and animal by-products in EU fertilisers
ESPP has discussed with the European Commission DG SANTE obstacles to nutrient recycling from animal by-products into EU fertilisers. To date, DG SANTE has only requested an EFSA Opinion (European Food Safety Agency) on those animal by-products which are already authorised for use as fertilisers (subject to certain constraints) under the Animal By-Product Regulation 142/2011. This mandate not given to EFSA until May 2020, whereas animal by-products were already an empty box in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation since March 2016 – see ESPP eNews n°50. DG SANTE indicated that EFSA has space to assess (for use in CE-Mark fertilisers) other recycled nutrient products derived from animal by-products, and suggested that industry submit dossiers to EFSA, via Member States. If your company produces a fertilising product from animal by-products, which you wish to be eligible for the CE Mark (under the EU Fertilising Products Regulation), please contact ESPP to discuss possibly preparing a dossier.
Call for input: recycling nutrients into animal feeds
The above meeting with EC DG SANTE also concluded that the current regulatory obstacles to recycling of secondary nutrients into animal feeds should be addressed. The EU Animal Feed Regulation 767/2009 (art. 6(1) and Annex III $1 and $5) currently excludes materials derived from manure “irrespective of any form of treatment” or from municipal or industrial wastewater “irrespective of any further processing”. This means that recovering commodity chemicals (e.g. phosphoric acid) from such secondary nutrients is problematic, in that it could be considered that these should only be sold subject to traceability and labelling “not to be used in animal feeds”. It was agreed that ESPP should collate short dossiers from companies operating such recovery processes, summarising possible secondary nutrient inputs, final products, process, contaminants, safety and potential market. The European Commission will then consider possible approaches to this problem. Please contact ESPP if your company wishes to provide input to this.
EU policy for algae
ESPP made input to the public consultation (closed 18th January 2021) on development of an EU policy for the algae sector. ESPP underlined that the proposed Roadmap did not actively address actively address the important potential for recycling of secondary nutrients and CO2 to feed algae (Circular Economy), that is combining algal production with wastewater and/or offgas cleaning. Algae production is already used full scale to treat municipal wastewaters, in particular for nutrient removal, thus recycling secondary nutrients to feed the algal production and enabling nutrient recovery. Algae can also be used to treat other wastewaters, including digestate. ESPP underlined that use of secondary streams is the only sustainable way to supply the nutrients needed if algae are to be produced large-scale, e.g. for biofuels. ESPP’s consultation input requests actions to clarify the eligibility of waste-grown algae for use under EU fertilisers and animal feed regulations, subject to appropriate safety criteria, and to define safety standards for algae grown on waste streams.
Public consultation “Blue bioeconomy - towards a strong and sustainable EU algae sector”, closed 18th January 2021, contributions consultable here.
Recycled nutrients in Organic Farming
ESPP has engaged with IFOAM Organics Europe and the EU project RELACS (Replacing Contentious Inputs in Organic Farming Systems, or Improving Inputs for Organic Farming, see ESPP eNews n°33 and n°40) to identify which recycled nutrient products could be acceptable or desirable as inputs to Organic Farming. The EU Organic Farming Regulation 2018/848 specifies as a principle “recycling of wastes and by-products of plant and animal origin as input in plant and livestock production”. The Organic Farming movement also has concerns about not using input materials which facilitate intensive farming, agronomic behaviour of recycled fertilisers, needs for different nutrients, chemicals used and LCA of recycling processes, possible contaminants. ESPP has submitted, for consideration by IFOAM and RELACS experts, twenty Fact Sheets, prepared by companies operating nutrient recycling processes, presenting product case studies different recycled nutrient products, including ash-recovered materials, struvites, biochars/pyrolysis, P, N, K, S and Fe materials.
EU consultation on Soil Strategy
A public consultation questionnaire is open on the future EU Soil Strategy to 28 April 2021. ESPP made input to the Roadmap for this consultation in December 2020. ESPP’s input to the current consultation will underline the importance of nutrients and of organic carbon for soil quality and fertility, links to EU water, sewage sludge and Farm-to-Fork policies, the value of recycling of nutrients and organic carbon, and the need to reduce contaminants in secondary nutrient sources (e.g. PFAS, persistent plastics additives, veterinary pharmaceuticals).
EU public consultation questionnaire “Healthy soils – new EU soil strategy”
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12634-New-EU-Soil-Strategy-healthy-soil-for-a-healthy-life
Nutrient stewardship and farmers
ESPP President, Ludwig Hermann, presented European phosphorus flows, phosphorus recovery possibilities and the SYSTEMIC project at a conference on “Sustainable Nutrient Supply” organised by the Government of the Austrian Federal State (Bundesland) Upper Austria, 9th December 2020, with around 100 farmers and agricultural stakeholders. The presentation addressed the overuse of nitrogen and phosphorus resources, planetary boundaries and EU water quality targets in the context of the European Green Deal and the Farm-to-Fork Strategy. The new EU Fertilising Products Regulation was summarised, and an overview of approaches and techniques for P-recovery and recycling was presented, with success stories from different countries. The presentation will be summarised in an article to be published in April 2021 in the journal “Der Pflanzenarzt”, circulated to 2 500 farmers and agricultural advisors.
Conference recording: https://blickinsland.at/boden-wasser-schutz-tagung-2020/ (in German)
EU consultation : Zero Pollution Ambition
Open to 10 February 2021. See ESPP eNews n°50.
“EU Action Plan Towards a Zero Pollution Ambition for air, water and soil” HERE
EU consultation: industrial and agricultural emissions
Open to 23rd March 2021. See ESPP eNews n°50
Public consultation “IED-EPRTR-Revision-OPC-2020” https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12583-Industrial-pollution-revision-of-the-European-Pollutant-Release-and-Transfer-Register-/public-consultation
Public and specialist consultations: Sewage Sludge Use in Farming
The public consultation on the Sewage Sludge Directive is open to 5 March 2021. Key questions concern contaminants and nutrient and organic carbon recycling. See ESPP eNews n°50
Additionally, a targeted stakeholder consultation has been mandated to Trinomics, and information is being collected via specific questionnaires, from wastewater and sludge processing stakeholders, agricultural and consumer associations, academics and experts, NGOs. If you wish to input to this specialist consultation, you should contact Trinomics by email here.
Public consultation on the Sewage Sludge Directive HERE
Phosphogypsum
IFA aiming for 100% use of phosphogypsum
The International Fertilizer Association (IFA) second phosphogypsum report outlines how to achieve the objective of 100% safe and sustainable use of phosphogypsum (PG), a major by-product of phosphoric acid production from phosphate rock, which in the past has often been stacked as a waste (PG is mainly calcium sulphate, resulting from the reaction of sulphuric acid with phosphate rock). The report outlines quality protocols and regulatory trends for PG use, and presents innovative case studies and country cases. Uses, depending on PG properties, can include agriculture, road building and cement production. PG provides sulphur and calcium to soils and the report presents examples of trials carried out in partnership with science and regulators in Canada (poplar, willow, squash, potato), Russia (rice, soybean, corn, wheat, flax), Kazakhstan (cotton), Morocco (rape, barley, maize). The case of Brazil is presented, where some 10 million tonnes / year of PG are today produced. Agricultural use in the Cerrado region improves the acid soil and provides sulphur, need by soybeans. Brazil now uses all PG currently produced and has started ‘mining’ historic waste stacks, with the objective of depleting these in the coming 7 years or so, enabling return to farming of the land currently used for the stacks.
“Phosphogypsum Leadership Innovation Partnership”, IFA, 2020. HERE.
Prayon: near 100% phosphogypsum recycling
Prayon, Engis, Belgium, is presented as a case study in the IFA document (above), as the company today recycles almost 100% of its nearly 800 000 t/y of phosphogypsum (PG) production to agriculture (8%) and construction products (production of stucco plaster by Kauf, 92%). This has been enabled by a reengineering of the production process and new purification technologies over recent decades, to generate a clean, quality PG, whilst at the same time increases P recovery rates from phosphate rock, improving phosphogypsum filtration and drying. The PG used in agriculture brings calcium and sulphur, but also retains water. This water retention property has also been shown to enable biodiversity improvement (anthrosol species).
“Phosphogypsum Leadership Innovation Partnership”, IFA, 2020.
Phosagro: phosphogypsum valorisation in road building
The Russia Federal Road Agency has approved hemi-hydrate phosphogypsum (HHPG) as a roadbed material for all classes of roads. This follows R&D led by Phosagro, using both HHPG. Tests show that the pressure on soils is nearly three times lower using HHPG than with conventional granulates, because the HHPG forms a high-strength lightweight slab, spreading pressure and so reducing deformations of road surface materials. The HHPG offers high tensile strength and elasticity, performs well in marshy terrain and is resistant to deformation when frozen. Use of sand and granulates can be reduced by 45 – 75%, so reducing environmental damage from quarrying, and enabling significant cost savings. To date, some 180 000 m2 of road have been build using HHPG, with up to 11 years of road life already.
“Phosphogypsum Leadership Innovation Partnership”, IFA, 2020.
EU Fertilising Products Regulation
Public consultation on STRUBIAS (Fertilising Products Regulation)
The final EU public consultation on the “STRUBIAS” criteria for struvite and phosphate salts, ash / ash derived materials and biochars and pyrolysis materials is extended to 15th February 2021. It is ESPP’s understanding that this consultation is a formality, prior to official publication of the criteria. The criteria have been discussed at length in the JRC STRUBIAS group and in the EU Fertilising Products Expert Group (ESPP is a member of both). ESPP will input indicating that we support the proposed criteria, which are important for placing on the market of recycled fertilising products and for the roll-out of nutrient recycling technologies, and that the criteria proposed are the result of detailed consultation and dialogue. ESPP will underline the problem that animal by-products (including manures) cannot yet be included in STRUBIAS fertilisers, because DG SANTE has not yet engaged the process of defining Animal By-Product ‘End-Points’ for relevant STRUBIAS materials and has not yet submitted a mandate for this to EFSA. ESPP also regrets that sewage sludge biochars are excluded in the proposed STRUBIAS criteria and reminds of the JRC commitment to further research this question.
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12136-Pyrolysis-and-gasification-materials-in-EU-fertilising-products
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12162-Thermal-oxidation-materials-and-derivates-in-EU-fertilising-products
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12163-Precipitated-phosphate-salts-and-derivates-in-EU-fertilising-products
Technical adjustments of the EU Fertilising Products Regulation
A public consultation on technical modifications to the Annexes of the EU Fertilising Products Regulation is open to 2 March 2021. As for the STRUBIAS annexes above, this consultation is intended to be a formality, prior to official adoption. The modifications concern traces of substances subject to limits for food and feed (limit values, labelling), clarifications concerning fertilising products which also have a plant protection effect, typologies of micronutrient fertilisers, contaminants in certain growing media, acceptance of natural, biodegradable and soluble polymers (e.g. in processing and handling additives), chelating agents, tolerance rules for labelling, fiberised plant materials, category 2 & 3 animal by products (including manures) in composts and digestates.
Public consultation open to 2 March 2021 “Fertilising products - technical update https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12135-Technical-amendments-to-the-annexes-to-the-Fertilising-Products-Regulation
Industry joint letter on additives and REACH
ESPP coordinated late 2020 a joint letter to the European Commission, DG GROW, expressing a number of questions on interpretation, and industry concerns about practicality of implementation of the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation (FRP). The points raised concern treatment of technical additives in CMCs (Component Material Categories), unreacted processing agents, chemical reactions between additives and CMC materials, and related REACH registration requirements. We have now received a detailed and documented reply from DG GROW. For a number of the points raised, the Commission concurs that questions exist and indicates that clarification will be included in Commission interpretation guidance (FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions document). The Commission’s answer also clarifies for some aspects what actions fertilising products manufacturers need to take with their supply chain to ensure that additives respect FRP-specific REACH requirements.
European Commission “FAQ” for the Fertilising Products Regulation – note that this document is updated regularly - here.
Joint industry letter and European Commission reply here.
Research
Phos4You videos on P-recovery
The EU Interreg project Phos4You has published several short videos offering overviews of routes for phosphorus recovery from sewage recovery. An ‘Overview’ (1’40) summarises different routes via sludge incineration or from sewage sludge, adapted to both smaller rural or larger urban wastewater treatment plants. Recovery via sludge incineration is summarised for the EuPhoRe process (1’11), where phosphorus is retained in the sludge ash used as fertiliser, tested by Emschergenossenschaft at Dinslaken, Germany, or other processes (presented by Innovatherm, 1’18) where the phosphorus is recovered as e.g. phosphoric acid. Trials of P-recovery via micro-algae or using fishery-waste adsorbents, appropriate for smaller sewage works, are presented (Glasgow Caledonian University, Veolia FiltraflowP, 1’34)
Phos4You videos.
Science reviews on algae for wastewater treatment
A review of micro-algae in wastewater treatment from Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, summarises data from nearly 40 studies. These are essentially laboratory work, with only two using reactors > 1 m3. Most of these studies show, in laboratory conditions, the ability of micro-algae systems to reduce phosphorus to low levels (e.g. < 0.5 mgP/l). Technologies are discussed including algae freely suspended in water, biofilms and algae immobilised in beads. No economic data are provided. The paper concludes that “micro-algae systems incur little or no operational costs”, but this ignores maintenance costs for cell immobilisation, biofilms, membranes, or inputs of light or CO2. A second review from China, summarises different micro-algae strains used, technologies (including diagrams: open ponds, photo bio reactor (PBR), membrane PBR, microalgae film, multilayer bioreactors, …). 11 studies testing with real wastewater are identified, but only one of these provides a cost estimate (0.1 US$/m3 operating costs, Sheng 2017).
“Integrating micro-algae into wastewater treatment: A review”, S. Mohsenpour et al., Science of the Total Environment 752 (2021) 142168, DOI.
“Microalgae-based wastewater treatment for nutrients recovery: A review”, K. Li et al., Bioresource Technology 291 (2019) 121934, DOI.
Sustainable diets are good for health
Two new studies confirm that diets which are good for the environment are also good for health.
Jarmul et al. reviewed literature on the environmental footprint of ‘sustainable’ diets, finding 18 studies (412 data points), covering 12 diet patterns, 7 health endpoints and 6 environmental endpoints. For nearly 90% of data points, sustainable diets showed positive health effects. Sustainable diets showed on average -25% lower greenhouse emissions (-70% lower for vegan diets), but water use (often) and land use (sometimes) were higher for sustainable diets, compared to baseline diets. Phosphorus use was generally estimated to be slightly lower (often reduction less than -10%) for sustainable diets, with nitrogen use showing somewhat larger reductions.
Scheelbeek et al. 2020 analysed real data from 557 722 participants for health outcomes and 5747 participants for environmental footprints from three UK cohort studies (EPIC, Biobank, NDNS), concluding that less than 0.1% adhere to all nine UK Eat Well Guide (EWG) recommendations, but 31% adhere to at least five of these recommendations. Health outcomes were recorded after 3 – 20 year follow-up, and showed 7% reduction in mortality for intermediate/high (compared to low) adherence to EWG recommendations. Environmental footprint was calculated from detailed food data from the participants, and showed that adherence to recommendations led to - 1.5 kg CO2eq/day and - 23 l water use/day.
“Climate change mitigation through dietary change: a systematic review of empirical and modelling studies on the environmental footprints and health effects of ‘sustainable diets’ “, S. Jarmul et al. 2020 Environ. Res. Lett. 15 123014 DOI.
“Health impacts and environmental footprints of diets that meet the Eatwell Guide recommendations: analyses of multiple UK studies”, P. Scheelbeek et al., BMJ Open 2020;10:e037554 DOI.
Crab shell waste tested for P-removal from sewage effluent
Within the Phos4You Project (INTERREG VB North-West Europe), Veolia (with the FILTRAFLOTM-P system) and the Environmental Research Institute (North Highland College, UHI, Scotland) are testing processed crab shell waste as a phosphorus adsorbent for tertiary phosphate removal from sewage effluent. Similar approaches have been used previously with other shell and shellfish wastes as P-adsorbents, often after thermal treatment (calcination and sanitisation), including oyster shells (SCOPE Newsletter n°84), mussel shells (SCOPE 89), snail shells (SCOPE 101) and brine-shrimp shells (SCOPE 119).
In this case, the crab shell/carapace (brown crab Cancer pagurus) is washed, dried, milled, then treated with potassium hydroxide to generate a stable, easy to handle, granular material (non-respirable), rich in chitosan and calcium carbonate (see Pap et al. 2020a and 2020b). The material was tested at the Scottish Water Horizons’ Development Centre at Bo’ness (operational WWTP), Scotland, operating a pilot-scale reactor (inflow 200 litres/hour, using between 15-20 kg of adsorbent material) for six weeks (four separate trials) as a tertiary treatment option (on secondary treated discharge). Quality assessment of the saturated adsorbent demonstrated c. 8% organic carbon content dw (total carbon c. 15% dw, part is inorganic) and a 1.1 – 1.3% P dw content, as well as other agronomically valuable components such as potassium (partly from the KOH), calcium, magnesium and chitin/chitosan, with very low heavy metal and organic pollutant levels and no target bacterial pathogens. Future work will involve pot (and/or field) plant growth trials to observe P uptake/availability (starting spring 2021).
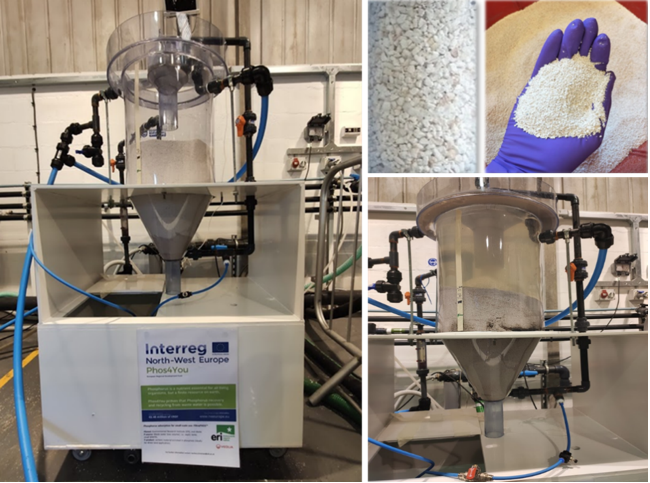

FILTRAFLOTM-P crab carapace-based P-adsorbent https://www.nweurope.eu/media/12161/phos4you_p-rich_biomass_en_nov2020.pdf
Calcined fish bones as fertiliser
Trials show that fish bones calcined at 300°C – 900°C are an effective fertiliser. The fish bones were from Round Sardinella (Sardinella aurita) collected from women filleting fish in the port of Saint Louis, Senegal, and were manually separated from offal and heads, then washed and scraped to remove organic tissue. They were then calcined at 300°C, 600°C or 900°C. The lower temperature calcination material contained organic products from collagen and fatty acids, and poorly crystalline hydroxyapatite (HAP), whereas 600°C and 900°C materials showed negligible organics and more crystalline HAP/TCP (tri calcium phosphate). The samples were tested for impact on germination and initial growth of Garden Cress (Lepidum sativum), all showing positive impacts in particular the 900°C material. They were then tested for fertiliser effect in 3-week pot trials with maize (Zea mays), soil pH 6.7. All three samples showed fertiliser effect (compared to control – no comparison was made to commercial fertiliser) but surprisingly the more crystalline 900°C calcined material (with lower solubility) showed higher maize biomass growth. The authors suggest that this may be because of the ‘biostimulant’ effect, as shown on the Cress. A previous paper by the same authors showed biostimulant effects on maize of nano-hydroxyapatite functionalised with humic substances, improving early growth, productivity (3 months), rhizosphere bacteria and salt stress resistance.
“Thermal conversion of fish bones into fertilizers and biostimulants for plant growth – A low tech valorization process for the development of circular economy in least developed countries”, F. Carella, A. Adamiano et al., J. Environmental Chemical Engineering 9 (2021) 104815, DOI.
“Synergistic Release of Crop Nutrients and Stimulants from Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles Functionalized with Humic Substances: Toward a Multifunctional Nanofertilizer”, H. Y. Yoon, A. Adamiano et al., ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6598−6610, DOI.
Possible significance of phosphine in global P cycles
A review of available information on phosphine (PH3) suggests that this form of phosphorus may be significant in global P cycles, in waste management and in links to climate change, but concludes that data is today insufficient to reach conclusions. Phosphine is a reactive gas which competes with methane and other reactive gases for hydroxyl radicals in the atmosphere, so prolonging their greenhouse impact. It is oxidised in air to phosphoric acid or phosphate ions, which may contribute to cloud formation, also impacting climate. It is estimated that around 40 000 t/y of phosphine is released to the atmosphere, representing around 10% of airborne phosphorus (to put into perspective: estimates suggest atmospheric deposition of P to the Mediterranean Sea is around half of that from rivers and coastal cities, see ESPP eNews n°43). Phosphine concentrations have been shown to be significantly higher in urban areas, and emissions can be related to anaerobic conditions (paddy fields, manure management, sewage treatment). Phosphate can be reduced to phosphine in redox conditions below -300mV. In specific conditions, up to nearly 20% of P removed from sewage in an oxygen limited membrane reactor was released as phosphine, and the authors suggest that this may be a possible route for P-recovery.
“Global phosphorus dynamics in terms of phosphine”, W. Fu & W. Zhang, Climate and Atmospheric Science (2020) 3:51 ; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41612-020-00154-7
Study suggests healthier diets increases dietary P intake
A study based on the McCance & Widdowson Composition of Foods Database, suggests that today’s average UK (meat-eater) diet has P intake of 1.35 gP/day, has decreased since the 1940s (it was around 1.6 gP/person/day in the 1950’s), but could increase if people start to adopt more vegetable intensive diets. Today’s average P intake is significantly lower than a vegetarian (1.53 gP/d = +13%), vegan (1.63 gP/d = +20%) or the proposed EAT-Lancet sustainable diet, see ESPP eNews n°48 (1.85 = +37%). Comparison of the Foods Database to data from UK food surveys suggests that the % of diet P coming from processed (as opposed to fresh foods) has increased from around 20% in the 1940’s to over 50% in 2016, corresponding to a general increase in consumption of processed foods. The % of diet P in animal products (meat, dairy, eggs, fish) increased from around 48% in 1942 to 59% in 1973 and then decreased back to c. 50% by 2016.
The authors found close agreement between the P load entering sewage work, calculated from detailed Environment Agency data, and the dietary P burden calculated from the diet surveys after accounting for estimated industry contributions.
Increased P intake with future sustainable diets and population growth would result in increased P in the inflow of many sewage works. The authors state that this could result in “greater non-compliance with regulatory targets for P discharge” assuming current treatment levels and if treatment efficiency (% P removed) stays constant as inflow P load increases. The view of ESPP, however, is that that for sewage works with a P-discharge consent, increased inflow P will generally not result in increased P discharge, because discharge is managed to respect the consent level (see Evans 2007), although it may result in increased treatment costs (increased chemical dosing, increased biosolids production). It would also result in increased P inputs to the environment in storm overflows. Some large UK sewage works do not today have a P discharge consent, because they do not discharge into eutrophication sensitive* waters. Around 3% of the UK population are not connected to sewerage and a further c. 3% are connected to small sewage works not subject to P discharge consents (figures taken from the study supplementary information p.3). Additionally, not considered in this study, around 3% of sewage is lost in exfiltration from sewage pipes before reaching the sewage works (from Gilmour et al. 2004). That is, in total maybe 10% of sewage is not entering sewage works with P discharge consents, and for this part increased sewage P levels will partly reach the environment and have environmental impacts.
The authors conclude planning and investment should take into account possible increases in P entering sewage works with healthier diets, in order to maximise recovery and recycling of this phosphorus.
“Plant-based diets add to the wastewater phosphorus burden, K. Forber et al., Environ. Res. Lett. 15 (2020) 094018
https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab9271
* the EU Waste Water Treatment Directive 91/271/EEC defines (Annex II) Sensitive Areas as waters which are “eutrophic or which in the near future may become eutrophic if protective action is not taken”.
Organic Farming can only feed the world with food system changes
A food system analysis of global agriculture suggests that a complete conversion to Organic Farming would require a “huge” increase in land use ( > +30% ) if other changes in the food system are not made, in particular reductions in food waste and in consumption of animal products. Only 20% conversion to Organic Farming would be possible without increasing land use by more than 5%, without other food system changes. Impact on phosphorus surplus is considered negligible, whereas nitrogen surplus would be completely avoided. However, it is noted that nitrogen supply for Organic Farming is a challenge, which previous authors conclude could only be met if cropping intensities were increased and fallow land and intercropping were to be systematically used for legume production, which may not be possible because of e.g. water supply and feasibility of legume production in intercropping in some regions (see Badgley C et al., 2007, Connor D. et al. 2008 and 2013).
“Strategies for feeding the world more sustainably with organic agriculture”, A. Muller et al., Nature Comunications, 8, 1290, 2017, DOI.
Calcium phosphate citrate nanoparticles effective in targeting cancer tumours
Tests on mice suggest that phosphate nanoparticles can reduce cancer tumours. A colloid of mesoporous amorphous nanoparticles with a very high surface area (Brunauer-Emmett-Teller > 900 m2/g) was produced by reacting Ca, P and citric acid at a ratio of 5:3:5. The particles were then coated in lipid or casein. These particles are non-toxic and release non-toxic molecules if broken down in the body, but can selectively kill cancer cells. The cancer cells take in the nanoparticles, leading to high intracellular levels of calcium and citrate which kills them. In vivo tests confirmed that the coated particles strongly decreased the viability of cancer cell lines, at concentrations down to 30 µg/l, but did not significantly reduce normal cell viability at up to 100 µg/l. Tests with mice showed that the particles reduced the size of two different aggressive pleural tumours by 40% and 70% after two applications, whereas up to eight applications showed no other adverse effects.
“Synergistic Combination of Calcium and Citrate in Mesoporous Nanoparticles Targets Pleural Tumors”, C. von Shirnding et al., Chem 7, 1–15, 2020 DOI.
How not to do Life Cycle Analysis
A paper in Science of the Total Environment by Golroudbary et al. claims in its conclusions that “phosphorus recycling is not a sustainable solution in a longer perspective”. The paper claims to compare energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions for P-recycling with those from phosphate rock mining and mineral fertiliser production. However, the authors seem to misuse data not relevant for P-recycling, and their conclusions are based on an inappropriate LCA allocation of all sewage works emissions to P-recovery, ignoring the fact that the principal function and obligation of the sewage works is to treat sewage.
LCA allocation factors are not mentioned in the paper, whereas a completely inappropriate 100% allocation factor is given to recovered P, zero to N, zero to clean water.
The authors base their analysis of energy demand for P-recycling on only a few papers, in particular Sanders 2003 (pig manure), Ye 2019 (wastewater, no quantitative data on energy or chemicals use), Piippo 2018 (wastewater, comparison of GHG emissions from different sewage sludge treatment routes in Northern Finland), Spångberg 2014 (wastewater, see below) and Buratti 2015 (solid waste).
They conclude that “70% of the GHG emissions from P-recycling is caused by wastewater processing”. This claims to be confirmed in the paper’s supplementary information, where “Energy requirements for wastewater recycling” are indicated as “179 MJ/0.15 kgP” taken from Spångberg 2014. In Spångberg, it is clear that this energy consumption (179 MJ) is for removing both 1.21 kgN and 0.15 kgP in a sewage works operating chemical P removal, not for removing phosphorus only, and not for recycling these nutrients. Attributing this number only to phosphorus recovery is therefore incorrect. Furthermore, and fundamentally, as the authors themselves point out, sewage treatment and phosphorus removal are in any case necessary for environmental protection. The conclusions comparing energy consumption and GHG emissions for P-recycling from sewage to phosphate rock mining and mineral fertiliser production are thus based on a false starting point.
The use of Sanders 2003 is equally inappropriate. This paper considers the overall LCA of several options for management of pig-manure, mostly assessing nitrogen not phosphorus. Use of this data to draw conclusions concerning emissions related to P-recycling is again incorrect, in that the manure must be managed in any case.
Buratti 2015, used for “solid waste”, is also not appropriate. This paper compares composting of food waste to production of chemical fertilisers for the same nutrient value, but again is not relevant for assessing emissions related to P-recycling because the treatment of the food waste is necessary in any case.
The Golroudbary paper is illustrative in several ways: 17 pages of mathematic formulae will not lead to useful results if inappropriate data and system allocations are used; life cycle analyses can be made to say different things depending how the ‘Functional Unit’ and ‘Boundaries’ are defined and how emissions are “allocated” to different functions; “peer reviewed” does not mean scientifically meaningful.
Note that the above is not in any way a criticism of the different papers cited by Golroudbary. These papers are respectable studies, which do what they claim to do, and their authors obviously cannot be held responsible for their subsequent misuse.
“Environmental sustainability of phosphorus recycling from wastewater, manure and solid wastes”, Science of the Total Environment 672 (2019) 515–524 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.439
Stricter nutrient thresholds needed for rivers
An assessment (1) based on nearly 1 000 samples comparing vegetation samples in rivers to nutrient concentrations in the Central-Baltic Region of Europe (Belgium, Denmark, Estonia, France, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Luuxembourg, the Netherlands, Poland) suggests that nutrient thresholds currently set by some countries are too high to achieve Good Ecological Status (as defined by the EU Water Framework Directive 2000/60/EC = WFD). The authors, led by the European Commission JRC Ispra, looked at both macrophytes (plants) and phytobenthos (bottom vegetation, algae and plants), concluding that both should be considered, compared to soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP), total phosphorus (TP) and total nitrogen (TN). They compared nutrient levels to EQRs (Ecological Quality Ratios), that is ratios between observed data for macrophytes and phytobenthos and expected ‘reference’ conditions (natural state in the water body), with assessment using the methods defined by each country in WFD intercalibration, e.g. density, species or taxon variety. They conclude that thresholds for Good Ecological Quality range from 30 - 90 µg/SRP/l and 1.0 – 3.5 mgTN/l, varying with river size, altitude and alkalinity. These are ln some cases lower that the boundaries set by Member States which range from 70 to 130 µgSRP/l and 2.3 – 10.0 mgTN/l.
A previous paper (2), led by the same authors at EU JRC Ispra, highlights the wide variety of different nutrient criteria used by EU Member States for quality status assessment under the Water Framework Directive, concluding that in some cases inappropriate criteria may be hindering achievement of good status. Different nutrients (N or P) are used for different water categories, whereas recent research shows that co-limitation is not uncommon. Difference in methods (soluble or total N or P, season of assessment, metrics) mean that thresholds are not comparable. Nutrient criteria are in some cases not clearly related to biological response, and so good ecological status. Criteria fixed by expert judgement tend to be higher (less demanding) than those based on data and modelling. Some countries are using thresholds “significantly above” known limiting nutrient concentrations, or even criteria taken from drinking water standards, which are not intended for this purpose.
(1) “Estimating river nutrient concentrations consistent with good ecological condition: More stringent nutrient thresholds needed Ecological Indicators”, S. Poikane (EU JRC Ispra) et al., 121 (2021) 107017 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107017
(2) “Nutrient criteria for surface waters under the European Water Framework Directive: Current state-of-the-art, challenges and future outlook”, S. Poikane et al., Science of the Total Environment 695 (2019) 133888, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133888
See also: “Deriving nutrient criteria to support ʽgoodʼ ecological status in European lakes: An empirically based approach to linking ecology and management”, S. Poikane et al., Science of the Total Environment 650 (2019) 2074–2084, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.350
Urban nitrogen budgets overview
An interesting analysis of different approaches to nitrogen flow and stock studies for urban areas. Over 60 studies are referenced and information drawn from around twenty of these is outlined and discussed. Nitrogen budget studies in the past have looked at soil systems, at water (river transported N comparing upstream and downstream of a city), atmospheric emissions, human and animal food chain, waste and wastewater treatment. Several studies note that nitrogen fertilisers are often used at very high rates in urban areas, both on lawns and in small farms on crops such as vegetables. Little data was found on nitrogen flows and losses in solid waste treatment. Wastewater treatment showed more significant nitrogen emissions (N2O, ammonia) both to air and to water and often low levels of nitrogen recycling.
Svirejeva-Hopkins, looking at Paris, suggested that the largest N flow was in human food, with around half of this N being finally converted to N2 in wastewater treatment, but the largest environmental impact was from fossil fuel burning, in particular traffic.
Studies, such as L. Baker 2001, suggesting accumulation of N stocks in cities may be flawed.
Several studies for Beijing (Zhang 2016, 2018, 2020) show that total N flows have increased slowly (+1% per year 1996-2012, with N input to farmland and animal feed falling considerably but transport emissions increasing strongly.
Overall, nitrogen recycling rates tend to be very low, e.g. 7% for Bangkok (Faerge 2001). The authors note the difficulty to compare studies, because methodologies differ, and the need to engage with experts beyond scientists to assess relevant flows and processes.
“Urban nitrogen budgets: flows and stock changes of potentially polluting nitrogen compounds in cities and their surroundings – a review”, W. Winiwater et al., J Integrative Env Sciences, vol. 17, n°1, 57-71, 2020 DOI.
ESPP members

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews050
Download as PDF
Consultations open
STRUBIAS (Fertilising Products Regulation) final criteria public consultation
EU consultation on Animal Feed : Circular Economy not considered
EU consultation : Zero Pollution Ambition
EU consultation: algae production and use
EU consultation: food “nutrient profiles”
EU consultation: industrial and agricultural emissions
EU consultation: Sewage Sludge Use in Farming
Events
CRU Phosphates 2021: “the” phosphate industry event
Save the date: Phos4You Final Conference
EAT – RagnSells webinar on nutrient circular economy
Insect production for sustainable food and feed
SERA-17 annual meeting: agricultural phosphorus run-off
Policy and science
ESPP input to EU Soil Strategy
Analysis and plant tests of 24 commercial struvites
Renewable Nutrients / QuickWash update
EIP-AGRI “Ideas for Operational Groups”
Students input to EU nutrient action plan
Regulatory options to align livestock farming with environmental objectives
EU Fertilising Products Regulation
JRC “By-Product” 2nd report open for comment
STRUBIAS criteria finalised
Possible new CMCs 9
Why are animal by-products not moving towards the circular economy? 9
ESPP members news
ESPP new member: P-TRAP
Ostara purchases fertiliser granulation facility
Call for partners P-recovery via incineration / gasification
ESPP members
Consultations open
STRUBIAS (Fertilising Products Regulation) final criteria public consultation
Open to 1st February 2021. The EU has published the final “STRUBIAS” criteria for struvite and phosphate salts, ash / ash derived materials and biochars and pyrolysis materials, prior to adoption and official publication of the criteria.
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12136-Pyrolysis-and-gasification-materials-in-EU-fertilising-products
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12162-Thermal-oxidation-materials-and-derivates-in-EU-fertilising-products
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12163-Precipitated-phosphate-salts-and-derivates-in-EU-fertilising-products
EU consultation on Animal Feed : Circular Economy not considered
Open to 25th January 2021. ESPP has input to this public consultation (see here) underlining that nutrient recycling is not addressed. The different animal feed Regulations (1831/2003, 767/2009 annex III and 178/2002) currently exclude, from use in production of animal feed additives, any nutrients resulting from processing of manure or wastewaters, even after e.g. incineration, acid extraction from ash and then solvent purification. ESPP fully supports strong safety requirements to prevent any risk of contamination in the animal feed chain, but considers that the blanket exclusion of appropriately processed nutrients poses an unnecessary barrier to nutrient recycling, by blocking added-value markets and potentially preventing sale of recovered nutrients to commodity chemicals markets.
Public consultation: https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12624-Feed-additives-revision-of-EU-rules
EU consultation : Zero Pollution Ambition
Open to 10 February 2021. Public consultation on the EU Zero Pollution Action Plan for air, water and soil, to be adopted in 2021. The Commission’s ‘Roadmap’ outlines as key orientations to: strengthen implementation and enforcement, improve the regulatory “acquis” on health and environment (including water, waste and wastewater), address soil pollution, improve governance and drive societal change / sustainable consumption. The public consultation questionnaire asks for input on questions such as to what extent pollution is felt to be negative, which populations are most exposed, which EU policies are known, which types and sources of pollution should be priorities, possible types of action (regulatory, financial, education, …), significance of digitalisation. “Excess nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus)” are proposed as one of the possible priority pollutants.
“EU Action Plan Towards a Zero Pollution Ambition for air, water and soil” HERE
EU consultation: algae production and use
Open to 18th January 2021. This Roadmap consultation will prepare possible targeted activities to support the algae sector, maybe including regulatory measures. The document submitted to consultation recognises fertilisers and bio-stimulants amongst different uses of algae and the need of nutrient inputs to algae production. Regulatory gaps cited include limitations to use of algae based animal feeds and fertilisers, and status of algae in the Organic Farming Regulation. Possible regulatory actions cited include binding targets for substitution of fish-based aquaculture feeds. ESPP notes that the proposed Roadmap does not mention the use of algae for waste water treatment (although nutrient removal as an ecosystem service is cited).
Public consultation “Blue bioeconomy - towards a strong and sustainable EU algae sector”
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12780-Towards-a-strong-and-sustainable-EU-Algae-sector
EU consultation: food “nutrient profiles”
Open to 3rd February 2021. This Roadmap consultation aims to implement the action announced in the EU Farm-to-Fork Strategy on “nutrient profiles” for foods and “mandatory front-of-pack nutrition labelling” for food products. The Farm-to-Fork strategy specifies also an action on ‘maximum levels for certain nutrients’ in processed foods, but this is not mentioned in this Roadmap. The term ‘nutrient’ is here used to cover only “fat, saturates, sugars, salt”. ESPP notes that this will make difficult general public communication concerning the links between plant nutrients (phosphorus, nitrogen …), food sustainability and health. The EU proposal does not consider phosphorus-content of food products, despite the significance of this for kidney disease patients (see ESPP eNews n°34, EFSA new ADI for phosphorus in food).
Public consultation:
“Facilitating healthier food choices – establishing nutrient profiles” = Roadmap for a “Proposal for a revision of Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 on the provision of food information to consumers”
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12748-Setting-of-nutrient-profiles-
EU consultation: industrial and agricultural emissions
Open to 23rd March 2021. This EU general public consultation questionnaire addresses emissions from industrial installations, livestock production and pollutant emission monitoring and information, via the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) and the European Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (E-PRTR). ESPP will input underlining the need to better address the Circular Economy and resource consumption (questions 1, 2, 3, 8, 19, 22, 23); the importance of livestock production (intensive pig and poultry units in question 7, and proposed addition of intensive cattle rearing in question 8). ESPP also underlines that PFAS/PFOS, pharmaceuticals (human and veterinary and microplastics should be added to the E-PRTR substances list, because they pose obstacles to nutrient recycling and the Circular Economy and should be monitored and emissions reduced at source. ESPP also suggests that the E-PRTR list should be automatically updated to be coherent with the Water Framework Directive Priority Substances list (certain pharmaceuticals, HBCDD brominated flame retardant).
Public consultation “IED-EPRTR-Revision-OPC-2020” https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12583-Industrial-pollution-revision-of-the-European-Pollutant-Release-and-Transfer-Register-/public-consultation
EU consultation: Sewage Sludge Use in Farming
Open to 5 March 2021. Public consultation to support revision of the EU Sewage Sludge Directive 86/278, as promised in the Circular Economy Action Plan. The presentation underlines that the objective is valorisation in agriculture of nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen, as well as organic carbon. The questionnaire is open to individuals, stakeholders and companies and includes general questions about whether the respondent considers sludge use in agriculture to have different positive or negative effects, cost-effectiveness of agricultural sludge application, whether sludge quality is improving and which contaminants are today relevant.
A presentation to the EU Fertilisers Working Group by DG Environment (Caroline Attard) indicated that the evaluation underway of the Sludge Directive will particularly look at nutrient recycling, as well as at methane emissions, impacts of stricter wastewater treatment requirements and pollutants in sewage sludge. A study has been launched into different pollutants in sewage sludge, their sources and risks, possible mitigation according to sludge treatment methods and possibilities for removing pollutants at source. This study will also look at benefits and cost-effectiveness of different sewage sludge use or recycling routes.
Public consultation on the Sewage Sludge Directive HERE
Events
CRU Phosphates 2021: “the” phosphate industry event
The annual industry conference and exhibition of the world phosphates industry (mining and processing, fertilisers, feed, food, technical applications), CRU Phosphates 2021, will take place online 23-25 March 2021. This conference annually brings together over 400 delegates from phosphate rock mining, processing and different user industries and stakeholders. This year’s online event includes a virtual exhibition and networking centre, interactive discussion groups, conference presentations with Q&A. ESPP members benefit from a 10% discount (on request from ESPP) on the €440 conference fee, which is significantly cheaper than the usual physical conference.
CRU Phosphates 2021 https://bit.ly/386jzjr and events showcase page on LinkedIn
Save the date: Phos4You Final Conference
After four years of cooperation, the Phos4You Interreg project’s final conference will focus on : Recovery, processing and distribution of novel phosphorus (P) products; Technologies and processes for deploying P-recycling in urban areas ; Technologies and approaches for enabling P-recovery in remote, rural and island locations; Quality assessment of recovered P materials and LCA-LCC of P-recovery processes. The programme will include plenaries, multi-stakeholders discussions, a poster exhibition, an excursion to a Phos4You demonstrator and plenty of opportunities to enjoy, exchange and network. Speakers will be Phos4You actors in the fields of wastewater treatment and sewage sludge incineration, recovery processes and research. Stakeholders in the agri-food value chain as well as policymakers from EU and national organisations will share their knowledge and engage in discussion
Phosphorus recovery from wastewater: approaches developed within Phos4You, 22-23 September 2021
Essen - Germany & online www.nweurope.eu/phos4you
EAT – RagnSells webinar on nutrient circular economy
“The science-based global platform for food system transformation”, EAT is a non-profit founded by the Stordalen Foundation, Stockholm Resilience Centre and the Wellcome Trust. RagnSells (EasyMining’s mother company) organised a session on nutrients as part of the EAT@Home online event.
Pär Larshans, Ragn-Sells and Anna Lundbom, EasyMining indicated the companies’ objectives to maximise recycling, remove contaminants and ensure long-term sustainability of recycling. Sara Stiernström, EasyMining, underlined that EU regulations for both fertilisers and animal feed are based on the origin of input materials, not on the quality of the product, thus posing a fundamental and inherent obstacle to recycling.
- Fabrice DeClerck, Director of Science at EAT, underlined that the United Nations will take critical decisions in 2021 on climate, food and the environment. Today environmental curves are still trending the wrong way, such as increases in dead zones driven by nutrient losses. Business as usual will result in +30% increases in planetary boundary transgression for phosphorus and nitrogen. Unlike climate change, the biggest potential impacts on nutrient losses come not from dietary choice, but from technology and waste reduction. The aim of respecting planetary boundaries is urgent and essential, but needs to be completed by actions towards circularity: “Farm to Flush”.
- Asger Christensen, Member of the European Parliament, underlined the potential for technology to improve nutrient use in farming and the potential of the Circular Bioeconomy as a new business model for farmers.
- Magnus Ek, Member of the Sweden Parliament, noted that Sweden is developing a new Circularity Strategy and Action Plan, which will include nutrients. To enable recycling, regulatory support is necessary and costs of externalities must be paid for resource consumption: today’s tax system is not fit for purpose for the circular economy.
- Pär Dalheim, Svenskt Vatten (Sweden municipal water federation) fully supports recycling, both of water and resources present in waste water, and aims to be a resource provider in the future.
- Klaus Kastenhofer, REWE Austria, underlined the need to convince consumers that recycled products are safe.
- Kristina Atkisson, WWF, emphasised the need to reduce nutrient losses to the Baltic, to reduce from eutrophication. Key actions include precision farming, manure treatment to facilitate transport (so enabling better use), reduction at source of contaminants and separative sewerage. WWF supports the setting of national nutrient recycling goals and nutrient accounting.
EAT@Home https://eatforum.org/event/eat-home/
Watch all sessions at https://youtu.be/Xtzl1eyboEs
Watch the RagnSells session on nutrients https://www.ragnsells.com/eat and to watch https://youtu.be/1Pi1aZ78X30
Insect production for sustainable food and feed
300 participants (including ESPP President, Ludwig Hermann, as a panellist) joined the IPIFF (International Platform of Insects for Food and Feed) webinar on circularity in insect farming, 19th November 2020. Sabine Jülicher, European Commission DG Santé, indicated that insect production is a relevant component of sustainable food chains. She noted that the use of food waste as feedstock for insect farming will be assessed by EFSA (no timescale yet). Bas Drukker, European Commission DG Agriculture, noted that insects can be used in Organic Farming in some Member States, and that 2021 should see adoption of EU standards for insect production, and consequently for their use as human food and animal feed / aquaculture feed products, as well as standards for insect frass (insect production “manure”). William Clark, Zero Waste Scotland, and Chris Atkinson, IFOAM (EU Organic Farming federation), both underlined the role of insect production in improving local and regional food system circularity.
IPIFF “The European insect sector reaffirms its commitment to supporting the EU sustainability agenda” information 20/2/2020 and webinar recording watch here
SERA-17 annual meeting: agricultural phosphorus run-off
SERA-17 is an expert network on phosphorus sustainability in agriculture. The group’s 2020 annual meeting, online 15th October 2020, led by SERA-17 chair, John Kovar, USDA-ARS Iowa, discussed four operational projects underway:
- Deanna Desmond, North Caroline State University: Collection of data on fertilisation practices and soil tests across the USA. Data from nearly 1300 field trials and 60 questionnaire responses from 48 States are collated so far. The objective is to develop a Fertilizer Recommendation Support Tool (FRST).
- Andrew Sharpley, University of Askansas: phosphorus trade-offs project, looking at trade-offs for practices such as 4R fertiliser application, no-till and cover crops, buffer strips …
- Lindsay Pease, University of Minnesota: 4R implementation in the Red River Basin, Northern Great Plains
- Pauline Welikhe, Purdue University: Network P Budget Project (USDA Long-Term Agroecosystem Research LTAR), analysing data on soil – plant system P budgets (data from 19 sites, 41 systems to date)
“SERA-17 Meets Virtually to Discuss P” 2/11/2020
Policy and science
ESPP input to EU Soil Strategy
ESPP submitted input to the public consultation on the EU Soil Strategy (Roadmap, 8/12/2020). ESPP underlined the importance of soil to food production, climate and biodiversity, and the critical role of phosphorus and other plant nutrients in soil quality and fertility. ESPP noted that the Soil Strategy should include ensuring a fir income for farmers, should contribute to increasing soil organic carbon (including by facilitating return to soil of carbon-rich secondary materials). Problematic contaminants must therefore be addressed at source, in particular PFAS, persistent plastics additives, veterinary pharmaceuticals. ESPP noted the need for EU policy and regulatory support for nutrient stewardship and carbon recycling, including the CAP FaST Tool, addressing obstacles to recycling of manures and animal by-products in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation and progressing recognition of nutrient recycling in Organic Farming.
ESPP input to EU Soil Strategy, 8th December 2020 here.
Analysis and plant tests of 24 commercial struvites
Despite variable characteristics, all the struvite samples showed similar fertiliser effectiveness, comparable to single super phosphate in 28 pot trials with maize. The authors estimate that around 900 – 1250 tP/y (phosphorus) were recovered as struvite in the EU in 2019. In this study, struvites from 24 European struvite production plants were sampled and tested, from a total of 39 plants identified in Europe (39 sewage works, 9 potato industry, one dairy wastewater). Organic carbon was always lower than the proposed EU Fertilising Products Regulation (FRP) STRUBIAS limit of 3% (and often very much lower) in struvites recovered from digestate or digestate dewatering liquor, but significantly higher for three struvites recovered from secondary wastewater treatment effluent (one of these struvites also showed P content below the FPR limit). Heavy metals were very much lower than the FRP limit. Biological indicators of pathogens were generally low in the struvites, and the data is considered to indicate that the crystallisation process selectively excludes pathogens, leaving them in the water phase. Nonetheless struvites can exceed limits for microbes, and should be analysis. Storage of the struvite causes a reduction in microbe levels. In pot trials, all the struvites gave maize biomass dry weight results similar to single super phosphate (SSP) and significantly better than phosphate rock or control.
“A systematic comparison of commercially produced struvite: Quantities, qualities and soil-maize phosphorus availability”, M. Muys et al., Science of the Total Environment 756 (2021) 143726, DOI.
Renewable Nutrients / QuickWash update
The QuickWash process, developed for P-removal and recovery from manures by the USDA (see SCOPE Newsletter n°119), is now developed and marketed by Renewable Nutrients. The process has been developed and can now be combined with ammonia removal for pig manure, cattle manure or municipal wastewater. The basic process involves acid dosing and solid/liquid separation, giving a low-P “acid recovered manure” adapted for local land application. Alkali (lime) is then dosed to precipitate and recover calcium phosphate. Polymer dosing improves precipitation to give a low P discharge effluent. A 2020 paper updates on experimental testing of the process for dairy manure. Course solids after the acidification stage are shown to be useable as cattle bedding, and the finer solids as low-P N fertiliser. Renewable Nutrients are now combining Quick Wash with ammonia recovery (as ammonia sulphate). They have also demonstrated the technology at a 7 200 head pig farm in Ohio. Tests have also shown that the technology can be combined with geotextile bag filtration of pig manure lagoon sludge.
Renewable Nutrients – QuickWash https://www.renewablenutrients.com/
“Chemical Extraction of Phosphorus from Dairy Manure and Utilization of Recovered Manure Solids”, A. Szogi et al., Agronomy 2020, 10, 1725; DOI.
EIP-AGRI “Ideas for Operational Groups”
The European Commission (DG AGRI) organisation EIP-AGRI has published a short document suggesting themes for “Operational Groups”. These are local innovation/demonstration projects, funded by the EU Rural Development Programmes (1 600 projects funded to date). A number of the proposed themes concern nutrients. This includes those originating in the EIP-AGRI Focus Group on Nutrient Recycling, proposed by ESPP (final report 2017, see ESPP eNews n°18)
- Integration of nutrient management in certifying schemes
- Demonstration of how tailor-made biobased fertilisers match plant requirements
- Cooperation business models to improve the production and marketing of tailor-made fertilisers
- Exchange of information and practices between farms on the use of bio based fertilisers
- Development of new fertilisers for organic farming
- Demonstration of nutrient recycling technologies such as low ammonia (NH3 emission techniques)
- Nutrient release of organic fertilisers in organic farming
- Fertiliser efficiency: developing advice based on a system approach,
- Increasing nutrient efficiency with cover crops and optimal use of organic manure
- Optimising the use of innovative organic sourced fertiliser
- Identify best practices to optimise energy/nutrient cycles
- Appropriate handling and use of organic fertilizer
- Manure composting
- On-farm implementation of green manure
- Promote legumes by inoculation of seeds of specific species with effective Rhizobium strains
- Improve fertilisation strategies to increase grassland production
- Livestock feed: how to analyse and get “on-line’ (fast) nutrient value for (by-)products
- Optimise and/or develop new forage conservation techniques to avoid nutrient losses …
- Improving knowledge exchange to increase nutrient use efficiency by including different experts
- Making fertiliser advice more farmer friendly and sustainable
- Remote sensing applications for agriculture, with a focus on … nutrient management
“Ideas for Operational Groups and other innovative projects, from Focus Groups experts”, EIP-AGRI, November 2020
Students input to EU nutrient action plan
Seven Masters students at the University of Amsterdam have prepared input to the European Commission for the future Integrated Nutrient Management Action Plan, announced to be developed as part of the Farm-to-Fork policy in 2021. They propose to develop a “Phosphates Directive” to limit the use of P in agriculture and concentrations in surface waters. Their specific proposals are to fix a mandatory level of recycled P in fertilisers, a tariff on phosphorus imports, lower cadmium limits, addressing legal obstacles to P-recycling , support for P-recycling investments and reducing consumption of meat and dairy (including by investing in meat replacement products, adjusting CAP funding and supporting farmers converting away from livestock). The recommendations are based on a readable 40-page summary of the context, challenges, scenarios and vision, on which the recommendations are based.
Input on the proposed considerations for the EU’s Integrated Nutrient Management Action Plan (INMAP), I. Stammes, T. Maassen, F. Miller Kerins, G. Votano, D. Palma Munguia, Z. Yuan, M. Gereadts, Amsterdam University, June 2020 online here.
Regulatory options to align livestock farming with environmental objectives
A study from the University of Rostock, Germany (ESPP member), assesses policy instruments to make livestock farming compatible with legally binding environmental objectives, including the Paris Climate Agreement, the Convention on Biological Diversity and disrupted nutrient cycles, in particular P and N surpluses resulting from concentrated livestock farming. The study considers a greenhouse emissions cap-and-trade system for livestock farming, and a livestock-to-land ratio fixed to limit greenhouse emissions per hectare. The authors note that the cap-and-trade system has less impact on livestock farmers, allows simpler protection at EU borders vis-à-vis countries not applying similar obligations (by ETS), but might be less effective in addressing biodiversity and nutrient cycles unless combined with a livestock-to-land ratio.
“Land Use, Livestock, Quantity Governance, and Economic Instruments—Sustainability Beyond Big Livestock Herds and Fossil Fuels”, A. Weishaupt et al., Sustainability 2020, 12, 2053, DOI.
EU Fertilising Products Regulation
JRC “By-Product” 2nd report open for comment
The second JRC report on “proposals for by-products as component materials for EU fertilising products” is open for comment to 25th January 2021. The report is available here. JRC proposes to allow use of (only) four classes of by-products under CMC11 of the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation, that is by-products from: fossil fuel refining (but this in fact seems to also include various chemical industry by-products, such as ammonium from caprolactum …), refining of minerals, ores and metals (but phosphogypsum seems to be not included), some gas cleaning systems (but not from waste or manure treatment, see below), processing of biomass, water, food, drink, biorefineries, including from the pulp and paper industries. For ammonia or sulphate salts recovered from cleaning of process gases, the report suggests (pp. 49-50) that these cannot be considered as by-products if there is any waste input into the process. This would exclude nutrient salts from stripping of biogas from digesters processing manure or food waste, or from stripping of municipal solid waste incineration off gases. It should be noted that this report concerns only use of by-products in fertilising products without further processing. If a by-product is used as a chemical reagent then this is eligible for CMC1 (e.g. sulphuric acid recovered from oil refinery sulphur removal from fuels, reacted with phosphate rock to produce phosphoric acid).
“Technical proposals for by-products as component materials for EU Fertilising Products” (2nd report), European Commission JRC, 27th November 2020 here, open for comment to 25th January 2021. Comments must be submitted via a member of the EU Fertilising Products Expert Group. ESPP is a member, so you can send comment to and we will forward them.
STRUBIAS criteria finalised
The EU Fertilisers Expert Group validated the finalised “STRUBIAS” criteria, which define under what conditions struvite & precipitated phosphate salts, ash-based materials and biochars and pyrolysis materials will be included in the list of materials which can be used in future CE-marked fertilisers (CMC = Component Material Categories of the EU Fertilising Products Regulation). The key principles defined in the JRC “STRUBIAS” report (2019) remain unchanged: phosphate salts recovered from sewage and materials recovered from sewage sludge incineration ash will be eligible, but biochars from sewage sludge will not. Materials not included in the new EU Regulation can nonetheless be authorised in national fertilisers. Manure and other animal by-products (ABPs) of Cat. 2 and 3 can be used as input materials for all three STRUBIAS categories, but only after definition of an ABP “End Point” by DG SANTE/EFSA (see below). Minor wording changes concern interaction with CMC1, frequency of Conformity Assessment audits, bio-waste, definition of waste water, incineration temperature clarification, definition of ash. A discussion concerning sewage sludge in biochars, currently excluded, confirmed that this should be reassessed if new scientific data is developed to demonstrate safety. The finalised criteria will now be subject to a one-month public consultation (in coming months), translation and publication, and will then logically be able to enter into implementation at the same time as the Fertilising Products Regulation itself in 2022.
Possible new CMCs
The European Commission has circulated to Member States and stakeholders, for comments, a table, prepared by ESPP, of secondary materials which cannot currently be used as input materials (CMCs) under the EU Fertilising Products Regulation, and which offer potential for nutrient recycling. This document can be consulted here and comments are welcome, either on the materials listed or proposals for other new CMC materials. The objective is to collect data and to engage discussion with the European Commission to hopefully launch assessment of these and proposal of CMC criteria, although the Commission has indicated that this will not be possible in coming months until other outstanding work is finished finalising and implementing the Fertilising Products Regulation.
Input welcome: “ESPP table of materials currently not included in the FPR as input materials (CMCs)”, v4/11/2020 here
Why are animal by-products not moving towards the circular economy?
At the EU Fertilisers Expert Group, a representative of DG SANTE was asked to update on progress towards including animal by-products (ABPs) into the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation, which was published in June last year. This is important for nutrient recycling because until the questions around animal by-products are resolved, manure and all other ABPs will be excluded from all CE-mark fertilising products (composts, digestates, biochars, precipitated phosphate salts, …).
CMC10 Animal By-Products, in the published Regulation last June, was an ‘empty box’: after several years of discussion of the draft Regulation, DG SANTE had not provided content, and still today, little progress has been made. This is particularly surprising in that manures and various other ABPs are authorised for use as fertilisers in the Animal By Products Regulation (art. 22 of Regulation 142/2011, that is since nearly ten years ago), subject to specified processing requirements to ensure safety. The difference is that under this regulation 142/2011 these ABP-derived products remain subject to traceability, which would not be the case when included in CE-mark fertilisers under the EU Fertilising Products Regulation FPR (note: this is ESPP’s understanding: ABP regulation is complex and we do not claim to fully understand).
The DG SANTE representative at the EU Expert Group Meeting provided neither slides nor documents, and seemed reluctant to release any information, indicating only that a consultation has been submitted to EFSA (European Food Safety Agency), whose Opinion is necessary before modification of the ABP Regulations. But in fact, the information is public: the mandate requesting an EFSA Opinion is publicly available (enter ‘Mandate Number’ 2020-0088 HERE). This mandate concerns only the following:
- meat meal, bone meal, meat-and-bone meal, hydrolysed proteins of Category 3 materials
- processed manure, compost, biogas digestion residues, feather meal, glycerine and other products of Category 2 or 3 materials derived from the production of biodiesel and renewable fuels,
- petfood, feed and dog chews that have been refused for commercial reasons or technical failures,
- derived products from blood of animals, hides and skins, hoofs and horns, guano of bats and birds, wool and hair, feather and downs, and pig bristles.
ESPP does not understand why it has taken nearly a year after publication of the Fertilising Products Regulation before this mandate was submitted to EFSA, whereas it could have been done immediately or even before publication (ABPs were already an “empty box” in CMC10 in the initial FPR proposal published in March 2016), especially as the mandate simply copies the list of materials already approved for use in fertilisers in the 142/2011 ABP regulation.
DG SANTE provided no answers concerning STRUBIAS materials using ABPs or manure. Similarly, the STRUBIAS process was launched by the European Commission in 2016 and the JRC final report published summer 2019. ESPP does not understand why no mandate on this has yet been given to EFSA.
ESPP members news
ESPP new member: P-TRAP
P-TRAP, a H2020 MSCA-ITN European Training Network – is a consortium of 16 international participants and hosting 11 Early-Stage Researchers (ESRs). A characteristic of these networks is a combined focus not only on science but also on training of a new generation of creative, entrepreneurial and innovative ESRs.
Scientifically, P-TRAP targets two interlinked global problems: I) the flux of phosphate (P) from agricultural areas to surface waters is wasting a resource which is becoming scarce, and II) on the other hand, an enhanced loading of surface water with P is the main cause for eutrophication. Both are in conflict with our understanding of circular economy and a key challenge in meeting the objectives of the EU Water Framework Directive. Within P-TRAP we will develop new methods and approaches to trap P in drained agricultural areas and in the sediments of eutrophic lakes, aiming to constrain the uncontrolled loss of P in one system and preventing others from overloading.
The project is organized in 3 scientific work packages (WPs), which are closely interconnected and each tackling specific objectives and tasks to ensure a successful project.
More information about the project and our participants can be found at https://h2020-p-trap.eu.
Ostara purchases fertiliser granulation facility
Ostara (ESPP member), and the world’s leading producer of recovered struvite from municipal wastewater, has acquired Oakley’s fertiliser granulation facility at St. Louis, Missouri, USA. Oakley will provide full logistic support and storage facilities. Ostara aims to start production of its Crystal Green® continuous release fertiliser at the site within a year, so increasing the company’s production capacity by a factor of ten.
“Ostara and Oakley Sign Letter of Intent for Purchase of Oakley’s St. Louis Granulation Facility”, 3rd November 2020
Call for partners P-recovery via incineration / gasification
ESPP’s new member ZSW is looking for partners in the area of phosphorus recovery via incineration / gasification of P-rich residual fuels (e.g. sewage sludge). The not-for-profit Centre for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research Baden-Württemberg" (ZSW, www.zsw-bw.de), Germany, is looking to participate in consortia or R&D projects into phosphorus recovery via incineration / gasification of sewage sludge or other wastes. The centre can offer testing at a 15 kWth fluidised-bed incinerator / gasifier with flexible feed gas dosing and high-temperature flue / product gas particle separation, as well as analysis of ash melting behaviour with rotational viscometer or thermogravimetry testing, and can contribute to theoretical studies (e.g. modelling and simulation works via IPSEpro, HSC Chemistry, own developed models), in synergy with a current Marie Curie project on P-recovery in fluidised bed incineration (ReCaPHOS, see https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/842138). Focus on Green Deal Calls and HORIZON EUROPE workprogramme.
If interested, please contact Ms. Dr.- Ing. Glykeria Duelli Varela, tel. +49 711 78 70-319 eMail:
ESPP members

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews049
Download as PDF
Online stakeholder dialogue webinar:
Friday 27th November: Nutrients in the EU Farm-to-Fork and Horizon Europe
Consultations & calls
Call for input: which recycled nutrient products for Organic Farming
EU consultation on Soil Strategy
EU consultation on Zero Pollution Ambition
EU consultation on environmental product claims
Horizon2020 R&D calls: Circular Economy, Farm-to-Fork
Call for presentations – Green Deal water & raw materials
Call for papers – Bio-based fertilisers
EU call for NGO Green Deal actions
Invitation for input on LCA guidelines for growing media
Policy
Meat and bone meal possibly excluded from Organic Farming
ESPP input on EU pollutant register
German Phosphorus Platform ‘Policy Memorandum’
EU to (nearly) ban all PFAS chemicals
Nutrient recycling
Lystek sewage sludge thermal hydrolysis
Upcycling manure to activated carbon adsorbent
Correction
N2 Applied LCA results
Webinars
European Commission webinar on P-recovery from municipal sewage
Biofertilisers and biostimulants from algae
IFS webinar presents nutrient recycling projects
Research and publications
Nearly half of the world’s cropland is phosphorus limited
Organic farms show P and K deficits
LCA of struvite recovery
Manure in the Baltic Region
Northern Ireland increasing phosphorus surplus
Nano calcium phosphate for cancer tumour treatment
Unsupported claim that P fertilisers impact biodiversity
Taiwan: diet phosphorus acceptable but calcium too low
Iran: diet phosphorus and calcium too low, sodium too high
New book “Phosphorus: Past and Future”
ESPP members
Online stakeholder dialogue webinar:
Friday 27th November: Nutrients in the EU Farm-to-Fork and Horizon Europe
Within the new Green Deal, the EU's 'Farm-to-Fork’ policy poses ambitious objectives for agriculture – food system sustainability, including to reduce nutrient losses by 50% and fertiliser use by 20% before 2030, to improve nutrient stewardship (revised Circular Economy Action Plan and European Integrated Nutrient Management Action Plan) and to address diet, including via consumer food product nutrition labelling. Horizon Europe also underlines circularity in the food system, and proposes to develop a “comprehensive EU policy to balance nutrient cycles”.
The objective of this webinar is to understand challenges and opportunities for nutrient management in 'Farm-to-Fork' policy implementation and enable dialogue between policy makers, NGOs, industry and professional organisations, scientists and regions/cities.
Friday 27th November, in three parts:
- 9h00 - 10h30 CET: dialogue and questions/discussion with experts
Nutrients in EU Green Deal policies: from objectives to actions
- 11h30 -12h30 CET: preparation of a contribution document for the European Commission
Input to the EU's Integrated Nutrient Management Action Plan
- 14h-15h30 CET: ESPP Annual General Assembly - members only.
Registrants to the ‘Farm-to-Fork’ webinar are invited to prepare before 23 November 2020 a contribution which be made available to all webinar registrants. ESPP will put online and circulate to all registrants one indexed pdf document containing all contributions received by this date as follows:
- please send to by 23rd November: maximum one page (but a well-spaced half page is more likely to be read); MUST be in WORD or RTF (NOT in pdf); can include hyperlinks to other documents, websites, etc; should include your contact email(s). Submissions which are too long or not in WORD/RTF will NOT be used.
Registrants are advised to also prepare a short statement which you can yourself post to the online ‘Chat’ at an appropriate point during the meeting, to link to this submission document and/or your website and/or to other publications. Registrants can also prepare in advance ‘Chat’ questions to submit online during the meeting to the webinar speakers and panellists
Webinar “Nutrients in the EU Farm-to-Fork and Horizon Europe”, Friday 27th November. 2020.
Registration: https://www.eventbrite.co.uk/e/nutrients-in-eu-farm-to-fork-policy-tickets-127743595533
Full programme and speaker updates here: https://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/events
Consultations & calls
Call for input: which recycled nutrient products for Organic Farming
ESPP is planning a webinar with Organic Farming associations across Europe to discuss which types of recycled nutrient products may be acceptable in Organic Farming, in order to then submit dossiers proposing their authorisation in the EU Organic Farming Regulation. Various organic or secondary materials (e.g. certain composts and digestates, plant biochar, certain animal by-products, wood ash) are already included in the Organic Farming Regulation (Annex I of EC 889/2008 as authorised fertilisers). Also, struvite recovered from sewage and calcined phosphates from sewage sludge incineration ash are currently expected to be added (EGTOP Opinion 2 February 2016 here). This webinar will be based on short presentations of various recycled nutrient products “candidates” for Organic Farming, based on discussion of Fact Sheets for candidate recycled nutrient products. If you wish to propose your recycled nutrient product to the Organic Farming movement, and present at this webinar, then you should prepare a Fact Sheet using the template here by 15th December 2020 (to send to ESPP as indicated on the template).
More information here
EU consultation on Soil Strategy
Open to 10th December. Consultation on an EU Soil Strategy “Healthy soil for a healthy life” (Roadmap), as part of the EU Biodiversity Strategy. Objectives fixed in the Biodiversity Strategy include to stop land degradation by 2030, with action to promote soil fertility, reduce erosion, increase soil organic matter, as well as addressing loss of wetlands and peatland and net land take and sealing. Problems cited include “Diffuse soil contamination by … antibiotics, excess fertilisers, microplastics, sewage sludge …”. Proposed actions include promoting sustainable soil management and improving soil quality monitoring.
Roadmap consultation HERE.
EU consultation on Zero Pollution Ambition
Open to 10 February 2021. Public consultation on the EU Zero Pollution Action Plan for air, water and soil, to be adopted in 2021. The Commission’s ‘Roadmap’ outlines as key orientations to: strengthen implementation and enforcement, improve the regulatory “acquis” on health and environment (including water, waste and wastewater), address soil pollution, improve governance and drive societal change / sustainable consumption. The public consultation questionnaire asks for input on questions such as to what extent pollution is felt to be negative, which populations are most exposed, which EU policies are known, which types and sources of pollution should be priorities, possible types of action (regulatory, financial, education, …), significance of digitalisation. “Excess nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus)” are proposed as one of the possible priority pollutants.
“EU Action Plan Towards a Zero Pollution Ambition for air, water and soil” HERE
EU consultation on environmental product claims
Open to 3rd December 2020. Consultation on product environmental claims & PEFs (Product Environmental Footprints) HERE
Horizon2020 R&D calls: Circular Economy, Farm-to-Fork
Calls for R&D proposals are open to 26 January 2021 on eight themes for the EU Green Deal (total one billion €). The themes include Farm-to-Fork, territorial Circular Economy, climate, biodiversity/ecosystems and zero pollution/toxic free environments.
The call on “Systematic innovations in support of the Farm-to-Fork Strategy” CL-GD-6-1-2020 specifically cites nutrient cycles, antimicrobial resistance and food waste as challenges. Proposals should address one of six proposed objectives including farm carbon sequestration, reducing fertiliser nutrient losses and fertiliser use, shifting to sustainable healthy diets.
The call on “Systemic solutions for the territorial deployment of the circular economy” LC-GD-3-2-2020 should be led by “circular territorial clusters”, bringing together companies, administrations and stakeholders for a “circular systemic solution”. Key product value chains cited are those of the EU Circular Economy Action Plan, including food, water and nutrients.
“European Green Deal Call is open - €1 billion investment in green and digital transition”, proposal submission deadline 26 January 2021 HERE.
Call for presentations – Green Deal water & raw materials
Organised by ESPP member MonGos, the first International Conference on Strategies toward Green Deal Implementation - Water and Raw Materials (ICGreenDeal2020) will take place online 14-16 December 2020. Proposals are invited to 30 November 2020 deadline for presentations or posters are invited on environmental engineering and management related to water or raw materials.
ICGreenDeal2020
Call for papers – Bio-based fertilisers
The journal “Agronomy” (Soil and Plant Nutrition) is calling for papers on "Integrated Nutrient Recovery from Organic Waste and Bio-Based Fertilizers" for a special issue. Submission deadline: 15th December 2020.
EU call for NGO Green Deal actions
The EU has pre-announced a call (to be published mid December) for NGO projects at the Members States’ level to mobilise and strengthen civil society participation and contribution to the implementation of the European Green Deal (under DG ENVI LIFE) EU budget 12 million €, maximum contribution 300 000 € per project.
Invitation for input on LCA guidelines for growing media
Growing Media Europe has published, for comment, proposed Life Cycle Analysis methodology guidelines (in accordance with the EU’s PEFCR Product Environmental Footprint Category Rules). Input is invited from stakeholders, industry, LCA experts, e.g. on document structure, methodology, applicability.
“GME draft Guidelines for LCA calculations open consultation”, deadline 14th December 2020 here.
www.growing-media.eu/
Policy
Meat and bone meal possibly excluded from Organic Farming
It is ESPP’s understanding that all MBM (meat meal, bone meal) may be excluded from use in Organic Farming in a proposed update of EU Regulation 889/2008. The EU Committee for Organic Production, 28-29 October 2020, discussed modifications to the Annex II (authorised fertilisers) of this Regulation to limit animal by-products to only Cat.3, thus excluding* meat meal and bone meal, which are Cat.2, despite they continue to appear in the list of authorised products. This would deprive Organic Farming of a significant source of recycled phosphorus (and potassium). If this is of concern to you, we suggest that you contact your national Organic Farming organisations, and your national Agriculture Ministry. ESPP would be interested in any feedback or information.
* Exact wording added: “animal by-products (including by-products of wild animals) of category 3 and digestive tract content of category 2 (categories as defined in Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009)”
ESPP input on EU pollutant register
ESPP submitted input to the EU consultation on the E PRTR (European Pollutant Release and Transfer Register), October 2020, supporting the European Commission proposal to improve the register’s contribution to Circular Economy objectives, and suggesting to include data on resource recycling. ESPP also suggested that large cattle production units should be included in the register (which already includes large poultry and pig units). ESPP also supported the proposal to widen the E PRTR to ‘emerging’ pollutants, such as PFAS/PFOS (perfluoroalkyl chemicals) and microplastics.
ESPP input to E PRTR consultation, October 2020 HERE.
German Phosphorus Platform ‘Policy Memorandum’
DPP (the German Phosphorus Platform) has published a ten page ‘Policy Memorandum’, taking position on key policy and regulatory questions relevant to phosphorus recycling. The document provides information on the current policy status, and makes proposals for policy changes or actions, with the aim of stimulating dialogue and gathering support of stakeholders and decision makers.
The DPP Memorandum notes that major challenges remain to enact German legislation which makes phosphorus recovery obligatory from larger sewage works in Germany (ordinance passed three years ago with implementation deadlines of 2029 / 2032), and that support is needed from politicians and administrations. Sewage sludge could replace around 10% of mineral phosphate fertiliser use in Germany. The German Platform underlines that leadership should be provided to municipalities by Federal and Land governments, including financial support for implementation, funding of R&D and development of Life Cycle Analysis studies and definition of a German nutrient strategy, based on knowledge of nutrient resources and flows (for at least P, N and K). It is noted that, in some cases, regional P-recovery installations are likely to be preferable, in order to reduce costs and optimise costs and improve logistics of recycled phosphorus use, and financial support is needed for construction of large-scale installations.
To facilitate market uptake of recycled phosphorus products, the German Platform considers that economic and market incentives should be implemented by the German government, e.g. by including environmental externalities in prices, quotas for recycled P use (for farmers, distributors and/or the fertiliser industry), subsidies, taxes, bans or use obligations, regulation fixing the same cadmium limits for all fertilisers. It is underlined that better information is needed on recycled nutrient products for farmers, and requested that appropriate recycled phosphorus products be authorised for use in Organic Farming. The German Platform also recommends to remove the current requirements of the national Fertiliser Ordinance (DüMV) on P-solubility and on specification of the origin of input materials, in order to evaluate all products neutrally on the basis of their quality. The German Platform proposes that plant phosphorus availability testing for fertilisers should be standardised and German regulation modified accordingly.
“Politikmemorandum der Deutschen Phosphor-Plattform DPP e.V. 2020 Positionen zur Umwelt- und Landwirtschaftspolitik” (Policy memorandum of the German Phosphorus Platform DPP e.V. 2020 Positions on environmental and agricultural policy), in German, 23 October 2020 www.deutsche-phosphor-plattform.de
EU to (nearly) ban all PFAS chemicals
The European Commission has published its new “Chemicals Strategy towards a toxic-free environment”, with an accompanying document specifically addressing PFAS (per- and polyfluoralkyl substances). The European Commission’s press release announces the objective to phase out of PFAS in consumer products “unless their use is proven for society”, and this is specified in the Action Plan annex to the Chemicals Strategy by “restrict PFAS under REACH for all non-essential uses”, but also by adding PFAS (as a group) the annexes of the Environmental Quality Standards Directive and of the Groundwater Directive and by “address the emissions of PFAS …through the revision of the legislation on sewage sludge” The document on PFAS states that it would be beneficial that regulation address PFAS as a group, in that regulation of one type of PFAS leads to regrettable substitution by another type. This document also indicates that the revision of the EU Sewage Sludge Directive1986/278 “could provide the opportunity to introduce limits for organic contaminants such as PFAS … including the possibility to have a limit for total PFAS”.
COM document on PFAS (per- and polyfluoralkyl substances) SWD(2020)249
EU Chemicals Strategy, 14 October 2020 COM(2020)667 and annex Action Plan COM(2020)225
Nutrient recycling
Lystek sewage sludge thermal hydrolysis
In North America, in 2020, Lystek will transform over 1.2 million tonnes of sewage sludge (c. 180 000 t DM) into a “concentrated” liquid fertiliser (15% DM) for agriculture, that is over 3 000 tonnes of phosphorus/year. Dewatered sewage sludge and/or food waste, is thermally hydrolysed (steam injection at 75°C, with alkali addition and physical shearing) for around 30 minutes, sufficient for sanitisation. The resulting liquid can be used as a fertiliser, and/or partly returned to the anaerobic digester (enhancing methane production by up to +25%). The liquid fertiliser is authorised for use in agriculture, depending on State or local regulations in the USA, either as Class A Biosolids or as an agricultural fertiliser product. Depending on the input material (e.g. sewage sludge anaerobically digested or not), the liquid fertiliser has 20 – 40 %/DM organic carbon and typically around 5-2-4 N-P-K. Recent installations by Lystek include St. Thomas - Ontario, Innisfil – Ontario, St. Cloud – Minnesota, Fairfield-Suisun – California, Goleta – California (food waste). www.lystek.com
Upcycling manure to activated carbon adsorbent
Earthcare, LLC (USA) is rolling out installations to dry and gasify (at 760 – 1000 °C) organic wastes on an industrial scale, producing a sterile Ecochar® (biochar), which can be used as an activated carbon adsorbent tertiary treatment to remove contaminants such as heavy metals and organic compounds in wastewaters.
The company has seven plants operating to date, each producing c. 4,000 t/y of biochar (Netherlands, USAx4, Russia x 2), and processing pig, cattle or poultry manure, food, fibre or bioethanol plant wastes, and/or animal by-products. An eighth plant with four adjacent gasifiers is underway in Ha’il, Saudi Arabia to process ~60,000 tons broiler chicken litter per year, producing ~17,200 t/y of biochar. Research shows that manure-derived and sewage-derived biochar is highly effective for contaminant removal, probably because of the fixed phosphorus it contains, see Kolodynska 2017.
The heat energy generated by combustion of the syngases has been shown in full scale systems to be sufficient to dry and process sewage sludge dewatered to 20% DM or more.
All of the input phosphorus and 15-20% of input nitrogen is bound into the biochar. The remaining nitrogen is converted to atmospheric N2 (the syngas combustion generates very low NOx) and emissions are filtered by both a chemical scrubber and a bio-bed.
The system is recognised as an agricultural Best Management Practice (BMP) by the US EPA / Chesapeake Bay Program for eliminating the runoff of nitrogen and phosphorus. When the biochar is used to remove organic contaminants from wastewater, it can be decontaminated and reused by thermally destroying the organic contaminants in the triple-pass rotary drum dryer. When the biochar is used to bind heavy metals on contaminated land or in wetlands, it can remain in place, but biochar adsorbing heavy metals at wastewater treatment plants would need to be disposed to approved landfill.
Website https://www.earthcarellc.com/
Contact: Peter Thomas
Correction
N2 Applied LCA results
We reported – incorrectly - in our last eNews results of a Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) of application of N2 Applied’s technology to transform nitrogen from the air with manure or digestate into an organic and mineral fertiliser. The LCA in fact showed that, compared to current practice (as defined by the Arla Foods Farm Tool), N2 Applied technology can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from dairy farming by -36%: anaerobic digestion of manure to produce biogas -16%, N2 Applied alone (treating manure) -27%; biogas + N2 Applied (treating digestate) -36%.
Further information including graphs showing LCA results HERE.
Webinars
European Commission webinar on P-recovery from municipal sewage
As part of the 18th European week of Regions and Cities, the European Commission organised a webinar on phosphorus recycling from municipal sewage works. 20th October 2020, introduced by Johanna Bernsel and Fleur Van Ooststroom-Brummel.
Chris Thornton, ESPP, summarised different routes for recycling nutrients from sewage, from application of composted or digested sewage biosolids in agriculture, through to “upcycling” where high quality chemicals or fertilisers are recovered and contaminants are removed. Slides here
In discussion, it was indicated that different routes are adapted for different contexts, depending on sewage works size, regional agronomic needs, etc.
Paula Lindell, Helsinki Region Environmental Services Authority (HSY), Finland, explained that the region’s first option for policy is to not incinerate sewage sludge, in order to return the carbon content to soil. Upstream actions to reduce at source contaminants from industrial discharges and form households are important to improve sewage sludge quality. Because iron or aluminium coagulants are used to achieve very low phosphorus discharge concentrations, no existing process is suitable for phosphorus recovery. HSY is therefore developing its own processes for P- and N-recovery (RAVITATM) and is testing pyrolysis (biochar production from sewage sludge).
Lukas Egle, City of Vienna, Austria, explained the city’s overall policy to improve sewage sludge valorisation: development of sludge anaerobic digestion to produce biogas and stabilise sewage sludge, then drying and mono-incineration. Actions underway with the aim of achieving energy-positive incineration and to facilitate phosphorus recovery from the ash include seeking authorisation to incinerate Cat.1 animal by-products (MBM meat and bone meal, which has both high energy content and high phosphorus content), reducing sand (filters) and substituting iron precipitants. Testing is at an advanced stage for use of the sewage sludge (mono)incineration ash in the fertilizer industry to partially replace phosphate rock in fertiliser production. However, intake of ash into this process is limited by sand (silica) and the iron present in the ash.
Challenges posed by the waste status of sewage sludge were discussed. Some progress has been made with the allocation of a specific waste number for sewage sludge incineration ash, which is thus recognised to be Non Hazardous. It may also be possible to have End-of-Waste status by self-declaration if the ash is used “to substitute a raw material”.
Caroline Attard, European Commission DG Environment, indicated that a prospective study on recycling and waste status is underway in the context of the evaluation of the Sewage Sludge Directive.
Robert Van Spingelen, Ostara, indicated that the Ostara has 22 Pearl struvite P-recovery reactors operating worldwide in sewage works. In all cases, the water company has an offtake contract with Ostara who ensure distribution and marketing of the Crystal Green® branded struvite fertiliser product.
He underlined the environmental benefits of struvite recovery in sewage works: lower greenhouse emissions (see struvite recovery “emergy” in ESPP eNews n°35), contribution to reductions of P and N discharges from sewage works, lower in-field nutrient losses. Agronomic research by Ostara shows that because the struvite pellets do not burn plant roots and only release nutrients as required by the plant, higher yields and lower nutrient losses can be achieved. In photos of trials, roots are shown to grow to cover the struvite granules. Tests show that organic acids are released by plant roots and solubilise the nutrients in struvite. The phosphorus is thus only released when the plant needs it and will take it up.
EU 18th European Week of Regions and Cities webinar “Recovered phosphorus from municipal wastewater” 20th October 2020: online here and link to replay video
Biofertilisers and biostimulants from algae
The EABA (European Algae Biomass Association) online workshop, 7th October 2020, opened by Jean-Paul Cadoret, Algama Foods and EBEA, enabled discussion and networking between 90 participants around the different value contributions of macro- and micro-algae to agriculture and the food chain. Algae can be applied to soils as harvested (e.g. dried) or after cell-lysis, or can be processed to extract specific substances, so as fertilisers, soil improvers or biostimulants.
Vince Ördög, Széchenyi István University, Hungary, presented review data showing that microalgae can increase soil nutrient content by nitrogen fixation, enhance growth of beneficial PGPR (Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria) and release antimicrobial compounds against soil-born plant pathogens. Algae have been shown to produce many different plant hormones. Auxins and polysaccharides produced by microalgae have beneficial effects including plant growth stimulation, increased chlorophyll content, photosynthesis and ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) scavenging; and improved plant tolerance against salt and drought stress.
Pi Nyvall Cohen, Olmix Group, presented industry experience processing red and green seaweed to products with fertiliser (nutrient content), soil improver and biostimulant effects. Field tests show that after several years’ application, soil carbon increases, crop root volume is improved, soil microbial biomass increases by up to +40% and mineral fertiliser application can be reduced by 5-10% for nitrogen, -40 kgP/ha, -80 kgK/ha and -50 kgMg/ha. Trials are underway in Brittany testing zero chemical intrant / zero mineral fertiliser production of wheat fertilised with the algal products. Regulatory challenges include acceptance for Organic Farming, and the fact that seaweed collected from deposits on beaches is considered a “waste”, but not the same seaweed collected in shallow water near the beach.
Theodora Nikolakopoulou, European Commission DG GROW, outlined the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation, and its significance in providing a European regulatory status for products such as biostimulants and soil improvers, and in providing “End-of-Waste” status for secondary materials when processed into an EU fertilising product (i.e. in a labelled and conformity assessed product). Maris Stulgis, European Commission, DG MARE, indicated that algae have significant industrial potential and DG MARE is there to help untap the potential of algae for various applications. Kristen Sukalac, Prospero and Partners, outlined the regulatory challenges facing the use of algae and derived components in biostimulants and organic fertilisers under the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation.
Questions in discussion of the EU Fertilising Products Regulation included the need to widen the list of micro-organisms for biostimulants (CMC7, currently limited to four species), the question of why cyanobacteria are excluded (CMC2), whether cell lysis of microalgae is acceptable processing (CMC3) and whether substances extracted from microalgae grown on wastewaters can be eligible for CMC1 (or are they excluded as being waste-derived)?
Gabriel Acien, University of Almeria, Spain, presented a marketing study for algae production (SABANA project 2016-2020 Horizon 2020). Algae production raceways are a proven technology, with commercially operating installations of 5 000 m2 and more. The cost of algae production is higher than their nutrient value for fertiliser, but the economics are different where algae production is used for wastewater treatment. Extraction of substances for biostimulants can provide a higher added value.
Companies participating included:
- Cécile Le Guillard, Agro Innovation International, Centre Mondial de l’Innovation Roullier, France, is producing algal extracts from seaweed and microalgae containing different kinds of bioactive molecules. CMI Roullier develops innovative solutions for agriculture, including plant biostimulants as well as products for plant nutrition and stimulation of plant defences.
- José Maria Goméz, BIOMASA PENINSULAR, using microalgae grown on biofilm for nutrient removal as tertiary sewage treatment, then lyophilisation and formulation with other secondary materials to produce recovered and bio-based fertilisers
- Robert Stenekes, ICL Group, The Netherlands, investigating new sustainable inputs to agriculture
- Christophe Vasseur, INALVE, cultivates and refines marine microalgae-biofilm into sustainable ingredients for aquafeed formulators: a microalgae-based protein to substitute fishmeal, a lipid fraction as a replacement for fish oil and a polysaccharides fraction to boost animal health.
- Frédérique Ferey, LafargeHolcim, looking into production of algae to take up CO2 emissions from cement production
- Franck Hennequart, Algaia, France, are producing a range of different products from seaweed in Brittany, including for food applications, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and also including plant biostimulants. Seaweeds bring nutrients to plants (e.g. N, K, Ca, Mg, Cu) and also amino-acids and sugars, and contain alginate, a chelating agent which facilitates crop access to minerals in soils.
- Luis Lombana, Ficosterra, Spain, processing algae and seaweed to produce biostimulants and organic soil improvers
Research presented included:
- Yagut Allahverdiyeva-Rinne, University of Turku, Finland, presented the NordAqua research consortium which is investigating improvements to algae production, including for wastewater treatment, and use of algae as a biofertiliser or biostimulant.
- Rok Mihelič, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia, processing algae grown in food waste digestate to produce biostimulants and algae grown in slaughterhouse waste to produce fertilisers in the Water2Return project (Horizon 2020, 2017-2020)
- Hans Reith, Wageningen UR, The Netherlands, Magnificent-Algae project (BBI 2017-2021), processing microalgae as nutritional ingredients, human food or animal feed or cosmetics
- Jesus Martin Marroquin, CARTIF, Algaecan project (LIFE 2017-2020), using microalgae to treat fruit and vegetable processing wastewater. The microalgae could be used as biofertilisers or animal feed
- Enrica Uggetti, Universitat Politècninca de Catalunya BarcelonaTech, projects on using algae for wastewater treatment then recycling the algae as biofertilisers: INCOVER project (Horizon 2020, 2016-2019) and looking at producing biofertilisers from microalgae: Al4Bio project (Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities (MCIU), Research National Agency (AEI), and European Regional Development Fund (FEDER), 2019-2021) and PAVITR project (Horizon 2020, 2019-2023)
EABA “Algae Biofertilizers and Biostimulants” technical webinar workshop, 7th October 2020 https://algaeworkshops.org/algae-biofertilizer-and-biostimulants/
IFS webinar presents nutrient recycling projects
As the IFS webinar of 10th November (70 participants, part of the IFS agronomy webinar series), two R&D projects into nutrient recycling were presented.
Romke Postma, Nutrient Management Institute, The Netherlands, presented the ReNu2Farm project (Interreg) which is looking at potentials for nutrient transfer between regions with livestock production towards crop growing regions. Desk study data compared the nutrient surpluses in some regions with crop needs in others, for N, P and K, and for organic matter, taking into account regional climate, soil and differing crop needs. Conclusions are that even in high manure regions, there is a need for concentrated nitrogen fertilisers to top-up manure nutrient inputs, and additionally for potassium for root crops. In low manure regions, there is a need for N, P and K, and additionally for organic matter for root crops. This should be taken into account when producing tailor-made fertilisers from recycled materials.
Results were presented of a survey of 1225 famers concerning attitudes to use of secondary nutrients (in Belgium, France, Germany, Ireland, UK, Luxemburg and The Netherlands, 2018-2019, carried out by which was performed by CIT, Cork, Ireland). Contaminants were the biggest concern for farmers (heavy metals, plastics, other pollutants, pathogens). Farmers currently using secondary materials underlined the importance of the nutrient ratio, organic matter and price; whereas non-users underlined price, ease of application and certification. Over all respondents, known nutrient content and nutrient ratios corresponding to crop needs were identified as key qualities to enable possible substitution of mineral fertilisers.
Martin Blackwell and Tegan Darch, Rothamsted Research, UK, presented the Thallo / Elemental Digest System process proposed for recycling of abattoir and other wastes, as presented in the PlosONE 2019 paper here. Bones and other Cat. 2 organic abattoir wastes are milled to a fine slurry, then combined with sulphuric acid and a metal catalyst, then pressure sterilised (20 mins. @ 133°C, 3 bars DEFRA method 1), before drying and granulation to produce a slow-release organo-mineral fertiliser (see patent WO2014202986, 2014). It is indicated that other wastes can be added, e.g. calcium phosphate from baby food production, biomass combustion ash or waste from fire extinguisher refilling (the silicones in fire extinguisher material is broken down by the high-pressure sulphuric acid treatment). It is suggested that proposed process offers advantages compared to current recycling routes for Cat. 2 abattoir by products (see EU industry data in “Understanding Animal by-products and phosphorus recycling in SCOPE Newsletter n°122), because on-site processing at the abattoir reduces waste, enables recovery of some materials for the human food-chain in an initial sorting stage, and can be adjusted to produce bespoke fertiliser formulations (including different micronutrients) adapted to local soil/crop needs.
The Thallo product typically contains 6.5% N, 3.1% “acid soluble” P, 3% K, 9% S, 9% Ca and up to 30% organic matter, and also many other elements including e.g. zinc (430 ppm), iron (115 ppm). Results from pot trials (16 weeks, with grass and wheat) were presented, comparing the Thallo product to standard NPK mineral fertiliser and slow-lease N fertiliser. Mostly, plant yields were very similar for the three different fertilisers. The Thallo product showed better yields in sand, presumably because of its organic matter content. Analysis of micro-nutrients in the grown plants showed complexity of results, suggesting interactions between different nutrients and micronutrients present.
International Fertiliser Society (IFS) webinar series: programme, registration, access to recordings of past webinars (free for IFS members) Here
Research and publications
Nearly half of the world’s cropland is phosphorus limited
A meta-analysis of 652 phosphorus addition experiments in the field, from 285 publications 1955 – 2017, suggests that 49% of croplands and 45% of natural terrestrial ecosystems are phosphorus limited. Phosphorus inputs increased aboveground plant production by an average of 14% in croplands (compared to no P addition controls), which are often already fertilised, and 35% in natural systems (compared to no P addition controls). The data set covered all continents except Antarctica and wide ranges of precipitation. Soil phosphorus limitation was not restricted to tropical soils, with data showing P limitation in natural systems across Europe and in cropland in Northern Europe.
“Global meta-analysis shows pervasive phosphorus limitation of aboveground plant production in natural terrestrial ecosystems”, E. Hou et al., Nature Communications (2020) 11:637 DOI
Organic farms show P and K deficits
A study of farm gate nutrient balances and soil nutrient status in twenty Organic farms I Germany shows wide variability, but a mean phosphorus deficit of -3 kgP/ha (SD = standard deviation ±6). Nutrient budgets were calculated as all inputs (fertilising products, manures, animal feed, seeds, plus estimated BNF = biological nitrogen fixation per crop) minus estimated offtakes in crops and by-products. Losses in leaching/runoff were not considered in the calculation. Mean farm balances for nutrients assessed, other than P, were all positive with wider variation: N = +19 (±26), K = +5 (±28), Mg = +7 (±10), S = +12 (±33). Levels of (extractable) nutrients in soils were not correlated to the nutrient balance for N, K, Mg, S, but were correlated for P. Some 14% of soils across the 20 farms showed extractable soil P below optimal levels (KTBL 2015, VDUFA 2018, groups A or B), 27% optimal soil P (group C) and 50% above optimal (D or E). The authors note that farms with a prolonged past of Organic Farming showed higher risk of P depletion in soils and that reliance on biological nitrogen fixation was linked to soil depletion of both P and K. The authors further conclude that “P and K scarcity (are) a major challenge for Organic farms with high reliance on BNF in the long term”.
“Reliance on Biological Nitrogen Fixation Depletes Soil Phosphorus and Potassium Reserves”, M. Reimer, Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 2020, DOI.
LCA of struvite recovery
A life cycle assessment (LCA) was carried out of the Nine Springs municipal wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) in Madison, Wisconsin (38,000 p.e. biological P-removal, biosolids used in agriculture) - with and without struvite recovery. In 2017, the WWTP implemented additional phosphorus release from the secondary (bio-P) sludge before gravity thickening and installed the Ostara Pearl struvite recovery system which operates on the sludge thickening liquor (filtrate). Although there was an increase in influent nutrient concentrations after 2017, resulting in a slightly increased discharge concentrations, the authors note that struvite recovery would generally improve effluent quality by reducing nutrient returns to the WWTP in the dewatering liquors. Taking into account the balance of increased chemical and energy consumption versus the recovery of phosphorus and nitrogen (modelled as an LCA offset for fertiliser value), the environmental impacts generally decreased with struvite recovery implementation. In this case, the net greenhouse impact of adding struvite recovery was a reduction in total emissions for the WWTP of around 1% or approximately 4 gCO2-equ./m3 wastewater treated.
“Environmental impacts of phosphorus recovery through struvite precipitation in wastewater treatment”, M. Sena et al., J. Cleaner Production 280 (2021) 124222 DOI
Manure in the Baltic Region
A report by the SuMaNu project summarises manure management in the Baltic region. Examples of Finland, Sweden, Germany and Poland, with maps, show the uneven distribution of livestock production (and so manure). An overview of different manure processing technologies is provided covering, with estimated investment and operating costs for some: solid-liquid separation, slurry acidification, composting, anaerobic digestion (AD), drying, vacuum evaporation, combustion, pyrolysis, gasification, ammonia stripping, membrane separation, struvite precipitation. For some technologies (AD, thermal drying of poultry manure, pelletisation, combustion, gasification vacuum evaporation) case examples are presented. The report concludes that manure processing is needed to enable storage and transport of manure from livestock intensive regions in the Baltic to crop-growing areas, where fertilisers are needed and nutrients can be used efficiently, but that to date manure processing is too expensive for farmers. It is emphasised that the final product must correspond to farmers needs (e.g. spreading equipment) and that reliable information for farmers on the product’s nutrient content and nutrient plant availability must be available.
See also reports on manure processing technology: Wageningen The Netherlands ESPP eNews n°45, NIBIO Norway 2020 ESPP eNews n°41, Washington State University USA 2018 ESPP eNews n°31, the detailed online data base (costs, farmer assessments …) operated by Newtrient in the USA and the specifications in the EUBAT document for intensive rearing of pigs and poultry (updated 2017)
“Manure processing as a pathway to enhanced nutrient recycling”, report of SuMaNu platform, S. Luostarinen et al., 2020, ISBN 978-952-380-037-3 access.
Northern Ireland increasing phosphorus surplus
The phosphorus stock and flow analysis for Northern Ireland (NI) carried out within the RePhOKUs project shows that the agricultural P surplus has increased by nearly +50% since 2008 (8.7 kgP/ha in 2008, 12.3 kgP/ha in 2017). This results from a c. +25% increase in P imported in animal feed (+3.4 kgP/ha increase) and a nearly +50% increase in mineral P fertiliser use (+1.4 kgP/ha). Over the same period, average river SRP (soluble reactive phosphorus) increased by around one third (62% of P-total inputs to waterbodies in NI are estimated to be from agriculture). Considering all inflows and outflows of P to NI, the regional P balance (2017) was +5.5 kgP/person (compared to around 0.6 kgP/person P intake in diet: only c. 10% of the net NI P import – export is actually being eaten). The NI food system “phosphorus use efficiency” is calculated by the authors to be 38% (P in agricultural food products / P inputs to the agricultural system). This low P use efficiency (PUE) is considered to be linked to livestock production. Manure produced in NI contains 20% more P than the region’s total P input needs, whereas only c. 10% of poultry manure is processed (2% of P in all NI manures).
“Phosphorus Stocks and Flows in an Intensive Livestock Dominated Food System” S.A. Rothwell et al., Resources, Conservation and Recycling, online here. A technical summary of the work and results from a subsequent stakeholder workshop can be found here.
Nano calcium phosphate for cancer tumour treatment
Researchers have developed a possible treatment route for cancer tumours using calcium phosphate nanoparticles (c. 100 µm diameter, mesoporous), which can be loaded with antitumour drugs (doxorubicin = DOX was tested) and coated with arginylglycylaspartic acid = RGD (a common peptide responsible for cell adhesion). Multidrug resistance of tumours is the primary cause of chemotherapy failure. The prepared nano calcium phosphate composite (called TCaNG) showed good tumour targeting. Once taken into the tumour cell, as well as delivering the drug DOX, the TCaNG releases calcium which suppresses cellular respiration, so reducing production in the cell of glycoproteins which remove cancer drugs. Glycoprotein production is reduced both by direct inhibition (due to calcium accumulation in mitochondria) and by blocking cellular ATP production (adenosine tri phosphate, necessary for energy cycling) so reducing the effectiveness of the glycoproteins. The TCaNG reduced the proliferation of drug-resistant tumours in mice by a factor of c. 13.
“Nanoenabled Intracellular Calcium Bursting for Safe and Efficient Reversal of Drug Resistance in Tumor Cells”, J. Liu, Nano Lett. 2020, DOI.
Unsupported claim that P fertilisers impact biodiversity
The title of a paper in ‘Nature Ecology & Evolution’ suggests that it shows phosphorus fertilisation to “eradicate” threatened plants in northern Europe. The paper is based on data from 16 sites in a few widely separated zones: seven in the band Netherlands – Belgium – Switzerland, five in Eastern Poland / Belarus, one in Sweden, one in Northern Scotland and two in Siberia. The paper shows, for these sites, correlations suggesting that both “availability” of phosphorus to plants and ratio of “available” P/N are more correlated to plant biodiversity and to threatened plant species than N or K. “Availability” is not here based on soil data, but is estimated from above-ground plant biomass nutrient ratios. As authors indicate, this sensitivity to P is to be expected as P is generally the “limiting nutrient” in nature. The authors then suggest that “An EU Phosphate Directive” is needed, based on speculation that reducing P-fertiliser application would reduce P availability in land relevant to threatened biodiversity. ESPP does not see evidence in the paper to support this: it seems likely that reduced P-fertilisation of a field might reduce P levels in land nearby, but it is not clear how reduced P fertilisation would significantly lower P availability in more remote areas (e.g. the Northern Scotland or Siberia sites in the study). Atmospheric phosphorus deposition is never mentioned in the paper, despite N deposition being discussed. Other sources suggest global phosphorus deposition may be quantitatively nearly 1/5th of P annually mined in phosphate rock, but that most atmospheric P deposition comes from natural sources (e.g. dust from deserts, pollen and other biogenic materials), see ESPP eNews n°43.
“Phosphorus fertilization is eradicating the niche of northern Eurasia’s threatened plant species”, M. Wassen et al., Nature Ecology & Evolution 2020 DOI.
Taiwan: diet phosphorus acceptable but calcium too low
Iran: diet phosphorus and calcium too low, sodium too high
Based on data from 7580 respondents in a national eating and drinking study, and analysis of 876 representative food product samples (purchased in supermarkets), it is concluded that average adult phosphorus intake in diet is around 1.2 gP/day, higher in toddlers, and with a small increasing trend with age from children through to the elderly. The phosphate intakes were higher than the AI (Adequate Intake) and lower than the UL (tolerable Upper intake Level), so “no significant risk” to health. The main dietary sources of phosphorus were grains (including rice), fresh meat and poultry and milk products. The authors note that none of these contain phosphate food additives. Calcium intake in adults is around 0.5gCa/day, compared to an AI of 1 gCa/day for adults, so are considerably too low.
In a separate study in the city of Shiraz, Iran, based on a dietary survey of 438 persons and analysis of 580 food samples from shops and markets, phosphorus intake is estimated at only 0.21 gP/day, considerably lower than the EAR (estimated average requirement) of 0.58 gP/day. Calcium intake was 0.24 gCa/day, again much lower than the EAR of 0.8 gCa/day. For both phosphorus and calcium, around 90% of the population had intakes below the EAR. Whereas sodium intake was 1.47 gNa/day compared to an EAR of 1.5 gNa/day. 70% of the population had sodium intakes higher than the UL of 2 gNa/day.
“Risk Assessment of the Dietary Phosphate Exposure in Taiwan Population Using a Total Diet Study”, M-P. Ling et al., Foods 2020, 9, 1574, DOI.
“Dietary Intakes of Zinc, Copper, Magnesium, Calcium, Phosphorus, and Sodium by the General Adult Population Aged 20–50 Years in Shiraz, Iran: A Total Diet Study Approach”, E. Babaali et al., Nutrients 2020, 12, 3370, DOI.
New book “Phosphorus: Past and Future”
By Jim Elser and Phil Haygarth, this new book, 250 pages, presents phosphorus’ roles in biology, human health and nutrition, ecosystems and in environmental sustainability. The importance of mined phosphate rock to global food production is explained, and the environmental problems generated by phosphorus losses to surface waters. Phosphorus sustainability efforts are presented, with solutions and possible future scenarios.
“Phosphorus: Past and Future, J. Elser & P. Haygarth, publication 1st January 2021, ISBN 978-0199916917
ESPP members

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews048
Download as PDF
EU consultations
EU consultation on Pollutant Release and Transfer Register
EU consultation on Zero Pollution Ambition
EU consultation on sustainable aquaculture
EU consultations on agriculture policy (CAP)
EU consultation on environmental product claims
Policy
Updated EU Critical Raw Materials List published
EU IED evaluation: resource use, recycling, agriculture
EFSA Opinion on PFAS
EEA Brief on biodegradable / compostable plastics
EU R&I Event: uncrossing planetary boundaries for nutrients
Webinars
Announced webinar: Phosphorus and climate change
German Phosphorus Platform (DPP) Forum
US Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance annual Forum
Sewage sludge incineration ash recycling
P fertilisation and legacy P
Variable effectiveness of bio-based fertilisers
Nutrient recovery
RAVITA P-recovery test results published
N2 Applied inaugurates new production hall
P-recovery from pharmaceutical industry wastewater
German national “RePhoR” P-recovery projects announced
Solubilisation of P from ash and other materials by microorganisms
Research
UN Oceans Science
Global soil P depletion due to erosion
Government dietary guidelines inadequate for health and environment
Circular Agronomics project update
Fate of pharmaceuticals in manure processing
ESPP Members
EU consultations
EU consultation on Pollutant Release and Transfer Register
Open to 26 October 2020. The E PRTR Regulation (EC) 166/2006 ensures that certain pollution emission data is made public. It currently covers emissions of 91 listed pollutants for installations in 65 sectors. Listed pollutants include nutrient emissions (total P, total N, ammonia). Confusingly, coverage is not the same as for the Industrial Emissions Directive IED: 30 000 installations in Europe concerned by the PRTR but 50 000 by IED. Sectors covered at present by PRTR include waste and wastewater treatment (whereas municipal sewage works* are not under IED), slaughterhouses, food and beverage industry, large poultry and pig farms (same thresholds as IED, see below) but also aquaculture which is not covered by the IED (> 1 000 tonne fish or shellfish per year). The consultation on the PRTR considers possible widening of scope, additional pollutants (e.g. to emerging pollutants), collecting information relevant to decarbonisation and the Circular Economy and improving public information access. ESPP notes that the E PRTR pollutant list currently does not include a number of substances on the Water Framework Directive “Priority Substances” list: PFOS and its derivatives, a number of pharmaceuticals, brominated flame retardant HBCDD
* i.e. those covered by the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive 91/271/EEC
EU public Roadmap consultation on the European Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (E PRTR) open to 26 October 2020 HERE
EU consultation on Zero Pollution Ambition
Open to 29 October 2020. The “EU Action Plan Towards a Zero Pollution Ambition for air, water and soil” stems from the Green Deal objective of zero pollution (see ESPP eNews n°39). The consultation document refers to pharmaceuticals, persistent and toxic chemicals and micro-plastics. It notes that pollution to soil should be addressed and is not well covered by existing EU regulation.
EU public Roadmap consultation on the Zero Pollution Ambition open to 29 October 2020 HERE
EU consultation on sustainable aquaculture
Open to 27th October 2020. See ESPP eNews n° 47. Consultation HERE
EU consultations on agriculture policy (CAP)
Open to 22nd October 2020. See ESPP eNews n° 47. Consultations here on water, on habitats, landscapes and biodiversity, and on sustainable management of soil.
EU consultation on environmental product claims
Open to 3rd December 2020. Consultation on product environmental claims and PEFs (Product Environmental Footprints) HERE
Policy
Updated EU Critical Raw Materials List published
The European Commission has published the 4th version of the Critical Raw Materials List (CRM). Phosphate Rock (in effect, phosphorus in any form: rock, fertiliser, chemicals, organics ….) and “Phosphorus” (in effect, P4 and derivatives) are maintained on the list. This new list is the previous 2017 list plus four minerals (bauxite, lithium, titanium, strontium). The Commission announcement recommends inclusion of CRM investments in Covid recovery plans, development of recycling and domestic sourcing of CRMs, actions on value chains and international trade. The accompanying document identifies EU dependency on imports (84% import dependency, of which Morocco and Russia total 44) for phosphate rock and for P4/derivatives (100% import dependency, of which 98% from Kazakhstan, Vietnam and China). Overall emphasis in the short term is strongly on the “rare earth and magnet value chains”, identified as relevant for renewable energy, defence and space. An accompanying study by EU JRC assesses CRMs relevant for “strategic technologies”, identified as: lithium ion batteries, fuel cells, wind energy, electric traction motors, photovoltaics, robotics, drones, 3D printing and digital technologies. Unfortunately, this study does not consider “Phosphorus” (P4 and derivatives), which is almost totally absent from the study (e.g. absent from the conclusions and study cover Sankey diagram, which covers 24 other materials). Also, in Annex 2 to the European Commission official CRM List Communication, Phosphate Rock and Phosphorus are indicated as relevant to “Energy intensive industries” (bizarrely) and “Agri-food” but not to other sectors where P-based chemicals are important: renewable energy (e.g. in batteries), digital (e.g. microchip etching), electronics, aerospace (e.g. flame retardants). ESPP will write to the European Commission to address these omissions.
European Commission Communication COM(2020) 474 final, 3rd September 2020 “Critical Raw Materials Resilience: Charting a Path towards greater Security and Sustainability” HERE
JRC “Critical Raw Materials for Strategic Technologies and Sectors in the EU – A Foresight Study”, 2020, ISBN 978-92-76-15336-8 HERE
EU IED evaluation: resource use, recycling, agriculture
The European Commission has published its evaluation of the Industrial Emissions Directive which regulates over 50 000 installations in Europe, including food and dairy processing, waste treatment and large poultry and pig farms (replacing several Directives including IPPC). The evaluation is based on input to stakeholder consultations (see ESPP eNews n°42, ESPP input submitted here). Conclusions are that the Directive is effective, cost-efficient, coherent and provides EU added value. Amongst aspects which work less well or are to be addressed, the Commission identifies resource use and Circular Economy, greenhouse gas emissions, implementation of BAT technologies, emerging technologies and possible widening of scope. The report states that a few highly-polluting activities are not currently covered by the Directive, including cattle farms, aquaculture and poultry farms below the current IED threshold of 40 000 birds, but notes that extending to cover cattle farms has previously been considered and rejected because of the administrative burden.
“Executive Summary of the Evaluation of the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED)”, European Commission SWD(2020)182 (Executive Summary) and SWD(2020)181 full report, 23 September 2020. The executive summary(182) is available by searching here. The full report (182) seems to not be publicly available at present but can in fact be found here.
EFSA Opinion on PFAS
Perfluorinated alkyl chemicals are a contaminant found in sewage sludge which raise particular concern (see SCOPE Newsletters n° 134, 129, 123) but which could be avoided if their use was restricted. The EFSA (European Food Safety Agency) Opinion covers PFOA, PFOS, PFNA and PFHxS (collectively termed PFAS). They are used in e.g. textiles, household products, fire-fighting foams, automotive, food processing, construction, electronics. EFSA indicates that there is evidence that these chemicals are bio-accumulative and are probably linked to reduced immune response, cholesterol, liver impacts, infant birth weight, with limited evidence of carcinogenicity. EFSA has fixed a TWI (tolerable weekly intake) of 4.4 nanogrammes/kg body weight (total PFAS substances).
“PFAS in food: EFSA assesses risks and sets tolerable intake”, EFSA press release 17 September 2020 and EFSA Scientific Opinion adopted 6 July 2020 “Risk to human health related to the presence of perfluoroalkyl substances in food”.
EEA Brief on biodegradable / compostable plastics
The European Environment Agency (EAA) has published a briefing document on biodegradable, compostable, bio-based and oxo-degradable plastics. This underlines the differences between these different categories: bio-based = fully or partly made from biological raw materials, but may or may not be readily degradable; compostable = in some cases in industrial composting systems (with controlled conditions), in other cases also in less well controlled garden composting; biodegradable = in natural media (soil, water …) but with no recognised standard for testing conditions, and degradability in soil may not mean degradability in water; oxo-degradable = include additives which cause breakdown into microplastic particles or chemical decomposition. This vocabulary is not well understood by the public: in one survey in Germany, nearly 60% thought bioplastic implied biodegradable. The report suggests that marketing of plastics as “biodegradable” or “compostable” may need to be prevented to reduce consumer confusion and misuse of such plastics, but that such plastics can be useful in specific applications (e.g. bags for household separate collection of food waste or agricultural mulches), subject to respecting precise standards adapted to the specific application.
“Biodegradable and compostable plastics challenges and opportunities”, European Environment Agency, Briefing 9/2020
EU R&I Event: uncrossing planetary boundaries for nutrients
John Bell, Director “Health Planet” at the European Commission DG Research, underlined that planetary boundaries are considerably exceeded for phosphorus and nitrogen and that urgent and systemic action is needed. Mark Sutton, International Nitrogen Initiative, underlined that both all nutrients need to be addressed, but that nutrients tend to be forgotten. He underlined the economic significance: nitrogen losses represent some 200 billion US$ fertiliser value worldwide, and societal a further 70 to 320 billion US$. That is in total, in Europe, around 1/3 of the CAP budget. He welcomed the proposed EU objective to halve nutrient pollution by 2030 in the Farm-to Fork strategy which echoes the United Nationals Environment Assembly resolution EA.4 (march 2019, see ESPP eNews n° 33). Chiara Manoli, ECOFI, underlined the progress made in organic fertilisers, with standardisation of production processes. This enables recycling of nutrients and carbon in secondary materials such as wine or food processing wastes, poultry litter from egg production, fish meal, residuals from tanning, etc., and brings organic carbon to soil, contributing to soil fertility and to water retention. She underlined the importance of the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation which puts in place, for the first time, EU criteria for organic fertilisers, but notes that outstanding regulatory difficulties remain with Organic Farming and with Animal By-Products. Jannes Mes, President of the European Council of Young Farmers, underlined that farmers are motivated to reduce nutrient pollution, but cannot fund actions to improve nutrient management without public support.
EU R&I Days 2020: 22nd September 2020, webinar with Katja Klasinc and John Bell, European Commission, Mark Sutton, International Nitrogen Initiative, Chiara Manoli, ECOFI and Jannes Maes, European Council of Young Farmers (CEJA) watch online
Webinars
Announced webinar: Phosphorus and climate change
A session at the prestigious American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) annual symposium, 8th February 2021, will address how phosphorus losses to surface waters can accelerate greenhouse gas emissions, and how climate change can feed back to accentuate eutrophication, with John Downing, University of Minnesota, Laura Johnson, Heidelberg University and Ahren Britton, Ostara. This is supported by the ESPP – US Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance joint SCOPE Newsletter special issues on nutrients and climate change: methane emissions (SCOPE Newsletter n°135); P runoff, catchment management and P in soil (coming soon); P and soil health links to climate; greenhouse emissions of nutrient management and recycling (both planned).
Phosphorus and Climate Change: A Vicious Circle, AAAS Annual Symposium, 8th February 2021, 12h – 12h45 ET https://meetings.aaas.org/
German Phosphorus Platform (DPP) Forum
The annual DPP Forum, 24th September 2020, took place as a hybrid event with 135 participants (75 in Frankfurt). Presentations covered questions concerning the implementation of the German Phosphorus Recycling Ordonnance, status of development of P-recovery projects and installations in Germany, industry requirements and experience in processing recycled nutrient materials, and farmers’ expectations concerning recycled nutrient fertilisers. The specific requirements of the Organic Farming movement for recycled P products were discussed, including safety, life cycle analysis and of use of chemicals in processing. The Forum also discussed a proposed DPP Memorandum under preparation to propose actions to politicians to move forward phosphorus recycling.
German Phosphorus Platform (DPP) annual Forum 2020.
US Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance annual Forum
The two-day annual North America phosphorus event this year was two three-hour webinar sessions, with over 70 Participants worldwide.
Struvite recovery
Chris Hornback, National Association of Clean Water Agencies, underlined the need for federal clarification of the status of struvite recovered from sewage plants. The EPA enacted in 2017 that struvite could be authorised case by case*. * ESPP note: For example, Ostara CrystalGreen struvite is authorised in 42 US States (see SCOPE Newsletter n° 124).
Aaron Fisher, Water Research Foundation, underlined the advantages of struvite precipitation in reducing P in biosolids, reducing polymer use in dewatering and improving dewatering (higher dry matter content of biosolids).
Robert van Springelen and Matt Kuzma, Ostara, presented application of the company’s Crystal Green PEARL® struvite recovery to phosphate rock processing water, both in operating installations and in leachate from phosphogypsum ‘stacks’ at closed sites. A pre-treatment step removes fluoride and silica using lime. After struvite precipitation and membrane finishing, the treated process water can achieve discharge water quality. The technique and process is in TRL 9 stage and proven successful in full scale.
Manure phosphorus
Rebecca Muenich, Arizona State University, underlined that manure is a major nutrient pollution challenge and the biggest potential source for P-recycling in the USA. There is no national inventory of CAFOs (Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations) or AFOs in that many do not have federal environmental permits*. R&D work is underway to develop a virtual mapping of AFOs and CAFOs across the USA based on remotely-sensed data. * ESPP note: the US EPA AFO web pages indicate that < 7 000 out of nearly 21 000 AFOs with numbers of animals above thresholds requiring NPDES permits did not have such a permit in 2019). The thresholds are equivalent to c. 700 dairy cows, 2 500 pigs or 125 000 broiler chickens. The EU requires permitting (under the Industrial Emissions Directive) from 2 000 pigs or 40 000 poultry (but not yet for intensive cattle installations).
Jeff Dawson, Renewable Nutrients, indicated that the company now holds the licence to the USDA QuickWash® process (see SCOPE Newsletter n°119). The enables P recovery from manure by acid solubilisation followed by calcium phosphate precipitation and can be combined with ammonia recovery using a gas-permeable membrane.
Rick Johnson, Applied Environmental Solutions, indicated that livestock farms face increasing manure management costs. NRC 590 limits spreading of phosphorus per hectare, so increasing manure transport distances and costs. P-recovery from manure can reduce the hectares needed for manure spreading by as much as 40%
An opportunity for the future was identified as mobile manure processing units, to enable cost-sharing between farmers.
Perspectives for nutrient management
Kerry McNamara, OCP, outlined the company’s actions to maximize phosphorus sustainability across its entire value chain, and to support sustainability at the farm level. We have to make nutrient stewardship economically sustainable for farmers. OCP is committed to optimal use and recycling of phosphorus, as part of the company’s overall sustainability objectives, which include 100% clean energy and zero non-renewable water use by 2040 and carbon neutral by 2040, as well as maximizing P recovery at all stages of its operations. As one example of that, OCP is currently exploring Ostara struvite recovery technology for its own processing discharge in Morocco, and also possibilities for phosphorus recycling from municipal sewage works.
Don Boesch, Maryland Center for Environmental Science, summarised actions to restore the Chesapeake Bay since the 1980’s. Objectives for nutrient input reductions fixed for 2000 and 2010 were not met. Mandatory TDMLs (Total Maximum Daily Loads) are now set for 2025, but reductions are likely to again fall short. Nutrient loads have been reduced since the 1990’s and smaller hypoxic areas are now seen in the Bay, but nutrient levels are not falling as fast as management models indicate. This could result from “lag time” due to P remobilisation from soil and sediments and nitrate storage in groundwater, but it could also be that agricultural nutrient BMP measures (Best Management Practices) are not being implemented as they should be, or that they are less effective than assumed. On the other hand, there seems to be more urban nutrient retention than management models estimate.
Agricultural nutrient loss models and their implementation
Carl Bolster and Barret Wessel, USDA-ARS, summarised work ongoing assessing models of farm nutrient runoff in the West Lake Erie Basin (TBET and Apple models). The objective is to be able to model losses by field, as a function of agricultural practice, with a model which uses available data and which is accessible to extension agents. Model results show high levels of uncertainties, and a challenge is how to identify these and how to communicate uncertainties to users.
Jon Winsten, Winrock International (a large non-profit organisation addressing agricultural, environmental, and social issues around the world) summarised test programmes in Ohio, Vermont, Wisconsin and Iowa. Farmers are paid for quantified outcomes, calculated for actions intended to reduce nutrient losses. Payments are, for example, c. 80 US$/kg P loss reduction, c. 11 US$/kg N, based on modelling, on a field by field basis. The models show very high variations between fields. Winrock provides farmers with field-by-field calculations of modelled nutrient loss reductions, of resulting payments, of estimated costs (e.g. income loss for land converted to buffer strips), and helps farmers find the most cost-effective actions.
Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance annual forum 2020 – watch online.
Sewage sludge incineration ash recycling
This webinar organised by EasyMining discussed possibilities for recycling phosphorus, iron/aluminium and silica sand recovered from sewage sludge incineration ash.
Dines Thorberg, Biofos (Copenhagen public water company), indicated that farmers are sceptical about possible value of sewage sludge incineration ash as a P-fertiliser, and zinc and chrome levels are too high for land application. Ash produced today has c. 10%P (dry weight), and Copenhagen has a landfill of 350 000 tonnes of sludge incineration ash from the past with average c. 5% P. In the past, part of the ash was recycled into mineral wool construction materials. Biophos is currently tendering to find a process to recover phosphorus from the sludge incineration ash.
Yariv Cohen, EasyMining, indicated that the company’s Ash2Phos process (see ESPP P-Recycling Technology Catalogue) enables recovery of c. 90% of phosphorus and c. 80% of calcium are recovered from ash as quality grade calcium phosphates. 60-80% of aluminium and 10-20% of iron can be recycled to sewage works as coagulants. Higher levels of iron could be recovered, but at a higher cost and chemical consumption, whereas there is at present no regulatory or market driver. Over 95% of heavy metals are removed, leaving a clean silica sand material which can be used in concrete production. A 30 000 t(ash)/y Ash2Phos plant will generate c. 13 000 t/y of calcium phosphate product and 23 000 t/y of silica sand.
Cement production has high climate emissions (5 – 8% of anthropogenic GHG), so partial replacement with this silica sand could be very attractive to cement companies and could bring climate offset income.
Lisbeth Ottosen, Technical University of Denmark, summarised testing of EasyMining recovered silica sand to replace cement in concrete production. Kg-scale trials have shown that 20% of cement in concrete can be replaced by recovered silica sand, on condition that it is briefly milled (10 seconds) and with use of plasticisers to improve concrete quality. The resulting concrete has a reddish colour (iron in the silica sand) which can have aesthetic advantages, and shows only a small loss of strength. Further research is needed to understand the chemistry of cement phases, to optimise plasticiser use and to test durability of the resulting concrete over time.
Katrine Orland Led, Ramboll, outlined conclusions of a market analysis study into use of silica sand to replace cement in concrete. Interest of the cement industry to reduce climate emissions could be a driver. Potential applications include facades, pre-fabricated concrete structures, ground stabilisation, binding layers, paving stones and fibro-cement materials.
“Value adding recycling of sewage sludge in concrete. Making concrete more sustainable”, EasyMining webinar, 2nd October 2020, available here https://www.easymining.se/article-startpage/sustainable-concrete-webinar/
P fertilisation and legacy P
Crop P needs in soils with “legacy phosphorus” were discussed as part of the IFS agronomy webinar series, with Sophie Nawara, currently working at the Soil Service of Belgium (the presented research was part of her PhD study at KU Leuven). Much of Europe had a highly positive soil P balance from the 1940’s (phosphorus application as mineral fertiliser and/or manure greater than crop offtake and runoff). There has been a decrease in phosphorus fertilisation in Western Europe over the last decades, and Western Europe’s overall P-balance is negative since around 2000 (from Fig. 5 in Zhang et al. 2017, see SCOPE Newsletter n°128). However, the over-fertilisation during decades has caused an accumulation of soil P (“legacy P”) resulting in current high soil P contents in some regions in Europe.
Two year greenhouse trials were carried out with eight different Flemish soils, using rye grass (fast growing, needs rapid P supply). Results showed that, in this specific case and after two years of P “draw down” by the rye grass, legacy P in soil alone (without addition P fertilisation) led to a significantly lower cumulative biomass than with P fertilisation in six out of eight of the soils, when adequate nitrogen was supplied, see Nawara et al. 2018.
Modelling suggests that a fast reacting P pool (e.g. adsorbed P in soil) can be accessed sufficiently rapidly by crops, but that legacy P is more present in a slow reacting P pool (e.g. into soil particles with ageing), which is only slowly accessible to plants. Fast growing plants experience P deficiency faster than slowly growing plants because of their higher P demand rate which exceeds faster the soil P supply rate.
Also some soil P tests were evaluated in their capacity to predict crop yield in a P depleting scenario. None of the soil P tests outperformed the others, meaning that, for European soils, the crop accessible P is generally well measured by the Olsen-P (0.5M NaHCO3) test and by the ammonium lactate soil test, both which are often used as standard soil P tests.
International Fertiliser Society ( IFS) webinar series: programme, registration, access to recordings of past webinars (free for IFS members): HERE
Variable effectiveness of bio-based fertilisers
Data from ongoing trials of different secondary or recycled P fertilisers materials were presented in the IFS agronomy webinar series, with Patrick Forrestal, Teagasc, Ireland. National testing in Ireland in 2019 (n=30,466) show that around ¾ of Ireland’s soils need P applied to meet crop off-take (Index 1, 2 and 3 under the Irish system). Half of soils (in Index 1 and 2) also need P application to fill soil P sinks to be raised to the agronomic optimum (Index 3).
Seven different bio-based P materials were compared to control (no fertiliser) and TSP (triple super phosphate) in field trials in 2019 (results presented) and 2020 (ongoing): two struvites, cattle manure slurry, chicken litter ash, sewage sludge incineration ash, dairy residues complexed with aluminium or calcium. Ireland produces some 140 000 t/y of P-rich dairy processing residues. Soil was Index 1 and pH was limed to 6.1. Phosphorus was applied at 60 kgP/ha/year was applied, as per agronomic recommendations with four grass cuts per year.
Control with no P application showed only 40% of the yield with TSP. Yields were broadly similar for all the bio-based materials and for TSP.
For P-uptake, which is significant because it impacts P levels in grazing cattle diets, struvite and slurry shows, in results to date, P uptake somewhat higher than for TSP, poultry litter ash and Al-complexed dairy residue similar to TSP, and sewage sludge incineration ash and Ca-complexed dairy residue somewhat lower.
These results should not be considered conclusive, and statistical analysis will be completed when the 2020 field trial results can be also included in the dataset.
Limerick collaborators showed that certain soil P solubilizing bacteria are more active with bio-based fertilisers than with TSP. Higher P uptake with struvite, compared to TSP, may be because slower P release from struvite could be an advantage in this field setting where soil is competing to fix available P while crop uptake is progressing.
This work is funded by the EU Interreg project ReNu2Farm and the EU H2020 project Nutri2Cycle. International Fertiliser Society ( IFS) webinar series: programme, registration, access to recordings of past webinars (free for IFS members): HERE
Nutrient recovery
RAVITA P-recovery test results published
Lab tests were carried out on sludges resulting from post-precipitation of phosphates from the Viikinmäki municipal sewage works, Helsinki: coagulant dosing downstream of secondary treatment, followed by disc filtration (RAVITA process, see SCOPE Newsletter n°132). The RAVITA sludges were precipitated using either iron or aluminium coagulant and were tested as received (11 – 14% DM) or after incineration (550°C for 2 hours). Leaching with phosphoric acid was done in previously optimised conditions: 0.5M acid, 6 hours for aluminium; 2M acid, 1 hour for iron. Results showed c. 85% extraction from sludge and 99% from ash for aluminium; but only c. 37% from sludge and 68% from ash for iron. Approx. 95% leaching of phosphorus was achieved with both ashes, but no data is given for P leaching efficiency from the sludges (because of water content). The higher leaching of P compared to Fe or Al suggests that a significant part of these elements is not bound to phosphorus. The authors note that with aluminium, the leached P is mainly as soluble phosphate, whereas with iron, most is as soluble FeH2PO42+ ions, so that further processing would be necessary to separate the phosphorus from the iron. Heavy metals were analysed in the RAVITA sludges and found to be low, but it is not clear whether this is because they are retained in the secondary sludge or whether the Helsinki sewage has lower heavy metals than generally in Europe. The authors conclude that incineration of the RAVITA sludges improves potential for recovery of P and of Fe/Al. However, this may not be practical because the organic content of these post-precipitation sludges is low.
“To incinerate or not? Effects of incineration on the concentrations of heavy metals and leaching efficiency of post-precipitated sewage sludge (RAVITATM)”, S. Reuna, A. Väisänen, Waste Management 118 (2020) 241–246, DOI.
N2 Applied inaugurates new production hall 
On 21st September, ESPP member N2 Applied opened a new nitrogen recovery unit production hall, with Raymond Robertsen, Norway State Secretary of Regional Development and Erik Solheim, former UNEP Director and Norwegian Minister, and Ola Hedstein, CEO of Norwegian Agricultural Cooperatives. N2 Applied’s plasma technology uses air, electricity and manure slurry to create an organic and mineral N containing fertiliser which has no odour, reduced emissions and higher nitrogen content. Farm installations fit into a haulage container. An LCA study by 2.-0 LCA indicates that a combination of digestion of manure to produce biogas and N2 Applied technology can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from dairy farming by -36% (compared to baseline): anaerobic digestion of manure to produce biogas -16%, N2 Applied alone (treating manure) -27%; biogas + N2 Applied (treating digestate) -36%.
P-recovery from pharmaceutical industry wastewater
A process to remove and recover phosphorus from wastewater from the production of the antibiotic, Fosfomycin (1R-2S-epoxypropyl phosphonic acid), was tested at the lab scale. The wastewater contains, in particular, high levels of antiobiotic, preventing biological treatment, refractory organophosphorus chemicals, solvents and the complexing agent EDTA. A thermal process (wet air oxidation WAO, 200°C, oxygen @ 1 MPa, pH 11.2, 3 hours) converted 99% of organic phosphorus into soluble inorganic phosphate and removed nearly 60% of COD. Phosphorus was then removed and recovered from the liquor (which had nearly 1 000 mgP/l) by precipitation of calcium phosphate or struvite, achieving in appropriate conditions over 99% P removal and residual phosphorus below 5 mgP/l. The precipitated phosphates showed low heavy metal levels, but organic or pharmaceutical residues would need to also be verified. The treated liquor was suitable for biological treatment.
“Phosphorus recovery from fosfomycin pharmaceutical wastewater by wet air oxidation and phosphate crystallization”, G. Giu et al., Chemosphere 84 (2011) 241–246, DOI
German national “RePhoR” P-recovery projects announced
The German Federal Research Ministry (BMBF) has published stage two results of its RePhoR = Regional Phosphorus Recycling call for projects. The call was published in February 2018 and consisted of two stages: a “concept” stage, and an “implementation” stage.
19 projects were selected in stage 1, which funded the preparation of “regional P-recycling and sewage sludge reuse strategies” (leading to a 25-page document). These are listed on page 343 of this document (article by Helmut Löwe, BMBF.
The list of projects now published corresponds to the second stage of this call, that is those selected to “receive funding for the implementation of the concepts”. The call states that these should be “large-scale implementation of … processes” and specifies “exemplary development and large-scale implementation of processes for P recovery under real conditions for different plant sizes and types (at least TRL 6 for short)”.
However, some of the seven selected projects nonetheless appear to be R&D scale and to not correspond to the large-scale process implementation specified in the call.
- ESPP member Outotec is part of the R-Rhenania project, which will build and operate an AshDec® plant to recover phosphorus from 30 000 t(ash)/y of sewage sludge incineration ash, with the Altenstadt – Emter sewage sludge incineration plant (Bavaria) and the fertiliser manufacturer sePura, with BAM, KWB, LfL in Bavaria, FEhS and Bonn University. AshDec: see SCOPE Newsletter n°132.
- Amphore (Ruhr) website, led by Ruhrverband, will address the full value chain of P recycling as an integral part of sewage sludge use, including the development of sludge and ash management structures organised by five public waterboards. The project will built a 3 tonnes/day (1 000 t/(ash)y) plant, at a site of Emschergenossenschaft / Lippeverband (ESPP member), using adjusted PARFORCE technology (see ESPP P-Recycling Technology Catalogue). Two other ESPP members, Yara and the German Phosphorus Platform (DPP), are also involved in the project.
- ESPP member Veolia (Veolia Klärschlammverwertung Deutschland GmbH) is part of the DreiSATS project (Saxony), website, with Carbotechnik Energiesysteme GmbH, Pontes Pabuli GmbH, Lufttechnik Crimmitschau GmbH, Fraunhofer IKTS and with MFPA at the Bauhaus University Weimar. The objective is to develop combining incineration of dried sewage sludge (DM > 90%) in a dust firing system. The ashes are then treated with acid, followed by a solid-liquid separation, then granulation of the treated ash solids (Pontes Pabuli process), to produce fertilisers. Heavy metals are removed in the incineration process by a hot gas filtration unit and additionally during the ash treatment process. A 20 – 50 kg/h ash demonstration plant is planned.
- KlimaPhoNds (Lower Saxony), website, led by CUTEC Research Centre of Technical University Clausthal) aims to combine P-recovery with sewage sludge drying and combustion technologies to enable reductions of greenhouse gas emissions. Struvite will be precipitated from sewage sludge liquors (by a new process), then calcinated to recover ammonia and remove organics, then processed using PARFORCE technology (different from the PARFORCE ash process cited in SATELLITE below) to produce phosphoric acid and magnesium chloride. Announced scale is 1-2 t/day struvite processing, with struvite production and sludge processing commercial scale.
- P-Net (Harz – Heide region), led by Technical University of Braunschweig, aims to improve process engineering of struvite production and to develop regional markets for recovered struvite, with a regional cluster of sewage works recovering struvite. Scale of R&D pilot plant not specified.
- RePhoRM (Frankfurt Rhein Main region) will extend the Glatt PHOS4green technology (see ESPP P-Recycling Technology Catalogue). Heavy metal content in sewage sludge incineration ash will be reduced by a wet chemical process. The ash will then be reacted with phosphoric acid to improve plant availability of phosphorus in the ash, then granulated as fertiliser. The heavy metal reduction process will be tested in a 50kg batch pilot. The PHOS4green technology will be tested up to 200 kg/batch. The enhanced PHOS4green technology will be implemented on a commercial scale (capacity to be defined) at the Hoechst Industrial Park, Frankfurt am Main.
- SATELLITE (Lower Saxony), website, led by ISAH Leibniz Universität Hannover, involves an inter-municipal cooperation for sludge incineration and P recovery (23 shareholders, sludge of over 40 communities, https://www.knrn.de/). Research focuses on upstream sludge quality and transport logistics and will also look at the potential of farm manure and nitrogen. The project includes decentralised recovery of P as struvite or calcium phosphate, ammonia recovery by sequential evaporation (SEQUESTA) and stripping, and centralised sludge incineration (37 000 tDM sludge/year) at Hildesheim. PARFORCE technology is cited for P-recovery from the sewage sludge (see ESPP P-Recycling Technology Catalogue This is different from the PARFORCE struvite process in KlimaPhoNds above). The SATELLITE project includes research in phase 1 of the project, implementation in phase 2.
RePhoR, Germany, regional phosphorus recycling joint projects, September 2020 https://www.bmbf-rephor.de/verbundprojekte/
RePhoR launch event and internal workshop, 3rd & 4th November 2020 https://www.bmbf-rephor.de/veranstaltungen/rephor-kick-off-seminar/
Solubilisation of P from ash and other materials by microorganisms
Several papers present tests ongoing in Poland (Wroclaw, Olsztyn, Puławy) solubilising phosphorus secondary materials using 7-day culture with microorganisms, granulating the resulting material, and then testing in field trials. Secondary materials used in the different tests reported are ground bio-P-SSIA (sewage sludge incineration ash from a sewage works operating biological P-removal), ground bones (cooked chicken or fish bones), MBM (meat and bone meal ash). Microorganisms tested include Bacillus magaterium, a large, rod-like, Gram- positive bacteria, naturally occurring in a range of habitats, and widely studied, and used in industry (to produce penicillin amidase, used to make synthetic penicillin) and Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans [a] Bacillus cereus, Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus thuringiensis (results not yet published).
For example, in a 2019 paper [b], at 30 litre batch reactor lab scale, with bio-P-SSIA and poultry bones as substrates, pH in the culture fell to c. 4-5 within one day, then was relatively stable. P in the culture solution increased after 7 days during B. magaterium culture from near zero to c. 200 mgP-PO4/l for sewage sludge incineration ash or over 600 mgP-PO4/l for poultry bones, that is c. 9% for ash and 23% of total P in the materials. Around 100% of the P in ash and was found to be extractable (with water or citrate) after 7 days.
Granulation has been tested [c] at semi-technical scale (c. 100 kg/h capacity batch plate granulator), after drying of the whole culture at 60°C for three days, thus retaining the P in the culture solution, using various granulation agents: dried blood, superphosphate, bentonite, gypsum, sodium lignosulphonate, molasses.
The granulated micro-organism-activated materials (based on bones and sewage sludge incineration ash) have been tested in four field trials in Poland with winter and spring wheat, showing fertiliser effectiveness similar to phosphate rock and to a low-medium dose of superphosphate (18 or 26 kgP/ha) but lower that a standard agronomic recommendation dose of superphosphate (35 kgP/ha) when comparing to the same dose of P in the recycled fertiliser material [f].
Contaminant levels in the produced recycled fertilisers were low with bones, but up to 22 mg/kg for lead, 0.8 mg/kg for cadmium and 880 mg/kg for copper (from sewage sludge incineration ash). However, application at c. 35 kgP/ha resulted in no detectable change in levels of cadmium or lead in soil or in crops grown [d].
Assessment in the field trials also showed that the use of these recycled fertilisers did not modify number, biomass or species composition of earthworms [e].
[a] Valorization of Phosphorus Secondary Raw Materials by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, M. Wyciszkiewicz, A. Saeid, et al., Molecules 2017, 22, 473; DOI: 10.3390/molecules22030473 and Valorization of ash and spent mushroom substrate via solid-state
solubilization by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, A. Saeid & A. Patel, Waste Management 87 (2019) 612–620, DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2019.02.048
[b] Production of phosphorus biofertilizer based on the renewable materials in large laboratory scale, M. Wyciszkiewicz, A. Saeid, et al., Open Chem., 2019; 17: 893–901, DOI: 10.1515/chem-2019-0057
[c] Obtaining granular fertilizers based on ashes from combustion of waste residues and ground bones using phosphorous solubilization with bacteria Bacillus megaterium, M. Rolewicz et al., J Env Management, Volume 216, 15 June 2018, Pages 128-132 DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.05.004
[d] New phosphorus biofertilizers from renewable raw materials in the aspect of cadmium and lead contents in soil and plants, M. Jastrzebska, A. Saeid, et al., Open Chem., 2018; 16: 35–49 DOI: /10.1515/chem-2018-0004
[e] Phosphorus Fertilizers from Sewage Sludge Ash and Animal Blood Have No Effect on Earthworms, M. Jastrzebska et al., Agronomy 2020, 10, 525; DOI:10.3390/agronomy10040525
[f] Fertiliser from sewage sludge ash instead of conventional phosphorus fertilisers? M. Jastrzebska, A. Saeid, et al., Plant Soil Environ., Vol. 64, 2018, No.10, 504–511 DOI : 10.17221/347/2018-PSE
Research
UN Oceans Science
OceanForesters are looking for partners, supporters or for other technologies to include, for a project for the United Nations Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development. The project will target “Nutrient Recycling Seafood Science”.
United Nations Ocean Decade. ‘Nutrient Recycling Seafood Science’ project page on the United Nations Decade website. Contact Mark Capron, OceanForesters.
Global soil P depletion due to erosion
Modelling of P inputs to and losses from cropland suggests that soils are losing 2 kgP/ha/yr on average worldwide (-1.5 for Europe). Worldwide, the study estimates that arable land is depleted of c. 6.3 MtP/y (1.5 lost in organic P and 4.6 lost as inorganic P). This compares to estimates of losses ranging from c. 1 to 18 MtP/y in other publications. Soil P depletion is worst in Africa and Eastern Europe. The authors estimate that around half of this worldwide soil P depletion is due to soil erosion by water, concluding that agricultural management practices to reduce soil erosion are important to reduce soil P depletion.
“Global phosphorus shortage will be aggravated by soil erosion”, C. Alewell et al., (2020) 11:4546, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-18326-7
Government dietary guidelines inadequate for health and environment
A modelling study published in the British Medical Journal (Springmann et al. 2020), publicised in the media (see e.g. The Guardian), compares national governmental food based dietary guidelines in 85 countries, WHO dietary recommendations and the EAT-Lancet Commission on Healthy Diets from Sustainable Food Systems 2019 recommendations (see ESPP eNews n°30). Based on country-specific data, impacts were compared to internationally agreed objectives on greenhouse gas emissions (Paris), health (Action Agenda on Non-Communicable Diseases), freshwater use, land use (Aichi biodiversity targets), nitrogen and phosphorus fertiliser application (planetary boundaries). Adoption of current national dietary guidelines would result in an overall reduction in premature mortality of 15% (obesity, heart disease, etc) and a similar reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. However, most of the national guidelines are not adequate to achieve the internationally agreed environmental or health objectives. The EAT-Lancet recommendations would deliver around 1/3 more reduction in mortality and around 3x more reduction in greenhouse gas emissions than the national guidelines.
Below: extracts from fig. 5 page 9 of the paper.
The analysis concludes that adoption of national dietary guidelines worldwide would not significantly modify global use of phosphorus and nitrogen fertiliser (slight increase in P consumption, near zero decrease in N consumption). This is not shown in extracts above where only Europe is shown, see fig. 5 page 9 of paper. This is because increased fertiliser use for fruit, vegetable and dairy production offsets reduced demand for staple crops (grains, potatoes), meat and sugar. In Europe, however (see extracts above), adoption of national dietary recommendations leads to around -10% reduction in N and P consumption, mainly because of reduced pork and staple crop consumption.
At the global level, adoption of the EAT-Lancet recommended diet would lead to significant (c. -10%) reduction in phosphorus use, and an even higher (c. -15%) reduction in N use, again mainly because of reduced consumption of pork and staples (grains & potatoes), despite the increases resulting from consumption of fruit & vegetables, oils, nuts & seeds.
The authors note that national dietary guidelines generally recommend an increase in dairy consumption (see extract figure for Europe above) whereas EAT-Lancet recommends to reduce dairy to one serving or one glass of milk per day. They also note that reducing dietary calory intake, particularly associated to staple crops and sugar, is significant in reducing phosphorus and nitrogen use, whilst also reducing health risk from obesity.
ESPP notes that the impacts on P and N use seem to differ significantly from the impacts on greenhouse gas emissions, in that the latter are principally driven by red meat consumption (which also drives health impacts) whereas P and N use are not mainly driven by red meat consumption. Also, adoption of national dietary recommendations leads to increased GHG emissions in all regions worldwide, whereas it appears to lead to reduced P and N use (fig. 6, page 10 of the paper). ESPP underlines, especially for P, that the results of this paper are based on other publications’ estimates of e.g. impacts of meat production on overall phosphorus use, which probably need further research, so that although the direction of conclusions is clear, further research is needed for quantification.
In an earlier study (2018), Springmann et al. modelled increases in environmental impact from the food system by 2050 resulting from world population and income increases, concluding c. 50% increases in phosphorus and nitrogen use and c. 90% increase in greenhouse gas emissions. Whereas changes in diets alone are estimated to potentially (with most ambitious scenario) reduce future GHG emissions to below current levels and close to respecting planetary boundaries, diet changes are estimated to have much lower impact on N and P use. On the other hand, technologies, including improved fertiliser and animal feed use, water basin management and manure management, alone, are estimated to potentially reduce P use below current levels and within planetary guidelines, and are also the measure with the highest mitigation potential for N use. The authors conclude that a combination of dietary change, technologies and reductions in food loss and waste is necessary to avoid increased environmental pressure from the food system and to enable respect of planetary boundaries.
“The healthiness and sustainability of national and global food based dietary guidelines: modelling study”, M. Springmann et al., MJ 2020; 370: m2322 DOI
See also the EAT-Lancet Commission on Healthy Diets from Sustainable Food Systems 2019 in ESPP eNews n°30
“Options for keeping the food system within environmental limits”, M. Springmann et al., Nature volume 562, pages519–525(2018) DOI
Circular Agronomics project update
This Horizon 2020 project is now running for 2 years and aims to improve agricultural nutrient use efficiency whilst reducing greenhouse emissions, protecting soil carbon stocks and addressing the social, economic and political dimensions. The project looks at practices including seeding, type and application of recovered fertilisers, dairy cow feed composition and manure derived fertigation. Nutrient recovery techniques including vacuum degassing and struvite precipitation without addition of chemicals are tested.
Despite difficulties related to Covid and to irregular weather conditions, the six case studies have already generated valuable results:
- Catalonia (Spain): precision feeding of cows reduced N concentrations in urine by 40% without impairing milk production.
- Brandenburg (Germany): low rainfall can lead to overapplication of up to 50 kg/ha N
- Lungau (Austria): above average (6,480 l/ha) milk yields in Organic Farming in the Austrian Alpes
- Emilia Romagna (Italy): fertigation by sub-surface drip lines with ultra-low N emissions and crop yield and energy (fuel) use advantages of sod-seeding (minimum tillage) of winter wheat
- Gelderland (the Netherlands): demonstration of struvite, not only as P fertiliser, but also as an effective N fertiliser with very low N2O and NO3 emissions compared to urea, and that digested pig slurry has much lower N2O emissions than raw slurry for the same crop yield. Perennial grass types, alone or in combination with clover can also have a significant impact on N emissions but clover monocultures should be avoided.
- Moravia (Czech Republic): whey from dairies can be used as nutrient carrier whereas dosage and application still need to be determined.
https://www.circularagronomics.eu/
Fate of pharmaceuticals in manure processing
Twelve pharmaceuticals were detected in pig manure and slaughterhouse sludge in Catalunya, Spain. All twelve were found in manure, at concentrations up to 6600 µg/kg in the solid fraction (for doxycycline, a tetracycline antibiotic used to treat pneumonia, Lyme disease, cholera …), and most were found in the slaughterhouse waste. Both these 12 pharmaceuticals and five ARG (antibiotic resistance genes) were measured through a processing plant handling c. 7 000 t/y of manure and 11 000 t/y slaughterhouse sludge with an anaerobic digester (mesophilic, 75-80 days, producing biogas), followed by solid/liquid separation (centrifuge) and finally reverse osmosis (RO) of the liquid digestate. Mass balances for the pharmaceuticals were calculated based on measured concentrations and flows. Results are complex, in that for some periods/substances the flow of pharmaceuticals out of the anaerobic digester seems to be higher than that in the inlet (negative removal). This could be explained by several factors, such as the collection of the samples within the same day and to some analytical constraints (i.e. matrix effects). Overall, the anaerobic digester very significantly removed macrolide antibiotics (tilmicosin, tylosin), somewhat removed flubendazole and flunixin, but did not generally remove (except in some specific cases) lincomycin, fluoroquinolone or tetracycline antibiotics. In solid/liquid separation, most of the pharmaceuticals were retained in the solid fraction (except lincomycin and tiamulin), with sorption not being correlated to logKow values. The RO membrane however generally removed up to 90% of the pharmaceuticals. For ARGs, reduction was also limited in the anaerobic digester, little or no reduction in solid/liquid separation and again significant reduction through the RO membrane.
“Fate of pharmaceuticals and antibiotic resistance genes in a full-scale on-farm livestock waste treatment plant”, M. Gros et al., Journal of Hazardous Materials 378 (2019) 120716, DOI
ESPP Members

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews047
Download as PDF
EU consultations
EU consultation on sustainable aquaculture
EU consultations on agriculture policy (CAP)
EU consultation on environmental product claims
Information and events
European Research & Innovation Days
EU mission on “Soil health and food” Mission
IFS agronomics webinars
Webinar on Nutrient recycling in the Baltic Sea Region
Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance Forum
Phosphorus Transport Modeling Group
Calls for materials for testing
Looking for samples: fertiliser testing of iron phosphate
Looking for biostimulant or iron releasing products for testing
ESPP members
UK Water Industry Research (UKWIR)
LCA of enhanced struvite recovery
Yara sustainable initiatives in Finland and Sweden
Policy
EU “Safemanure” (RENURE) report published
Mineral fertilisers recovered from manures not addressed
ESPP input to the EU on the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive
Societal costs of eutrophication in Lake Erie
Limited effectiveness of detergent P bans
Irish Nutrient Platform launch webinar
How effective is phytase in pig feed?
Research
Call for papers: Sustainable phosphorus use in agriculture
Phosphorus flows in Brussels
LCA of enhanced struvite recovery
Review of struvite LCA studies
Struvite safety
Solubility of feed phosphates and overall P use efficiency
Microalgae to remove and recycle nutrients from digestates
Baltic BONUS RETURN final webinar
Technologies for nutrient management in the Baltic
ESPP members
EU consultations
EU consultation on sustainable aquaculture
The EU has opened a public consultation on EU Strategic Guidelines for Aquaculture, open to 27th October 2020. The current Guidelines (COM(2013)229) are misleadingly titled “Sustainable Development of EU Aquaculture), whereas in fact they address only competitivity (simplification of licensing, marketing, level playing field) and facilitating implantation (spatial planning). ESPP submitted to the prior Roadmap consultation suggesting to include nutrient efficiency of aquaculture feed and nutrient footprints (making the link to the nutrient strategy proposed in Horizon Europe) and underlined the need to reduce nutrient losses from both offshore and fresh water aquaculture and to develop nutrient recycling. Sustainability and fish feed do appear in the short online questionnaire for the current consultation.
EU consultation on aquaculture HERE
EU consultations on agriculture policy (CAP)
The European Commission has opened, to 22nd October 2020, three public consultations on the impacts of EU agriculture policy on water, on habitats / landscape / biodiversity and on sustainable management of soil. The objective is to assess the impacts of the CAP (Common Agricultural Policy), as per the 2013 reform, which includes the obligation for farmers (condition of subsidies) to respect mandatory rules (“cross-compliance”), including both statutory management requirements (SMR) and standards of good agricultural and environmental conditions (GAEC). Additionally, there exist voluntary agri-environment-climate measures (AECM) and subsidies for farmers in areas subject to natural constraints (Natura 2000, Water Framework Directive restrictions). The consultation consists of a public questionnaire asking whether respondents consider that the CAP contributes to different environmental objectives and questions on effectiveness or unintended consequences of CAP measures.
EU public consultations open to 22nd October 2020 on the impacts of the Common Agricultural Policy on water, on habitats, landscapes and biodiversity, and on sustainable management of soil.
EU consultation on environmental product claims
An Eu public consultation is open to 3rd December 2020 on “Substantiating claims of environmental performance for products, services and businesses”. This targets PEFs (Product Environmental Footprints) but also addresses ecolabels, greenwashing, environmental performance reporting, sustainability ratings, harmonisation of environmental information. The consultation aims to respond to the aim of establishing “labelling on the sustainability performance of food products” announced in the Farm-to-Fork Strategy. The announced objective is to identify policy options for substantiating environmental claims using Environmental Footprint methods. The online questionnaire addresses, in detail, what types of environmental claims should be authorised and under what conditions, how environmental footprint results should be communicated, how claims should be verified (conformity assessment).
EU consultation on product environmental claims and PEFs (Product Environmental Footprints) HERE
Information and events
European Research & Innovation Days
This EU annual event (this year virtual, 22-24 September 2020) aims to make links between policymakers, researchers and stakeholders to shape the future of R&I in Europe. The event’s ten virtual ‘hubs’ include Green Deal, Missions and Horizon Europe. The programme includes, 22 September Green Deal Hub: 12h45-13h30 Uncrossing Planetary Boundaries: How to get nutrient flows back within safe ecological limits? and 14h-15h Workshop on Circular and Bio-based: towards a carbon neutral and sustainable economy
Programme and registration here
EU mission on “Soil health and food” Mission
An interview of the chair of this Horizon Europe R&D “Mission”, Cees Veerman, suggests that the Mission seems to have changed its name to “Caring for soil is caring for life” and that there now seems to be now no content directly addressing food (other than that healthy soil is important for food production). The Mission now seems to be entirely orientated towards soil quality. (other than that healthy soil is important for food production). A short and confidential consultation (not announced on the EU’s public consultation website, 1st to 14th September 2020 only) HERE and #MissionSoil called for ideas for this Mission inviting submission of up to 5 short idea “proposals” (actions, priorities) to address soil health, and inviting to vote on proposals already on line. An interview of chair of the Mission Board, Cees Veerman, indicates that the Mission seems to have changed its name to “Caring for soil is caring for life” and there now seems to be now no content directly addressing food in the mission, which seems entirely orientate towards soil (other than that healthy soil is important for food production).
Online consultation HERE and #MissionSoil
IFS agronomics webinars
To replace the annual Cambridge agronomy conference, the International Fertiliser Society (IFS) is organising a series of webinars, to February 2021, covering themes such as P availability and depletion in soil (2nd October), fertilisers from recycled materials (10th November), digital tools and soil nutrient sensors, accurate fertiliser application, nitrogen fertilisation of cereals, soil boron, …
“Phosphorus (P) availability during the depletion of soil P”, Sophie Nawara, Fien Amery, Hilde Vandendriessche, Roel Merckx and Erik Smolders, Friday 2nd October 14h00 CEST
“Exploring variations in demand for fertilisers derived from recycling in NW Europe” and “New developments in the production of plant-available phosphorus from abattoir waste”, Romke Postma, Martin Blackwell, Tegan Darch, Tuesday 10th November 14h00 CEST
Full details of IFS webinar series (programme and registration): HERE
Webinar on Nutrient recycling in the Baltic Sea Region
Organised in the framework of the 11th Annual Forum of the EU Strategy for the Baltic Sea Region (EUSBR), with SuMaNu and BSAG, this workshop will discuss input to the HELCOM Regional Nutrient Recycling Strategy to be adopted in 2021, including eutrophication mitigation, manure management, Circular Economy and links to climate change. Breakout groups will address markets for recycled fertiliser products, cooperation in P management in the Baltic region and reducing contaminants in sewage to ensure safety of recycled nutrient materials;
Webinar workshop: ““Unlocking the nutrient recycling potential in the Baltic Sea Region” (SuMaNu – EU SBRS):
30th September 2020, 13h-15h30 CET – programme and registration
HELCOM Regional Nutrient Recycling Strategy: see presentation by Marja-Liisa Tapio-Biström.Finland Ministry for Agriculture, at the 12th HELCOM Meeting of the Working Group on Reduction of Pressures from the Baltic Sea Catchment Area 21/4/2020 HERE
Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance Forum
The SPA’s annual Forum is this year virtual, 30th September and 1st October, 12h-15h00 EST. This year’s programme addresses regulation of recycled nutrient products, nutrient recovery operation, climate change and eutrophication, pay-for-performance nutrient pollution mitigation, phosphorus transport modelling …
Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance Forum 2020, 30th September and 1st October, 12h-15h00 ET (New York time) on both days. HERE.
Phosphorus Transport Modeling Group
The Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance Phosphorus Transport Modeling Group brings together researchers and practitioners to discuss use and improvement of soil, water and watershed P transport models, such as Annual Phosphorus Loss Estimator Tool (APLE) or Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT). The group’s second meeting in late 2019 identified the need to cross-validate models, to integrate across scales and to compare with real edge-of-field P runoff data.
Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance Phosphorus Transport Modeling Group HERE and summary November 2019 meeting HERE.
Calls for materials for testing
Looking for samples: fertiliser testing of iron phosphate
The University of Seville is interested in samples of iron (II) phosphate (vivianite), which can form spontaneously in sewage works or in anaerobic digesters, for pot and field fertiliser tests. The objective, part of the EU-funded P-TRAP project, is to assess whether this form of iron phosphate can provide plant available phosphorus or iron to crops.
Contact
Looking for biostimulant or iron releasing products for testing
The University of Vienna is looking for biostimulant products possibly able to release phosphorus from iron in soils (certain ligands, humic substances, siderophores …) for testing. As part of the EU-funded P-TRAP project, the objective is to identify products or chemicals which can be used to improve the fertiliser value of secondary materials containing iron phosphates (e.g. iron materials after use in phosphorus traps, sewage sludge from works operating chemical P-removal), or to deliver to crops in a combined fertilising product containing both iron phosphate (possibly as iron (II) phosphate, vivianite) and an iron-accessing biostimulant.
Contact
ESPP members
UK Water Industry Research (UKWIR)
The UK & Irish water industry’s joint research organisation, UKWIR, has joined ESPP. UKWIR is the national research organisation serving all the water companies in the UK & Ireland. Our members are the 19 water companies of England, Scotland, Wales, Ireland and Northern Ireland. Our research covers the whole managed water cycle and aligns well with the activities of ESPP in a number of key areas. In particular, how do we maximise recovery of useful resources and achieve zero waste?. Also, how will we deliver an environmentally sustainable wastewater service that meets customer and regulator expectations?. Maximising recovery of phosphorous from wastewater, and limiting its use in the treatment and distribution of potable water, are real challenges for the water industry as a whole, here and world-wide. UKWIR is therefore keen to collaborate in new research projects through ESPP and learn from ESPP’s member organisations and network both in Europe and around the world.
www.ukwir.org
LCA of enhanced struvite recovery
As part of the LIFE ENRICH project (ESPP member), a Life Cycle Analysis study compares two scenarios for struvite recovery before anaerobic digestion in a sewage works operating biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) in the Murcia-Este WWTP, Spain. In the first scenario WAS (waste active sludge) is thickened using dissolved air flotation and fermented during 24 h to maximize poly-P release then elutriated in gravity thickeners with primary sludge. Struvite recovery from the overflow was modelled, considering different thickening and mixing rates. In a second scenario, WASSTRIP-based phosphorus release was modelled: primary sludge was fermented to generate volatile fatty acids then mixed with WAS in anaerobic P-release tanks and the resulting soluble-P enriched solution, after dewatering, was sent to the struvite precipitation. The different scenarios were evaluated for the LCA based on real data from the existing WWTP and modelling of different configuration changes. The modelling concludes that under the elutriation scenario around 43% of influent phosphorus (P inflow to the WWTP) could be recovered as struvite, increasing to 48% with WASSTRIP. Greenhouse effect and total costs (TAEC, per m3 wastewater treated), related to the sludge line operation, were modelled to be respectively 2% and 18% lower with struvite recovery via elutriation than without struvite recovery, whereas they were both higher with the WASSTRIP-based configuration compared to without struvite recovery.
“An integral approach to sludge handling in a WWTP operated for EBPR aiming phosphorus recovery: Simulation of alternatives, LCA and LCC Analyses”, M. Roldan et al., Water Research 175 (2020) 115647 DOI
For further information, LIFE ENRICH project website
Yara sustainable initiatives in Finland and Sweden
Finland-based, global fertiliser company (and ESPP member) has launched in Finland a 100% recycled, organic granular fertiliser product, eligible for Organic Farming. BIO 8-4-2 (NPK) is recommended as a supplementary fertiliser for all crops, for spring or autumn application, including for oilseeds, cereals, grassland, potatoes … 60% of P-content is calculated as plant accessible, and soil moisture facilitates nutrient release. Yara has also announced, with Lantmännen, a pilot project to use renewable energy for mineral fertiliser production, with the aim of reducing total CO2 impact of cereals by -20%. By working with the whole food chain, the objective is to reduce climate impact whilst minimising the price impact for consumers, despite the higher cost of renewable energy. Lantmännen is an agricultural cooperative of 25 000 Swedish farmers, with 10 000 staff and operations in 20 countries, in agriculture, machinery, bioenergy and food products and brands including AXA, Bonjour, Kungsörnen, GoGreen, Gooh, FINN CRISP, Schulstad and Vaasan.
Yara BIO 8-4-2 (in Finnish)
“Lantmännen and Yara lead the way towards world’s first fossil free food chain”, 13th September 2020
Policy
EU “Safemanure” (RENURE) report published
The European Commission has published the final JRC “Safemanure” report (now termed REcovered Nitrogen from manURE = RENURE), proposing criteria to authorise manure-derived recycled fertilising products to be used above the 170 kgN/ha for manure-derived nitrogen fixed by the Nitrates Directive.
This is absolutely not (proposed) “End-of-Manure” criteria, in that RENURE materials will remain be subject to specific management and use constraints (additional to those applicable to mineral fertilisers) to be fixed regionally for each Nitrates Vulnerable Zone by each Member State, concerning “timing and application rates …, good agro-environmental practices …ammonium emissions on field … and emissions to air resulting from storage”. The RENURE criteria also do not give an Animal By-Product End Point. Traceability and identification of RENURE materials as manure-derived will therefore be necessary.
In addition to these specific regional use criteria, RENURE materials must have a TOC:TN ratio ≤ 3 or a mineral N:TN ratio ≥ 90%. The JRC report suggests that such materials “have a similar N leaching potential and agronomic efficiency to Haber-Bosch derived and equivalent chemical N fertilisers, when applied under good management practices”. ESPP input to the RENURE process underlined that these criteria effectively penalise organic carbon input to soil: ESPP suggested that the stability of the TOC should be taken into account. ESPP also noted that materials such as 90% raw manure spiked with 10% urea would pass the criteria, as do some raw manures and most liquid fractions of manures. At this stage, these criteria are a JRC (EU Joint Research Centre) technical proposal which must now be validated by the Member States (EU Nitrates Committee) and will then face the risk of possible legal challenges, in that some environmental or agricultural NGOs and some Member States may consider that this is an attempt to facilitate intensive livestock production and allow increased manure spreading in nutrient surplus regions by circumventing the provisions of the Nitrates Directive to limit spreading of nitrogen, art. 2(g) “excreted by livestock or a mixture of litter and waste products excreted by livestock, even in processed form"
“Technical proposals for the safe use of processed manure above the threshold established for Nitrate Vulnerable Zones by the Nitrates Directive (91/676/EEC)”, European Commission JRC, September 2020, D. Huygens et al., ISBN 978-92-76-21539-4
Mineral fertilisers recovered from manures not addressed
In March 2020, ESPP wrote to the European Commission concerning that the Safemanure approach (see above) “can make a positive contribution to nutrient recycling by facilitating local use of nutrients in certain manure or digestate fractions, under appropriate and specifically defined conditions and in line with existing legislative requirements” but underlining that this “will not resolve the current obstacle posed by the Nitrates Directive to placing on the market of high-quality fertilising products derived partly or completely from manure”.
ESPP suggested that, independently of Safemanure, the European Commission should develop criteria under which nitrogen chemicals extracted from manure, which no longer contain organic carbon, should no longer be considered manure “in a processed form” (art. 2(g)). ESPP suggested that organic carbon content <1% and conformity to Fertilising Products Regulation criteria for ‘Mineral Fertiliser’ would be appropriate to ensure that chemical properties are same as synthetic mineral N fertilisers (and so e.g. leaching risk). Also, biological and contaminant safety should be ensured.
ESPP letter to European Commission requesting action on mineral fertilisers recovered from manure, 10th March 2020 http://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/regulatory
ESPP input to the EU on the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive
ESPP submitted input to the EU public consultation The European Commission (closed 8th September 2020, see eNews n°46) , on revision of the EU Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive (UWWTD 1991/271). The UWWTD is recognised has having been effective in reducing pollution and in improving water quality. ESPP welcomes the proposed objectives of coherence with the Circular Economy (nutrient recycling) and “extended producer responsibility” for emerging contaminants of concern in sewage (industrial chemicals, pharmaceuticals, micro-plastics) which can be an obstacle to sewage sludge valorisation and nutrient recycling. ESPP underlined in particular the problem of perfluorinated chemicals (PFAS, PFOA). ESPP also welcomed that eutrophication is identified as a key issue needing to be addressed, in particular with storm overflows, small agglomerations < 2000 p.e. and septic tanks.
EU public consultation on the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive” (closed 8th September 2020) and ESPP input submitted HERE.
Societal costs of eutrophication in Lake Erie
A new study estimates that (based on 2015 situation) algal blooms in Lake Erie (USA and Canada) cost some 272 million US$/year, mainly from recreation and inherent value placed on the lake by residents living < 100km from its shores (115 M€), tourism economic losses (110 M$) and loss of property value (36 M$). Accounted over 30 years, this means a total cost of over 5.3 billion US $). Actions to reduce nutrient losses, including reducing and improving fertiliser application, agricultural buffer measures, artificial wetlands, stormwater management and improvement of sewage treatment plants is estimated at 1.3 billion US$, whereas such actions are estimated to reduce algal bloom costs by 2.8 bn$ (over 30 years), so are considered cost-effective. There are few estimates of how much nutrient losses to surface waters cost to the economy and to society. Three are cited: Dodds 2007 (see SCOPE Newsletter n°72): eutrophication costs for the USA 1.5 – 4.8 bn$; Hoagland & Scatasta 2006 algal bloom costs (only) USA 82 m$ and EU 813 m$; Steffensen 2008 management of algal blooms (only) Australia 180 – 240 mAus$.
“Estimating the economic costs of algal blooms in the Canadian Lake Erie Basin”, R. Smith et al., Harmful Algae 87 (2019) 101624 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2019.101624
Limited effectiveness of detergent P bans
A discussion paper suggests that detergent phosphate bans in the USA will have only limited impact in reducing overall nutrient loads to surface waters. 95% of phosphate use in the USA is estimated to be in agriculture. Detergent P bans will not reduce inputs to surface waters where sewage passes through treatment works with binding P discharge consents, because operators will optimise to continue to discharge P to the specified limit, irrespective of changes in works inflow P load. In Minnesota, this was estimated to reduce the effectiveness of a detergent phosphate ban by 24 – 59%, and maybe by 80% in nutrient sensitive waters where most sewage treatment works are strictly consented. Local regulations, such as county-wide lawn P fertiliser bans, may show reduced effectiveness as consumers bypass the ban by purchasing online or in nearby regions: 40% of detergent purchases were estimated be coming from outside the county when Spokane had a local dishwasher P ban. The authors argue for a wide approach to policy addressing all sources of phosphorus.
“The Effectiveness of Phosphate Bans in the United States”, D. Kaiser, Review of Environmental Economics and Policy, volume 14, issue 2, Summer 2020, pp. 331–338 DOI
Irish Nutrient Platform launch webinar
The launch webinar of the island of Ireland (Ireland and Northern Ireland) Nutrient Platform registered nearly 100 participants, 3rd September. Vincent O’Flaherty, NUI Galway, explained that a three-year programme had been funded by the EPA, to assess the feasibility of such a platform and then to prepare its establishment. A meeting a year ago, with 26 participating organisations, agreed objectives and terms of governance. Key objectives are to enable networking, to facilitate business opportunities in recycling and nutrient management, and dialogue with regulators and policy makers. Philip Cosgrave, Yara, presented the company’s commitment ongoing improvement of fertiliser sustainability, from production through packaging to use on the farm, in particular with advice to farmers. Yara is also actively developing recycling, including via the Nutrient Upcycling Alliance (see ESPP eNews n°41), for example with the launch in Finland of a fertiliser including recycled organic phosphorus (see above). Patrick Barrett, Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine, outlined national bioeconomy policy development and funding opportunities in Ireland and at the EU level for circular bioeconomy activities, and noted the potential of the new Platform to help develop and scale-up business opportunities and value-chains and inform bioeconomy policy implementation. Ian Marshall led a final panel, including ESPP, which discussed the interest of developing a nutrient balance for the whole island of Ireland, the challenges and opportunities for nutrient management from EU policies: fertiliser use commitments and the Integrated Nutrient Management Action Plan in the Green Deal, achievement of Water Framework Directive objectives with climate change, the new Common Agricultural Policy and the FAST (Farm Sustainability) Tool for Nutrients, Eu R&D funding possibilities … The important role of nutrient platforms in facilitating dialogue and consensus between different industries and stakeholders was underlined.
https://nutrientsustainability.ie/
How effective is phytase in pig feed?
The addition of phytase enzyme to pig feed to improve uptake of phosphorus is today standard procedure in most pig production. A significant part of phosphate in grains and seeds is in ‘phytate’, the plant’s natural phosphorus storage molecule, which is not digestible for non-ruminants (pigs, chickens, humans). By breaking down phytate, phytase enables pigs to take up this protein, so reducing P-loss to manure and reducing the need to add mineral feed phosphates (e.g. calcium phosphates). Recent trials suggest however that standard agronomic recommendations may overestimate the benefits of phytase. 72 pigs were fed diets with different levels of added phytase for 25 days, with either a diet with adequate P for optimal growth, or a P-deficient diet. Phytase improved P digestibility by nearly 50% in the P-deficient diet, but only by 12% in the optimal diet. The authors note that P-release curves for phytase are based on research using P-deficient diets, in order to obtain clear results, so that current diet recommendations may be overestimating the effects of phytate use on pig P uptake, and so resulting in feed supplying below optimal P levels. In both diets, phytase slightly improved digestibility of dry matter, gross energy and crude protein.
“Does phytase release less phosphorus than we think?”, K. Olsen & J. Patience, Iowa Pork Industry Centre, Iowa State University, 7th July 2020 https://www.nationalhogfarmer.com/nutrition/does-phytase-release-less-phosphorus-we-think
Research
Call for papers: Sustainable phosphorus use in agriculture
Research or review papers are invited for a special issue of the journal Agronomy on sustainable use of phosphorus in agriculture: N and P in manure and crop requirements, soil-crop systems, from feed through livestock to manure nutrient mass balances and efficiencies, runoff and erosion, policies and governance, economics, ecotechnologies.
Submission deadline is 31st March 2021.
Agronomy Journal special issue submission form
Phosphorus flows in Brussels
A study analysed phosphorus flows through the Brussels Capital Region, Belgium (1.2 million people, 160 km2, of which <1% agriculture). Currently wastewater is treated at two sewage works, most food waste is incinerated with municipal refuse, and green waste is collected and composted. P inputs in the food system are estimated from food consumed by population, visitors, and commuters (based on Belgium national Food Consumption Survey data) plus food waste generated in consumption and trade. P in pet food, detergents and green waste is also estimated. The data suggests an average per capita dietary intake of 1.2 gP/day. The study concludes that main annual inflows are (approximately) 700 tP/y in food products, 100 tP/y in detergents, 100 tP/y in pet food and 100 tP/y in wastewater from outside the region treated at one of the sewage works. The main outflows are (approximately) 560 tP/y in treated sewage sludge, 140 tP/y in sewage works discharge and 160 tP/y (mainly from food waste) in municipal refuse incineration ash. Currently, the sewage sludge is either wet air oxidised, dried, then used as cover material in landfills, or incinerated in Belgium and Germany. The principal opportunities for P recycling are from sewage sludge, and secondly from food waste when separate collection will be scaled up. P losses from the sewage works to surface waters (currently 16% of inflow P) should be reduced with ongoing upgrades to the two works. Separate collection and anaerobic digestion of food waste within the city would increase the amount of electricity generated; P-recovery from sewage sludge does not affect the energy balance, because energy from sludge digestion is already valorised within the sewage works. The authors conclude that the potentially recyclable phosphorus could cover the fertiliser needs of the two neighbouring Brabant provinces, but only if the regulatory framework and social acceptance of such recycling are improved.
“Phosphorus and energy flows through the food system of Brussels Capital Region”, A. Papangelou, W. Achten & E. Mathijs, Resources, Conservation & Recycling 156 (2020) 104687, DOI
LCA of enhanced struvite recovery
As part of the LIFE ENRICH project, a Life Cycle Analysis study compares two scenarios for struvite recovery before anaerobic digestion in a sewage works operating biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) in the Murcia-Este WWTP, Spain. In the first scenario WAS (waste active sludge) is thickened using dissolved air flotation and fermented during 24 h to maximize poly-P release then elutriated in gravity thickeners with primary sludge. Struvite recovery from the overflow was modelled, considering different thickening and mixing rates. In a second scenario, WASSTRIP-based phosphorus release was modelled: primary sludge was fermented to generate volatile fatty acids then mixed with WAS in anaerobic P-release tanks and the resulting soluble-P enriched solution, after dewatering, was sent to the struvite precipitation. The different scenarios were evaluated for the LCA based on real data from the existing WWTP and modelling of different configuration changes. The modelling concludes that under the elutriation scenario around 43% of influent phosphorus (P inflow to the WWTP) could be recovered as struvite, increasing to 48% with WASSTRIP. Greenhouse effect and total costs (TAEC, per m3 wastewater treated), related to the sludge line operation, were modelled to be respectively 2% and 18% lower with struvite recovery via elutriation than without struvite recovery, whereas they were both higher with the WASSTRIP-based configuration compared to without struvite recovery.
“An integral approach to sludge handling in a WWTP operated for EBPR aiming phosphorus recovery: Simulation of alternatives, LCA and LCC Analyses”, M. Roldan et al., Water Research 175 (2020) 115647 DOI
For further information, LIFE ENRICH project website
Review of struvite LCA studies
Seven LCA studies of phosphorus recycling as struvite from wastewater are summarised, plus six of struvite from urine, dating from 2012 to 2018 (not including the paper above). The authors note considerable variation both in the LCA methodology and in the boundaries considered. Most of the LCAs include some “offset” for the environmental impacts of producing conventional fertilisers replaced by struvite, but some consider both N and P and some either only N or only P. Some of the LCAs include a sludge or nutrient management credit. Other aspects also vary considerably, with some of the LCAs, but not all, considering infrastructure, some considering that struvite might increase eutrophication (based on nutrient content of struvite applied as fertiliser), others that struvite reduces eutrophication (calculating the struvite nutrient content as removed from sewage works discharge), some but not all considering electricity consumption, etc. Furthermore, only two of the studies used data from full-scale struvite recovery installations, the others relying on literature or pilot plants. The authors suggest that that the most reliable (of the 13 studies assessed) is likely Remy & Jossa 2015 (P-REX deliverable 9.2, see summary in SCOPE Newsletter n°115), which is based on data from full scale and pilot plants, includes fertiliser offsets and infrastructure, and considers a range of impact categories. This P-REX LCA concluded that struvite precipitation has net beneficial impacts on greenhouse emissions, and eutrophication and (for configurations with precipitation downstream of sludge dewatering) on human and environmental toxicity.
“Life cycle assessment review of struvite precipitation in wastewater treatment”, M. Sena, A. Hicks, Resources, Conservation & Recycling 139 (2018) 194–204 DOI
“Sustainable sewage sludge management fostering phosphorus recovery and energy efficiency”, P-REX deliverable 9.2 report, C. Remy & P. Jossa, 2015, 86 pages HERE
Struvite safety
Two recent publications add to existing data confirming that struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate, a form of phosphate in which phosphorus is recovered from wastewaters) is safe and non-toxic.
Shim, Won et al.. (2019) tested the oral toxicity of struvite on rats. The struvite was precipitated from pig manure centrate in a 20 litre lab reactor, then pre-treated by microwave irradiation or heat sterilisation (550°C x 30 mins). 30 rats were fed, for 28 days, 1 or 10 mg/kg body weight/day either one of the two pre-treated struvites or no struvite (P levels as in standard rat diet). Rats were then sacrificed, body weight and blood metabolites measured and histopathological examinations carried out on liver, kidney, lung and heart. No significant differences were found in the struvite-fed rats and no abnormalities. The authors conclude no oral toxicity of struvite over 28 days at these doses. Based on solubility tests, they suggest that such pre-treated struvite could replace currently-used feed phosphates in livestock diets.
Kim et al. (2019, partly the same authors as Shim et al. above) tested the same pre-treated struvite in broiler chicken diet (204 chickens, inc. controls) for 28 days. Growth showed to be the same as with standard feed phosphate (dicalcium phosphate). No significant differences were found in histopathological examination of key organs: heart, kidney, liver, gizzard, intestines, tibia. The authors again conclude no oral toxicity under these conditions and at the dose of agronomic diet P levels, and possibility to use pre-treated struvite as a poultry feed P-additive.
NOTE: ESPP reports these studies because they add to other evidence of the toxicological safety of struvite, which is relevant for its handling etc. when used as a fertiliser or in industry. ESPP does not recommend using struvite recovered from wastewater or manure in animal feed, for reasons of public confidence. This might also be illegal in Europe because the Animal By-Products Regulations prohibit use of “faeces, urine … (or) … waste obtained from wastewaters …irrespective of processing”
“In Vivo Toxicity and In Vitro Solubility Assessment of Pre-Treated Struvite as a Potential Alternative Phosphorus Source in Animal Feed”, S. Shim et al., Animals 2019, 9, 78, DOI:10.3390/ani9100785
“Evaluation of Struvite Recovered from Swine Wastewater as an Alternative Phosphorus Source in Broiler Feed”, M. Kim et al., Agriculture 2019, 9, 221, DOI:10.3390/agriculture9100221
See also: .“Design and optimization of fluidized bed reactor operating conditions for struvite recovery process from swine wastewater”, S. Shim, S. Won, et al., 2020, Processes, 8, 422 – 438 DOI: 10.3390/pr8040422 (Open Access)
See also: “Simultaneous Removal of Pollutants and Recovery of Nutrients from High-Strength Swine Wastewater Using a Novel Integrated Treatment Process”, S. Shim, S. Won et al., Animals 2020, 10, 835; DOI: 10.3390/ani10050835
S. Shim, A. Reza, S. Kim, N. Ahmed, S. Won, and C. Ra. 2020. “Simultaneous removal of pollutants and recovery of nutrients from high-strength swine wastewater using a novel integrated treatment process”, animals, 10, 835 – 853.
Solubility of feed phosphates and overall P use efficiency
Tests with 384 piglets and modelling suggest that use of a highly water soluble phosphate feed additive significantly improves whole-system PUE (phosphorus use efficiency), increases pig weight gain and reduces manure phosphorus, compared to use of a less water soluble phosphate. The 35-day pig trials used four different diet levels (0.05% to 0.2%) of water soluble MDCP mono-dicalcium phosphate and standard feed phosphate DCP dicalcium phosphate. Whole-system takes into account manure application to soil, feed crop production (soy, maize), fertiliser use, soil P accumulation and so phosphate rock consumption. The fertiliser value of manure from the piglets on different feeds was assessed by pot trials using lettuce, because manure is often recycled for vegetable production in China. Conclusions are that, for example, for 1 kg meat production, 0.1% water soluble phosphate feed additive improves whole system PUE by 18% compared to 0.2% DCP.
“A higher water-soluble phosphorus supplement in pig diet improves the whole system phosphorus use efficiency”, L. Liu et al., J. Cleaner Production 272 (2020) 122586 DOI
Microalgae to remove and recycle nutrients from digestates
A review from China presents data and summarises opportunities for use of microalgae to remove nutrients from anaerobic digester effluents, with data mainly from pig manure digestate. Microalgae production can be used for extraction of lipids, biofuel production, as biomass to feed back into the digestor and increase methane production, or as an organic fertiliser and soil amendment. Microalgae have shown to tolerate high organic compound concentrations in digestates, and to be able to remove 30 – 96% of COD, 20 – 95% of ammonia-N and 20 – 98% of phosphorus, depending on conditions. Although microalgae prefer to metabolise ammonium nitrogen (rather than nitrate), high ammonium levels can be toxic to microalgae (> 120 mg/l). Another challenge is turbidity, limiting light and so microalgae photosynthesis. One simple solution to this is to dilute the digestate, but this poses logistic problems.
“Nutrients removal and biomass production from anaerobic digested effluent by microalgae: A review”, G. Li et al., Int J Agric & Biol Eng, 2019; 12(5): 8–13, DOI Open Access.
Baltic BONUS RETURN final webinar
The BONUS RETURN project final conference (webinar 8 September 2020), attended by ca. 50 stakeholders, presented conclusions and recommendations on how ecotechnologies can turn nutrients and carbon from environmental problems into circular solutions in the Baltic Sea Region. The program was moderated by Arno Rosemarin (SEI). In the first session, the coordinator Karina Barquet (SEI) welcomed the audience and gave a short introduction to the program. Biljana Macura followed with a review of ecotechnologies for circulating nutrients and carbon in the Baltic Sea Region. Erik Kärrman (RISE) and Soren Marcus Pedersen (UCPH) presented a sustainability analysis of the three catchment areas selected as target regions for the program – river basins of 1,000-2,000 km² draining to the Baltic Sea – Fyrisån River (Uppland, Sweden), Vantaanjoki River (Helsinki Metropolitan Area, Finland) and Slupia River (Slupsk, Poland), offering to study pressures from agricultural and forest activities as well as from large, densely populated agglomerations. Jari Koskiaho (SYKE) and Tomasz Okruszko (WULS) presented the SWAT modelling results of the impact of ecotechnologies on nutrient levels in the three river basins. After the coffee break Sten Stenbeck (RISE) introduced the circular innovations that were pilot-tested during the project, referring to three selected emerging ecotechnologies for nutrient and carbon reuse (see below). After a review of barriers and opportunities for closing the loop in the Baltic Sea Region presented by Linn Järnberg and Nelson Ekane (both SEI), Mark Rasmussen, Olle Olson (both SEI), Marek Gielczewski (WULS) and Jari Koskiaho (SYKE) gave an overview of project related success stories. The use of phosphogypsum on cropland to retain phosphorus and reduce losses, proved particularly promising for widespread application in the Baltic region, potentially preventing 2,000 annual tons of phosphorus inflows to the Baltic Sea if implemented over large areas in a number of the riparian countries (see ESPP eNews n°36). After altogether ten years of testing, this practice can now be recommended for extensive application, using low-contaminant phosphogypsum (a by-product from processing of igneous phosphate rock), or natural gypsum where available, without worries for soil health and water quality. Finally, Steven Bachelder (Uppsala University) showed an amusing learning game before Karina Barquet (SEI) summarized and closed the session with recommendations for future policy and research
BONUS RETURN project, 2017-2020: a joint program of 6 science partners from Denmark (University of Copenhagen), Finland (SYKE) and Poland (Warsaw University of Life Sciences), Sweden (Stockholm Environment Institute, Research Institutes of Sweden, Uppsala University), coordinated by the Stockholm Environment Institute.
Recording of 8th September 2020 webinar.
Technologies for nutrient management in the Baltic
The BONUS RETURN project (see above) has published final reports on ecotechnologies for nutrient management in river basins and for nutrient and carbon reuse. The report on river basin management compared impacts of source separation of black water (toilet) and grey water (other household wastewater), nutrient removal in municipal wastewater and agricultural nutrient Best Management Practices (BMPs, including constructed wetlands). This concluded, in the catchments studied, that agricultural BMPs could reduce nutrient loads (N and P) by 30-40%, compared to 4-12% for actions addressing municipal wastewaters, or <1% by increasing agricultural soil carbon content. The report concludes that a combination of different measures will be needed, depending on local catchment situations, to reduce nutrient inputs to the Baltic, and that other benefits must also be considered such as nutrient recycling and soil productivity improvement.
BONUS RETURN also selected and tested three promising ecotechnologies for nutrient and carbon reuse, with pilot plants set up and tested in Sweden, Finland and Poland. The selection process is described in a first report 28/6/2018 (press release 5/4/2018). An open “Challenge” was organised. Thirteen entries were received (not listed), from which four finalists and then from these three winners for pilot testing and pre-commercialisation support were selected. The three selected for testing are: BioPhree (Aquacare, NL, see ESPP eNews n°29), Ravita (HSY Helsinki) and Terranova Energy (Germany), both see ESPP’s SCOPE Newsletter n°132) and the fourth finalist was Carbonext, a technology for splitting biogas (methane) to produce a clean coke fuel and hydrogen gas.
BioPhree was tested in Knivsta Stockholm at pilot container scale. No data or results from the tests are provided at this stage.
Ravita post-precipitation recovery of iron phosphate was tested at a pilot plant at the Viikinmäki, Helsinki, municipal wastewater treatment plant (1000 p.e. scale, since 2019 see ESPP’s SCOPE Newsletter n°132). Development of recovery of phosphorus, nitrogen and iron (recycling as a coagulant) from the iron phosphate is underway.
TerraNova was tested in Gävle, Sweden. see ESPP’s SCOPE Newsletter n°132. No data or results from the tests are provided at this stage.
BONUS RETURN effective ecotechnologies in river basins Deliverable D.4.2. (29/2/2020) report and “Carbon and nutrient recycling ecotechnologies in three Baltic Sea river basins –the effectiveness in nutrient load reduction”, J. Koskiaho et al., 2020 Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology in print, DOI.
BONUS RETURN ecotechnologies for nutrient and carbon reuse: press release 5/4/2018 and Deliverable D.3.7 (28/6/2018) report
ESPP members

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews046
Download as PDF
EU public consultations
EU consultation on sewage sludge
EU consultation on Urban Waste Water Treatment
EU consultations on agriculture policy (CAP)
Covid
UK sewage Covid detection research
Policy
Towards a White Paper on resource recovery from wastewaters
Water Framework Directive to be maintained
Global call for action on phosphorus
ESPP member news
Kemira to market Vivimag P-recovery technology
Nordrhein-Westfalen P-recycling plans
Wheatsheaf Group acquires Ostara
Research and projects
Phosphorus governance and regulation
P-recovery from lake Sediment
Fish bones as an Organic Farming fertiliser
Nitrogen emissions from livestock production
Events
IWA nutrient recovery conference
VDI Conference on sewage sludge treatment
Phosphorus chemistry webinar series
ESPP members
EU public consultations
EU consultation on sewage sludge
The European Commission has opened, to 25th August 2020, a public consultation on the ‘roadmap’ for re-evaluation of the EU Sewage Sludge Directive (86/278). This first consultation enables to input concerning the objectives of this re-evaluation, which will include a second, wide consultation on sewage sludge use in agriculture, announced for late 2020. The Commission’s proposed ‘Roadmap’ underlines that the Directive aims to encourage the use of sludge in agriculture, under safety conditions, and that nutrient recovery (citing phosphorus) should be a core objective, coherent with the EU Circular Economy Action Plan, Green Deal, Bioeconomy Strategy and Farm-to-Fork Strategy. The need to take into account “contaminants of emerging concern (e.g. organic chemicals such as pharmaceuticals, PAH and PFAS, cosmetics and microplastics)” is noted. This consultation enables to input to the definition of the Purpose and Scope of the sludge directive re-evaluation.
EU public consultation open to 25th August 2020 “Sewage sludge use in farming – evaluation” (Roadmap). Input can be as a simple text statement (max 4000 characters) and/or upload of a document.
EU consultation on Urban Waste Water Treatment
The European Commission has opened, to 8th September 2020, a public consultation on the ‘roadmap’ for revision of the EU Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive (UWWTD 1991/271). The proposed roadmap identifies as key questions: storm water overflows, inadequate treatment of wastewater from agglomerations < 2 000 p.e. (the Directives currently specifies only that treatment for such small agglomerations should be “appropriate”), inadequate treatment and monitoring for individual homes (septic tanks), contaminants of emerging concern (CEC) including pharmaceuticals and micro-plastics, eutrophication, embedding in the “clean and circular economy” (sludge management, nutrient recovery, recovery of raw materials), energy recovery, waste water surveillance for pandemic monitoring. Proposed policy objectives emphasise the importance of sewage sludge: treatment / decontamination and “subsequent use as a fertiliser, including the option of “applying extended producer responsibility”. It is specified that economic analysis will include consistent application of the polluter pays principle.
EU public consultation open to 8th September 2020 “Water pollution – EU rules on urban wastewater treatment
(update”, Inception Impact Assessment “Revision of the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive” (Roadmap). Input can be as a simple text statement (max 4000 characters) and/or upload of a document.
EU consultations on agriculture policy (CAP)
The European Commission has opened, to 22nd October 2020, three public consultations on the impacts of EU agriculture policy on water, on habitats / landscape / biodiversity and on sustainable management of soil. The objective is to assess the impacts of the CAP (Common Agricultural Policy), as per the 2013 reform, which includes the obligation for farmers (condition of subsidies) to respect mandatory rules (“cross-compliance”), including both statutory management requirements (SMR) and standards of good agricultural and environmental conditions (GAEC). Additionally, there exist voluntary agri-environment-climate measures (AECM) and subsidies for farmers in areas subject to natural constraints (Natura 2000, Water Framework Directive restrictions). The consultation consists of a public questionnaire asking whether respondents consider that the CAP contributes to different environmental objectives, questions on effectiveness or unintended consequences of CAP measures.
EU public consultations open to 22nd October 2020 on the impacts of the Common Agricultural Policy on water, on habitats, landscapes and biodiversity, and on sustainable management of soil.
Covid
UK sewage Covid detection research
Research is underway in the UK and Spain to sample wastewater in several cities, to define how sewage sampling could establish an early-warning system for identifying Covid outbreaks. he Covid-19 virus does not readily spread through sewage, but non-infectious residues of the virus can be identified. These are released even by asymptomatic infected persons, possibly enabling identification of outbreaks a week earlier than by medical testing of the population. Methods to track virus traces in wastewater are very different from medical infection testing, and are not yet standardised. The research involves Northumbrian Water and other UK water companies, CEH, Newcastle University and other UK universities, the University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain, government agencies and health bodies. Six testing labs are already operational across the UK. In France, testing by the Paris public water company suggests that the virus may be starting to develop again in July following the end of lockdown. Monitoring of virus traces in sewage is also developing rapidly in the USA.
Efforts to monitor Covid using sewage sampling across Europe are being coordinated by the European Commission JRC (see call in ESPP eNews n° 45) and some 80 research organisations across Europe have already responded to this call.
BBC News 2nd July 2020 and Newcastle University 2nd July 2020. CWEA webinar California 14th July 2020.
Policy
Towards a White Paper on resource recovery from wastewaters
A web workshop organised by Water Europe (Resource Recovery Working Group), 26th June 2020, moderated by Pieter de Jong, Water Europe, launched work on a white paper on addressing regulatory obstacles to resource and nutrient recycling from wastewaters, in particular End-of-Waste. Recovered materials obtaining national End-of-Waste status currently face considerable obstacles for transport, sale and use in other EU Member States. The heterogeneity of status between countries makes roll-out of recycling technologies problematic. Mattia Pellegrini, European Commission DG Environment, indicated that a study has been carried out (to be published shortly) inventorying national Best Practices for End-of-Waste, with the aim of spreading these. A stakeholder process is planned with JRC to take this forward in consultation with stakeholders. He further underlined the current public consultation on the EU Sewage Sludge Directive (86/278), open to 28 August 2020 indicating that revision of this Directive could bring in circularity, for example by defining European End-of-Waste criteria for sewage sludge with defined quality and processing standards, in coherence with the EU Fertilising Products Regulation (which currently excludes sewage-sourced materials, although struvite and nutrients recovered from sewage sludge incineration ash should soon be admitted via STRUBIAS). Simplification of waste transport is also being considered, for example by removing the “prior consent” requirement for intra-EU waste transport for wastes respecting specified sectorial standards. Aalke Lida de Jong, AquaMinerals (The Netherlands) presented examples of the difficulties and complexities which pose obstacles to resources recycling from wastewater, citing examples of struvite and recovered cellulose. Concrete obstacles include fertiliser authorisation, End-of-Waste, transport, and permitting of industrial sites wishing to take in waste for recycling to replace virgin materials. Carmen Mena Abela, European Commission EASME, presented projects into resource recovery from wastewater funded under Horizon 2020, emphasising the policy recommendations from these projects (see ESPP eNews n°41 and see here). She noted that several major new projects on resource recycling from wastewater are now starting: Ultimate, Wider Uptake, ReWaise, B-WaterSmart, Rewaise and Water-Mining. Chris Thornton, ESPP, underlined the opportunities of the EU Fertilising Products Regulation, the difficulties of REACH (art. 2(7)d which is important to facilitate recycling, but fails to structure dossier funding) and obstacles in the Animal Feed Regulation (767/2009) which excludes even pure and reprocessed materials from wastewater. Martijn Bijmans and Francesco Fatone, Water Europe invited further cooperation, with this workshop aiming to start the preparation of a stakeholder White Paper on addressing obstacles to resource recycling from wastewater.
Water Europe Resource Recovery Working Group
Water Framework Directive to be maintained
Media report that the European Commission has decided that the Water Framework Directive will not be revised. This follows the publication in December 2019 (ESPP eNews n°39) of a REFIT assessment of the Directive concluding that it is effective and that benefits outweigh costs. The Commission has declared that it will now focus on implementing and enforcing the Directive, which is a major challenge as all Member States are considerably behind the Directive’s objectives of Good Quality Status in all surface and ground waters by 2027 at the latest. The Commission will specifically look at updating the Directive list of “Priority Substances” and at the daughter Groundwater Directive, and will integrate the Green Deal Zero Pollution Action Plan. The water industry (Eureau) has welcomed the decision, underlining the need to ensure coherence with legislation such as REACH and the Industrial Emissions Directive and the importance of the principles of the Water Framework Directive of prevention of pollution at source, and of ensuring polluter-pays and appropriate water pricing to justly finance implementation. Environmental organisations (EEB) equally welcomed the decision, underlining that to date less than half of the EU’s surface waters are in Good Quality Status and that strong action must now be engaged, with appropriate funding, to ensure that quality objectives are ensured by 2027.
“European Commission decides not to revise the WFD” Eureau 24th June 2020. “EU water law will NOT be changed, confirms European Commission” EEB 23 June 2020.
Global call for action on phosphorus
Over 500 scientists and experts have already signed the ‘Our Phosphorus Future’ call for international action on phosphorus. Since the launch of this call at 3rd European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference, Helsinki, 2018, some 80 authors from around the world have been working together to identify key challenges and solutions to develop a roadmap to improve global phosphorus sustainability. The Our Phosphorus Future report (currently in proof-reading) and online communications tools and related videos will be released in Autumn 2020. Aims of this initiative include to develop and communicate scientific evidence to support phosphorus stewardship, coordinate with stakeholders and engage with UN-Environment and global governance.
Sign the “Call for International Action on Phosphorus” here: www.opfglobal.com
ESPP member news
Kemira to market Vivimag P-recovery technology
The global chemicals company, Kemira, an ESPP Member, has acquired the technology patent of the Vivimag phosphorus recycling process, which has been developed by a consortium of partners including Wetsus, TU Delft, Outotec and EIT RawMaterials. The process (see ESPP eNews n°26) uses iron salts to precipitate phosphorus from sewage, as widely practiced today (chemical P-removal). Iron(III) phosphate then reduces to iron(II) phosphate in the anaerobic conditions of sludge digesters. The iron(II) phosphate, vivianite, is non-soluble and paramagnetic, so can be separated and recovered using magnetic separators. The vivianite can then be separated into phosphorus using alkali (pH 12), for recycling to industrial or fertiliser applications, and iron, which can be recycled back for use in sewage phosphorus removal.
Kemira press release 22nd July 2020.
Nordrhein-Westfalen P-recycling plans
The German Phosphorus Platform, DPP, is a partner in a project with the Nordrhein-Westfalen (NRW) Land of Germany to define how phosphorus will be recovered from sewage and recycled, as required by the German Sewage Sludge Ordinance (AbfKlärV, 27th September 2017). The project will prepare summary documents presenting around ten different processes for P-recovery from sewage sludge incineration ash. It will also analyse legal questions concerning the Ordinance obligations, in particular concerning the possibility of co-incineration of sewage sludge with other phosphorus-containing wastes followed by P-recovery from the resulting ashes, and also concerning P-recovery from imported sewage sludge. Power plant operators are looking at the possibility to incinerate sewage sludge with low-ash coal, then to recover phosphorus from the resulting combined ash. Currently, 90% of sewage sludge in the NRW Land is incinerated, with the remainder valorised to farmland. Agricultural use is expected to decrease, even though it remains legally possible under the Ordinance (depending on the sewage works size and sludge P content), because of tightening pressure on agricultural spreading due to implementation of the Nitrates Directive nutrient application limits (German manure ordinance Düngeverordnung DüV of 26th May 2017).Sewage sludge incineration capacity is expected to therefore be increased, and throughput to be increased by drying of sludge.
“Phosphorrückgewinnung in NRW” https://www.deutsche-phosphor-plattform.de/project/phosphorrueckgewinnung-in-nrw/
Wheatsheaf Group acquires Ostara
Wheatsheaf Group, the food and agriculture investment arm of the UK-based Grosvenor Estate, has acquired the world leader in struvite production technology for phosphorus recycling, Ostara (ESPP member). Wheatsheaf states as its objectives “a more holistic approach to improve yields, soil and nutrient efficiency and reduce waste … Food production cycles must be improved at every stage and … must be commercially viable” and places the Ostara acquisition in a “far-sighted perspective to deliver lasting commercial, social and environmental benefit”. It is indicated that the acquisition will support Ostara’s growing international operations and accelerate development of Ostara’s phosphorus recycling technologies( Pearl® nutrient recovery and Crystal Green® struvite fertiliser) by enabling strategic investment and access to expertise in Wheatsheaf food and agriculture portfolio companies. Monty Bayer, Executive Director of Wheatsheaf Group, said: “Ostara is a business of outstanding potential which is naturally positioned to offer solutions with significant end-user and environmental benefits in both the water management and crop nutrition environments”.
Press release 7th July 2020.
Research and projects
Phosphorus governance and regulation
A paper from the University of Rostock, Germany, analyses links between phosphorus governance and legislation in Europe, in particular the EU Common Agricultural Policy CAP (both as existing, and the Commission 2018 proposals for CAP revision, currently under discussion), soil and water law. The authors note that proposals in the CAP revision, if adopted, could significantly contribute to improving nutrient management and reducing nutrient losses, in particular the proposed FaST (Farm Sustainability Tool for Nutrients) and references to Water Framework Directive requirements to control diffuse phosphorus losses, but they not that this may depend considerably on Member State implementation and funding allocation. The authors underline the importance of the EU Nitrates and Water Framework Directives, both of which should prevent losses of nutrients from agriculture leading to eutrophication of surface waters or nitrate contamination of groundwaters, but underline that water quality is not achieving quality objectives in many countries and compliance with these Directives is widely failing. The authors recognise the importance of the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation and of circular economy policy in facilitating phosphorus recycling, and underline that this needs also to be brought into Organic Farming regulations. Recommendations to address regulatory failures include developing EU soil conservation legislation, introducing a mandatory link between arable land and livestock production and economic tools, such as “cap and trade” (e.g. emissions trading systems).
“Sustainable phosphorus management in European agricultural and environmental law”, B. Garske, J. Stubenrauch, F. Ekardt, University of Rostock, RECIEL. 2020; 29:107–117. https://doi.org/10.1111/reel.12318
P-recovery from lake Sediment
In Lake Kymijärvi, Finland, phosphorus recovery is tested from hypolimnetic water (that is, just above the surface of the lake bed sediments). The aim is to restore the eutrophied lake, by harvesting P naturally released from anoxic sediments, and to recycle this phosphorus. Water from the bottom of the lake is pumped through a filter then a wetland to remove suspended solids and nutrients. A 30 m3 pilot filter system has been operated intermittently during the summers of 2018 and 2019 with different filter media. Sand and calcium carbonate both achieved >70% total P removal following oxygenation of inflowing water and precipitation of iron oxide bound P. Addition of quicklime (Ca(OH)) further improves retention by stimulating calcium phosphate precipitation. The resulting calcium phosphate could be recycled to land as a fertiliser, but heavy metals from the sediments, also trapped in the filter, may be an obstacle. A paper by the same authors at the University of Helsinki, looking at nearby Lake Vesijärvi, Finland, shows that phosphorus accumulated in sediments from inadequately treated sewage in the past is being released from deep sediment layers, due to mineralisation of organic matter and dissolution of iron – manganese oxides. The released phosphorus diffuses upwards through the sediment and into the lake water, with a flux comparable to current total P inflows to the lake. This could retard lake restoration to good water quality by decades. The work demonstrates the need for long term restoration strategies aimed at reducing lake water P concentrations.
“A new application of hypolimnetic withdrawal and treatment for lake restoration and nutrient recycling”, S. Silvonen et al., Conference: Symposium for European Freshwater Sciences 11, June 2019
"Impacts of a deep reactive layer on sedimentary phosphorus dynamics in a boreal lake recovering from eutrophication”, T. Jilbert et al., Hydrobiologia 2020
Fish bones as an Organic Farming fertiliser
The RESTOR project, Norway, has tested fish bones and algae fibres as fertilisers or Organic Agriculture. The fish bones came from a fish processing factory (mainly cod Gadus morhua and saithe Pollachius virens), after removal of fish oil and soluble proteins which go to aquaculture feed, ground and conserved in formic acid (resulting in hydrolysis). This is a waste material currently usually incinerated. The algae fibres were residuals after liquid fertiliser extraction from knotted wrack Ascophyllum nodosum seaweed (harvested from natural growth on the Norway coast). The fish bones are rich in N (mainly in ammonium form), P and Ca. The algae fibres contain K, Mg and S. The fish bones showed good fertiliser effectiveness, for both N and P, for leeks, oats and rye grass, in various pot and field tests, with yields up to +75% higher than for control (no fertiliser) and with the nutrients showing rapid plant availability. The algae fibres showed less first-season fertiliser effectiveness, and in some cases negative effects, but positive effects the year after application.
NORSOK project “Marine rest raw materials for fertilizers to organic agriculture (RESTOR)” and summary of results in “Harvesting our fertilisers from the sea – an approach to close the nutrient gaps in organic farming”, A-K Løes et al., OWC 2020 Paper Submission 2020.
Nitrogen emissions from livestock production
A study by authors from FAO, EU JRC, The World Bank and several R&D institutes shows that livestock production emits some 65 million tonnes of nitrogen per year to the environment, of which nearly half (29 MtN/y) to surface and ground waters and the remainder to the atmosphere (mainly ammonia 26 MtN/y, plus NOx and N2O). This is around 40% of anthropogenic nitrogen emissions to water, and 60% of ammonia emissions to air. Nearly all these emissions come from animal feed and fodder production and from manure management. Ruminants (mainly cattle, for beef and dairy) account for 70% of total emissions. The study identifies possible key areas for action, including: improving fertiliser management in Asia and North America (to make better use of manure), moving away from concentration of livestock production and geographical separation from fodder crop production in Europe, North America and Asia (again to enable better recycling of manure). However, it also concludes that reductions in livestock consumption and production will be necessary in parts of the world, in order to respect planetary boundaries for nitrogen, noting that this should be targeted to maintain diversified livestock production where it is integrated into nutrition and food systems.
“Nitrogen emissions along global livestock supply chains”, A. Uwizeye et al., Nature Food 1, pp. 437–446 (2020)
Events
IWA nutrient recovery conference
The IWA Nutrient Removal and Recovery (NRR) virtual conference www.iwa-nrr.org online 1-3 September 2020, registration (early bird to end July) 63 – 273 €. Organised by Aalto University, Helsinki Region Environmental Services HSY and the IWA Nutrient Removal and Recovery Specialist Group. Will address removal and recovery of phosphorus, nitrogen, carbon in municipal wastewater, groundwater, natural waters, pulp and paper sector and others. The previous IWA-NRR conference was in Brisbane, Australia, in 2018
VDI Conference on sewage sludge treatment
The annual VDI (German Association of Engineers) conference on sewage sludge, 16-17 September 2020, Hamburg, Germany (VDI-Fachkonferenz Klärschlammbehandlung), will look at implementation of the German phosphorus recycling ordonnance, in particular possibilities for sludge incineration in either smaller or large centralised installations, and routes for recovery of phosphorus, nitrogen and other materials from sewage. The Conference includes a site visit to Hamburg’s sewage sludge mono-incineration plant on 15th September Conference in German.
www.vdi-wissensforum.de/06KO006020
Phosphorus chemistry webinar series
A bi-weekly series of scientific webinars on phosphorus chemistry is running from May into August, with 20 or 40 minute presentations from phosphorus chemistry scientists or young researchers, followed by discussion. Subjects already scheduled include phosphorus-carbonyl chemistry, phosphorus heterocycles, synthesis of phosphiranes, phosphorus redox catalysis, phosphaborenes, black phosphorus …
The P-Chemistry Webinar series is moderated by Christian Hering-Junghans (LIKAT, Rostock) and supported by AG P-Chemie" (phosphorus interest group) of the GdCh (Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker - Society of German Chemists). Schedule of webinars here:
https://phosphorus-chemistry.weebly.com/schedule.html
ESPP members

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews045
Download as PDF
Events
Webinar on phosphorus and iron in wastewater, agriculture, recycling
IWA nutrient recovery conference
VDI Conference on sewage sludge treatment
Phosphorus chemistry webinar series
Covid
Coordinated sampling of sewers
Consultations
EU consultation open on sewage sludge
ESPP input on calls for Farm-to-Fork and Circular Economy
ESPP comments on “by-products” in EU fertilisers regulation (FPR)
ESPP new member
MonGOS circular economy for water and wastewater
Agriculture
Organic Farming: IFOAM and ESPP press for recycled phosphates
FAO Fertiliser Code implementation
Netherlands study on manure processing economic incentives
Nutrient recycling
ReCaPHOS: P recovery in sewage sludge incineration
Easymining – Hitachi Zosen potassium recovery
LCA of P-recovery vs. mineral P fertilisers
Reviews: nutrient recovery from organic materials
Research
Do global nutrient balances impact human health?
EEA: Europe’s nutrient footprints exceed safe boundaries
Replacing P4 is still “in its infancy”
ESPP members
Events
Webinar on phosphorus and iron in wastewater, agriculture, recycling
This online workshop, in three 1-2 hour sessions 13-14 July, 2020, will look at how iron salts used for phosphorus removal (in sewage treatment or in drainage ditches) impacts phosphorus recycling and fertiliser value of sewage biosolids. Session themes are: Iron phosphorus interactions in natural systems and in wastewater ; Iron and phosphorus crop availability ; Iron for P-removal from aquatic systems ; and P-recovery from iron-containing waste streams. Presentations/papers will be available to participants before the event and the three web sessions will concentrate on discussion and questions, completed by an online forum. Register now.
Programme and register: https://iron-phosphate.eventbrite.co.uk
IWA nutrient recovery conference
The IWA Nutrient Removal and Recovery (NRR) virtual conference www.iwa-nrr.org online 1-3 September 2020, registration (early bird to end July) 63 – 273 €. Organised by Aalto University, Helsinki Region Environmental Services HSY and the IWA Nutrient Removal and Recovery Specialist Group. Will address removal and recovery of phosphorus, nitrogen, carbon in municipal wastewater, groundwater, natural waters, pulp and paper sector and others. The previous IWA-NRR conference was in Brisbane, Australia, in 2018
VDI Conference on sewage sludge treatment
The annual VDI (German Association of Engineers) conference on sewage sludge, 16-17 September 2020, Hamburg, Germany (VDI-Fachkonferenz Klärschlammbehandlung), will look at implementation of the German phosphorus recycling ordonnance, in particular possibilities for sludge incineration in either smaller or large centralised installations, and routes for recovery of phosphorus, nitrogen and other materials from sewage. The Conference includes a site visit to Hamburg’s sewage sludge mono-incineration plant on 15th September Conference in German.
www.vdi-wissensforum.de/06KO006020
Phosphorus chemistry webinar series
A bi-weekly series of scientific webinars on phosphorus chemistry is running from May into August, with 20 or 40 minute presentations from phosphorus chemistry scientists or young researchers, followed by discussion. Subjects already scheduled include phosphorus-carbonyl chemistry, phosphorus heterocycles, synthesis of phosphiranes, phosphorus redox catalysis, phosphaborenes, black phosphorus …
The P-Chemistry Webinar series is moderated by Christian Hering-Junghans (LIKAT, Rostock) and supported by AG P-Chemie" (phosphorus interest group) of the GdCh (Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker - Society of German Chemists). Schedule of webinars here:
https://phosphorus-chemistry.weebly.com/schedule.html
Covid
Coordinated sampling of sewers
The European Commission (JRC) is organising, with Eureau and Water Europe, a coordinated action across Europe to understand how Covid virus fragment monitoring in sewers can support public health information. Levels of Covid virus RNA in untreated sewage (inflow to sewage works) have been shown to reflect levels of public infection in several countries. Monitoring of sewage could maybe provide an early-warning system to identify new outbreaks of the virus. Sampling is being organised through an existing EU system at selected sewage plants. Data and methods will be coordinated to define a Covid monitoring system. Further partners wishing to join the exercise should contact rapidly JRC.
Contact:
Consultations
EU consultation open on sewage sludge
The European Commission has opened, to 25th August 2020, a public consultation on the ‘roadmap’ for re-evaluation of the EU Sewage Sludge Directive (86/278). This first consultation enables to input concerning the objectives of this re-evaluation, which will include a second, wide consultation on sewage sludge use in agriculture, announced for late 2020. The Commission’s proposed ‘Roadmap’ underlines that the Directive aims to encourage the use of sludge in agriculture, under safety conditions, and that nutrient recovery (citing phosphorus) should be a core objective, coherent with the EU Circular Economy Action Plan, Green Deal, Bioeconomy Strategy and Farm-to-Fork Strategy. The need to take into account “contaminants of emerging concern (e.g. organic chemicals such as pharmaceuticals, PAH and PFAS, cosmetics and microplastics)” is noted. This consultation enables to input to the definition of the Purpose and Scope of the sludge directive re-evaluation.
EU public consultation open to 25th August 2020 “Sewage sludge use in farming – evaluation” (Roadmap). Input can be as a simple text statement (max 4000 characters) and/or upload of a document.
ESPP input on calls for Farm-to-Fork and Circular Economy
ESPP submitted comments on two of the eleven proposed Horizon 2020 R&D calls to support the Green Deal. For the proposed “Farm-to-Fork” call, ESPP welcomed the specific references to phosphorus and nitrogen, suggesting to add reference to recycling of nutrients and to include in the call the need to assess economic and policy barriers to sustainability of food systems, including food pricing. For the proposed call on territorial demonstration of the Circular Economy, ESPP again welcomed the specific inclusion of recycled fertilisers and suggested to better make the link between local circularity and sustainable food systems. These calls are expected to be published in September 2020 with submission deadline January 2021.
European Green Deal Call
ESPP comments on “by-products” in EU fertilisers regulation (FPR)
ESPP submitted detailed comments to the JRC proposals for a “framework” for criteria for “by-products” in CMC11 of the EU Fertilising Products Regulation. These proposals are the first step towards defining “agronomic efficiency and safety” criteria for CMC11 “By-products” by July 2020 (art. 42.7). ESPP received and integrated input from several stakeholders. ESPP noted the importance of ensuring that the same material should have the same status across Europe (not be considered a “by-product” in one Member State but a waste in another), but also that the FPR should not generate new definitions of “by-products” parallel to waste legislation. ESPP questioned the proposed “positive list” approach, in that cataloguing all relevant by-products does not seem feasible, and would require traceability contradicting fact that by-products are placed on the market. ESPP underlined that a wide range of by-products may be used in small quantities as additives, to improve processing, handling or product characteristics: listing all of these does not seem realistic, and it would be appropriate to not limit use of non-hazardous additives used at very low concentrations.
RC report on “By-Products” under the FPR (CMC11) and ESPP submitted comments: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/regulatory
ESPP new member
MonGOS circular economy for water and wastewater
The objective of the MonGOS project is to develop a circular economy monitoring framework for the European water and sewage sector. The Circular Economy is an EU political priority and poses many challenges for this sector. MonGOS will identify and assess the potential for Circular Economy transformation in the water and sewage sector, exchange good practices and transfer knowledge between leading scientific institutions in Europe, develop a framework for monitoring transformation towards the Circular Economy in the water and sewage sector, disseminate research results internationally. One of the key areas of project is an identification of circular strategies for management of sewage sludge and sewage sludge ash, which are important source of phosphorus. Specific indicators for the recovery of phosphorus will be defined and proposed.
MonGOS (project “Monitoring of water and sewage management in the context of the implementation of circular economy objectives“ 2020-2022) is financed by the Polish National Agency for Academic Exchange (NAWA) under the International Academic Partnerships Programme. Website. Contact: Dr. Marzena Smol
Agriculture
Organic Farming: IFOAM and ESPP press for recycled phosphates
A joint letter, signed by IFOAM EU, the European umbrella organisation for organic food and farming, and by ESPP, has been sent to the European Commission requesting that struvite recovered from municipal wastewater and calcined phosphates be added to the “authorized fertilisers” annex of the EU Organic Farming Regulation 2018/848. The letter reminds that these two recycled phosphate materials were assessed by the official committee EGTOP (Expert Group for Technical Advice on Organic Production) recommending 2/2/2016 (see ESPP eNews) their authorisation for Organic Farming, under certain conditions, subject to their being authorised as EU fertilisers. This condition is now being resolved with their inclusion in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation with the STRUBIAS annexes (underway).
IFOAM EU – ESPP joint letter 17th June 2020 June 2020 http://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/regulatory
FAO Fertiliser Code implementation
Nearly 500 participants from 90 countries took part in a Global Soil Partnership (GSP) webinar on 19th May to discuss implementation of the FAO’s International Code of Conduct for the Sustainable Use and Management of Fertilizers. The Code was endorsed by the 41st FAO Conference in 2019. It provides a locally adaptable framework and set of practices for stakeholders involved with fertilisers, with the objective of improving nutrient management for sustainable agriculture and food security, by addressing overuse, underuse and misuse. FAO underlined the need for countries to have national plans to implement the Code, the importance of incentives and smart subsidies for sustainable nutrient management, covering both mineral fertilisers and organic nutrient materials such as manure or sewage biosolids. The webinar confirmed interest worldwide in national implementation of the Code.
Summary of the FAO – CSP webinar Fertiliser Code’s implementation, 19th May 2020
Netherlands study on manure processing economic incentives
A study by Wageningen UR for the Netherlands Agriculture Ministry concludes that nearly half of the nitrogen applied to farmland in the country (total 530 ktN) is as mineral fertilisers, that is around a quarter of this nitrogen could in theory be replaced by processing manure, but that costs are significant, and increase as a higher replacement target is fixed (more expensive processing becomes necessary). Only around 10% of phosphorus applied in The Netherlands is as mineral fertilisers, so the processing must enable separation of phosphorus into a form which can be exported. Replacing just 16% of The Netherlands’ mineral N consumption with processed manure is estimated to cost 360 million € (average = 4 300 €/tN note: this is not per tonne of manure). The report concludes that funding this by a levy on mineral fertilisers is not administratively feasible and that the increase in fertiliser price would be so high that it would lead to reduced agricultural productivity. The report proposes to subsidise manure processing. The report also notes that around 115 ktN of nitrogen is lost in emissions to the atmosphere from manure in The Netherlands (from a total of512 ktN in manure) and that some of this could be recovered and recycled as fertiliser by air stripping from manure storage or from stables, but that in many cases this requires significant modification of livestock farm installations.
“Vervanging kunstmest door dierlijke mest, Verkenning van opties voor de inzet van financiële instrumenten”, (Replacement of fertiliser by animal manure, exploring options for using financial instruments), T. de Koeijer et al., Wageningen Economic Research Rapport 2019-103 | Projectcode 2282200520, 2019 https://doi.org/10.18174/504407
Nutrient recycling
ReCaPHOS: P recovery in sewage sludge incineration
A 3-year Marie Curie Individual post-doc Fellowship at ZSW (Center for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research Baden-Württemberg), 2019-2022, ReCaPHOS ("Phosphorus extraction in the context of the high-temperature thermal treatment of sewage sludge") will develop phosphorus recovery integrated into fluidised bed sewage sludge incineration, considering both a new plant and retrofitting to an existing incinerator. The project will lead to design of a demonstration plant and estimation of economic potential. Calcium oxide (quicklime) will be used for phosphorus adsorption in the incineration process or from the outcoming ash, with heavy metal removal by thermal treatment.
ReCaPHOS information on Cordis and ZSW www.zsw-bw.de ZSW is a member of the German Phosphorus Platform DPP
Easymining – Hitachi Zosen potassium recovery
ESPP members EasyMining (Ragn-Sells group) and Hitachi Zosen Inova have together developed a new process, Ash2Salt, to recover potassium and other elements from municipal solid waste incineration fly-ash (ash separated out in incinerator exhaust gas filters). This fly ash can contain 10 – 40% w/w as salts (calcium, sodium, potassium chlorides) and an average around 2 - 3% potassium (K). This is recovered as high purity potassium chloride salt, appropriate for industry markets. Ammonium sulphate can also be recovered (from ammonia added to exhaust gases to prevent NOx emissions). The new plant under construction near Stockholm will have a capacity of 130 000 t/y of incinerator fly ash, sufficient to take the fly ash from Sweden’s current 15 municipal waste incinerators. Commissioning is planned for 2022.
“Ragn-Sells partners with Hitachi Zosen Inova for building circular fly ash plant”, 26th May 2020
LCA of P-recovery vs. mineral P fertilisers
A report published by UBA Germany compares the environmental footprint of phosphorus recovery from sewage, as required by the German Sludge Ordinance (2017), to mineral phosphate fertilisers. The LCA calculates c. 27 MJ/kgP (27 MJ/kg P2O5) as the average energy input for mineral phosphate fertiliser on the German market, of which more than half is related to sulphuric acid production (this figure will thus depend on “allocation” in that sulphuric acid is a by-product). The production of 1 kgN requires 4-5x this energy, and given that plants require nearly 7x nitrogen than phosphorus (Redfield ratio), the energy footprint of mineral fertilisers is principally for nitrogen not phosphorus. Energy requirements for P-recovery are identified as varying widely depending on the process. The report suggests that the environmental footprint of all fertilisers is principally in the use phase, that heavy metal content may have significant impact (will depend on levels in the fertiliser) and also phosphogypsum disposal (but this is not relevant if disposal has no environmental impact or if the phosphogypsum is valorised). The report notes that an important environmental question is to implement NOx mitigation for sewage sludge incinerators.
“Ökobilanzieller Vergleich der P-Rückgewinnung aus dem Abwasserstrom mit der Düngemittelproduktion aus Rohphosphaten unter Einbeziehung von Umweltfolgeschäden und deren Vermeidung” (LCA comparison of P-recovery from wastewater with fertilisers from mineral phosphates, including environmental damage and how to avoid it), F. Kraus et al., UBA-FB 002759 2019
Reviews: nutrient recovery from organic materials
A 470 page book from Ghent University, Belgium, presents different aspects of nutrient recovery from biomass and organic waste streams. Chapters written by over 100 hundred authors discuss nutrient flows and food systems, policy, nutrient recovery from manure, wastewater, food processing by-products and urine, ammonia stripping, struvite recovery, membrane filtration, mineral concentrates, pyrolysis, digestate drying and pelletisation, agricultural performance and soil behaviour of recovered fertilisers, energy intensity of recovery processes, modelling and optimisation.
Elsewhere, a review paper from China summarises biological nutrient removal and recovery from manures. The authors state that China alone generates 2 billion tonnes/year of livestock manures, considered to contain metals (copper, zinc, arsenic), pathogens and antibiotic pharmaceuticals. Processes considered include : composting, underlining the importance of process control and the interest of using co-substrates which improve bulking (aeration in composting) and increase the C/N ratio (improving composting and reducing ammonia losses and odour); anaerobic digestion and digestate processing; biological nitrogen removal; bio(electrical processes; micro-algae production to recover nutrients and provide biofuel feedstock; duckweed; macrophyte wetlands; cation adsorbent or ion-exchange systems. The authors see as perspectives: composting of solid fraction of digestate after anaerobic digestion processes (such as sodium hydroxide) to breakdown cellulose remaining in solid fraction of digestate, development of biological cultivation processes to reuse nutrients from manure (algae, plants, solider fly …) and hybrid processing combining several of these.
“Biorefinery of Inorganics: Recovering Mineral Nutrients from Biomass and Organic Waste”, E. Meers et al., 2020, €140-160 https://www.wiley.com/en-be/9781118921456
“Biological nutrient removal and recovery from solid and liquid livestock manure: Recent advance and perspective”, M. Zubair et al., Bioresource Technology 301 (2020) 122823 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122823
Research
Do global nutrient balances impact human health?
A paper by several environmental scientists states in its title that ratios between different elements (modified by human activities) “link environment change to human health”. This is misleading, because the paper’s intent is to explore ecological stoichiometry as a framework to understand how changes in biogeochemical cycles may impact health. The paper suggests that nitrogen fertiliser use may contribute to the prevalence and severity of infectious diseases, based on Townsend 2003, whereas this is a conceptual framework, not evidence. The paper suggests that human activities may lead to excess carbon availability in soil (ESPP comment: whereas most agronomists underline the need to restore soil organic carbon), leading to reduced N:C ratios in crops (no studies are cited linking this to human health), but the paper also suggests that increasing nitrogen may lead to increased N:C ratios in crops, suggesting possible links to changes in pests on cotton and in species diversity in natural areas (no link to human health). The paper points to decreasing environmental P:N ratios. Confusion seems to be made between nutrient balances and basic healthy diets: for example, Jacka 2017 is referenced under dietary stoichiometry and mental health, whereas in fact this study (of 67 persons only) suggests only that a generally healthy diet (fruit, vegetables, fibres, vitamins …) improved mental health and does not in fact mention elements. The paper was developed through Woodstoich 4, an event designed to expand the conceptual boundaries of ecological stoichiometry. ESPP recognises that the concept of ecological stoichiometry is interesting, and that human activities have significantly modified nutrient ratios in the environment, but regrets the use of a title which suggests that there is evidence of human health impact, when this is not the object of the paper.
“Elemental Ratios Link Environmental Change and Human Health”, R. Paseka et al., Frontiers in Ecology, vol. 7, art. 375, 2019 DOI.
EEA: Europe’s nutrient footprints exceed safe boundaries
A joint report by the European Environment Agency (EEA) and the Swiss Federal Office for the Environment (FOEN) finds that Europe’s footprints exceed safe limits (planetary boundaries) by a factor of 2x for phosphorus losses, 3.3x for nitrogen losses and 1.8x for and land use. Europe’s freshwater use does not exceed planetary boundary limits, but does suffer local and regional over-consumption and scarcity problems. The report considers different possible European shares of total planetary resources, not only on equity (per person) but also related to human needs, suggesting that Europe could have a 2.7% to 21% share (Europe has 8.1% of world population). The phosphorus footprint for Europe (corresponding to the biogeochemical flow of phosphorus) is in this report calculated as P release from agriculture plus P losses from urban waste water, that is c. 0.13 MtP/year (2011), using data from Exiobase. This is more than two times lower than the 2.9 MtP/y (2005) phosphorus losses from the European agrifood system calculated by Van Dijk et al. (see SCOPE Newsletter n°106 page 11) and would represent only 6% loss of phosphorus use in Europe (assuming Europe uses 10% of 17 – 24 MtP/y in worldwide phosphate rock production, see ESPP Factsheet), implying that 94% of P used annually is lost via other routes not taken into account, or is stored in landfill or soil, which seems unlikely. It is not clear whether the report methodology takes into account “exported” phosphorus footprint (e.g. phosphorus losses from agriculture in countries growing animal fodder crops imported into Europe to feed livestock). The report notes that the 2x exceedance of limits for Europe’s phosphorus footprint is the same as the global exceedance, whereas for nitrogen Europe’s footprint exceedance of 3.3x is twice the global exceedance of 1.7x.
“Is Europe living within the limits of our planet? An assessment of Europe's environmental footprints in relation to planetary boundaries”, Joint EEA/FOEN Report, EEA Report N° 01/2020, ISSN 1977-8449 https://www.eea.europa.eu/highlights/europes-environmental-footprints-exceed-several
Replacing P4 is still “in its infancy”
An overview of possible processes concludes that “the only industrially practicable way” to produce organophosphorus chemicals is today via P4 (white phosphorus). The reactive potential of P4 [+3 oxidation state, P(III)] is conserved in traded ‘vector’ chemicals such as PCl3 or PMIDA (phosphonomethyliminodiacetic acid) which can be used to produce organophosphorus chemicals for sectors such as fire safety, agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, lubricants, catalysts, metal extraction … However, P4 production requires a high-temperature reduction furnace and is very energy consuming, and there is no production today in Europe (P4 is on the EU Critical Raw Materials list). Other possible routes to organophosphorus chemicals from inorganic phosphates [+5 oxidation state, P(V)] have been tested at the lab scale: phosphate esters from phosphoric acid by phosphorylation of alcohols; reduction of trimetaphosphate by trichlorosilane (but this is currently produced from silicon, itself from a reducing furnace, so with similar energy costs to P4); PCl3 from calcium phosphate by hydrogen chloride. Another route could be recycling of industrial chemicals already containing reactive phosphorus, such as electrolytes from lithium ion batteries. In nature, inorganic phosphate is biologically converted to organophosphorus chemicals (e.g. ATP, natural phosphonates …) via the starting molecule PEP. At present, PEP can be produced via P4, but could possible be produced using enzymes. The authors also suggest that P4 could possibly be produced by electrochemical reduction, analogous to an experimental route for silicon production.
“Let’s Make White Phosphorus Obsolete”, M. Geeson & C. Cummins, ACS Central Science 2020 https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.0c00332
ESPP members
Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews044
Download as PDF
Events
Webinar on iron phosphate chemistry applied to phosphorus stewardship
Environmental efficiency of wastewater treatment plant configurations
Postponement ESPC4 and PERM 31st May – 2nd June 2021
Rescheduling ... RAMIRAN 2020, Systemic, ESNI
Consultations for your input
Urgent: Consultation open on R&D to support the Green Deal
Urgent: Input requested for by-products in EU Fertilising Products Regulation
ESPP, SuMaNu, Water Europe input on Circular Economy Action Plan
Input your ideas for a European nutrient strategy
EU Farm to Fork Strategy
EU Integrated Nutrient Management Action Plan
Industry news
Prayon acquires Ecophos process technology
Research and demonstration
FERTIMANURE now online
WATER MINING P-recovery from iron
REPARES project launched: antibiotic resistance
NITROMAN
Polyphosphate biology and methane
ESPP members
Events
Webinar on iron phosphate chemistry applied to phosphorus stewardship
This workshop remains fixed 13-14 July, 2020, but the schedule and event design is completely revised for webinar. Presentations/papers will be available to participants before the event and the three web sessions will concentrate on discussion and questions, completed by an online forum. Themes are: Iron phosphorus interactions in natural systems and in wastewater, iron and phosphorus crop availability, iron for P-removal from aquatic systems and P-recovery from iron-containing waste streams. Register now: limited to 100 participants.
Programme and register: https://www.eventbrite.co.uk/e/iron-phosphate-chemistry-applied-to-phosphorus-stewardship-and-p-recovery-tickets-96759011809
Environmental efficiency of wastewater treatment plant configurations
Kemira webinar, 16th June 14h00 CET. Presentation and discussion of a new study by IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute comparing three different wastewater treatment plant configurations: pre-precipitation, simultaneous precipitation, and biological phosphorus removal. Differences in environmental efficiency in terms of carbon footprint, energy balance, impacts of stricter effluent limits.
Kemira and members of INCOPA (European Inorganic Coagulants Producers Association) have contributed to this study. Link for registration or to receive the webinar recording afterwards: REGISTER
Postponement ESPC4 and PERM to 31st May – 2nd June 2021
Given the development of the international corona virus situation, and after re-discussion with the venue hotel and the Belvedere Palace, Vienna, we have decided to postpone ESPC4 and PERM (4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference and European Phosphorus Research Meeting) from June 2020 to Vienna 31st May – 2nd June 2021 https://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
Rescheduling ... RAMIRAN 2020, Systemic, ESNI
The manure and organic resources recycling conference, RAMIRAN, is rescheduled (provisionally) to 20-23 September 2021, Cambridge, UK.The SYSTEMIC workshop on nutrient recovery from anaerobic digestion and ESNI (European Sustainable Nutrient Initiative) are rescheduled to 26 – 27 October 2020, Brussels
Ramiran: www.ramiran2020.org
ESNI and SYSTEMIC workshop on Eventbrite
Consultations for your input
Urgent: Consultation open on R&D to support the Green Deal
EU Green Deal Call consultation, open to 3rd June https://ec.europa.eu/info/research-and-innovation/strategy/european-green-deal/call_en
Urgent: Input requested for by-products in EU Fertilising Products Regulation
“Technical proposals for by-products as component materials for EU Fertilising Products. Background document.” European Commission JRC, 24th April 2020 (42 pages) available here. Comments to by latest 4th June.
ESPP, SuMaNu, Water Europe input on Circular Economy Action Plan
European Committee of Regions Stakeholder Consultation "New Circular Economy Action Plan" https://cor.europa.eu/en/events/Pages/New- Circular-Economy-Action-Plan.aspx
Input your ideas for a European nutrient strategy
Document online – send us your input by 30th June 2020 http://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/regulatory
EU Farm to Fork Strategy
EU Integrated Nutrient Management Action Plan
EU Farm-to-Fork Strategy, COM(2020)381, 20th May 2020
Industry news
Prayon acquires Ecophos process technology
Prayon press release 6th May 2020.
Research and demonstration
FERTIMANURE now online
FERTIMANURE (Horizon 2020) https://www.fertimanure.eu/en/the-project-s-response
WATER MINING P-recovery from iron
* To our understanding, the Everglades Foundation George Barley Prize never delivered the 10 million dollar “prize” promised, because the conditions fixed by the organisers for building the demonstration plant for the final stage of the prize were refused because unrealistic by all candidates concerned. The prize website is no longer online
Water Mining is led by Delft Technical University.
ESPP webinar on iron phosphate chemistry, 13-14 July 2020, register here.
REPARES project launched: antibiotic resistance
REPARES: http://repares.vscht.cz/
NITROMAN
NITROMAN https://www.vcm-mestverwerking.be/en/faq/21214/nitroman and https://www.facebook.com/NITROMANproject
Polyphosphate biology and methane
“The potential for polyphosphate metabolism in Archaea and anaerobic polyphosphate formation in Methanosarcina mazei”, F. Paula et al., Nature Scientific Reports (2019) 9:17101
ESPP Members

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Events
Workshop on iron phosphate chemistry applied to phosphorus stewardship
Postponement ESPC4 and PERM à 31st May – 2nd June 2021
Rescheduling … RAMIRAN 2020, Systemic, ESNI
Covid 19
French safety agency opinion on Covid risk in sewage sludge
FAO expert group: coming months critical for global food supply
Public consultation and calls
Integrated Nutrient Management Action Plan
Call for input: Nutrient technologies and climate change
2020 BBI JU call for proposals open
New ESPP member
Prosumer feasibility study of P-recovery in Italy
Communications
BBC features phosphorus recovery
Two new books on phosphorus
Atmospheric phosphorus deposition
Nutrient inputs to the Mediterranean
Global P flows from atmospheric deposition
ESPP members
Events
Workshop on iron phosphate chemistry applied to phosphorus stewardship
This workshop remains fixed 13-14 July, 2020 either with a physical meeting in Utrecht, the Netherlands, or by webinar (in which case the programme will be organised differently). So: save the date! Themes will cover: Iron phosphorus interactions in sediments, in soils and engineered systems, Strategies for phosphorus release and P-recovery from iron phosphates, Iron - phosphate interactions in agriculture and Markets for recovered iron phosphate materials.
Contact: Registration: here.
Postponement ESPC4 and PERM 31st May – 2nd June 2021
Given the development of the international corona virus situation, and after re-discussion with the venue hotel and the Belvedere Palace, Vienna, we have decided to postpone ESPC4 and PERM (4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference and European Phosphorus Research Meeting) from June 2020 to Vienna 31st May – 2nd June 2021
https://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
Rescheduling … RAMIRAN 2020, Systemic, ESNI
The manure and organic resources recycling conference, RAMIRAN, is rescheduled (provisionally) to 20-23 September 2021, Cambridge, UK.
The SYSTEMIC workshop on nutrient recovery from anaerobic digestion and ESNI (European Sustainable Nutrient Initiative) are rescheduled to 26 – 27 October 2020, Brussels
Ramiran: www.ramiran2020.org
ESNI and SYSTEMIC workshop on Eventbrite
Covid 19
French safety agency opinion on Covid risk in sewage sludge
ANSES, the French national agency for health, food and environment safety, has issued an opinion on the risks of Covid19 in sewage sludge. This confirms the WHO statement that there is no evidence of survival of viable (infectious) Covid19 in sewage. ANSES concludes that systems already considered as ensuring sanitisation of sewage sludge under current regulations will largely remove possible Covid risk. 70% of France’s sewage sludge is used in agriculture, and this is mostly sanitised before spreading. ANSES recommends that monitoring of this sanitisation be reinforced. A small amount of sludge from smaller sewage works is currently spread without sanitisation. ANSES recommends that this sludge be incinerated or treated during the Covid pandemic.
ANSES Opinion 27th March 2020
FAO expert group: coming months critical for global food supply
The FAO CWFS (Committee on World Food Security) High Level Panel of Experts has issues a preliminary paper on possible impacts of Covid-19 on food security and nutrition. The Committee expects that the most affected will be the poor and vulnerable, especially migrants, conflict regions. Impacts will be from disruption of food processing and distribution chains, from the expected world economic slowdown and resulting unemployment, and in the medium term from losses in production if farmers to not have access to inputs for this Spring (Northern hemisphere) planting season. Another problem worldwide is workforce shortages on farms because of restrictions to workers’ movements. The experts note that although there are no significant issues with food supply at present, disruption of transport systems and workforces in coming months will be critical for future food supply because this is when most of the world’s food production takes place.
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations), 24th March 2020: “Interim Issues Paper on the Impact of COVID-19 on Food Security and Nutrition (FSN) by the High-Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and nutrition (HLPE)” paper,
Public consultation and calls
Integrated Nutrient Management Action Plan
The EU Committee of Regions (CoR) has opened a public stakeholder consultation to 1st May on input to the new EU Circular Economy Action Plan. This Plan includes as proposed actions to “develop an Integrated Nutrient Management Plan with a view to ensuring more sustainable application of nutrients and stimulating the markets for recovered nutrients”. ESPP will input to this CoR consultation underlining our support for this proposed Integrated Nutrient Management Plan and the interest to link to the proposal in Horizon Europe Orientations Orientations to develop “comprehensive EU policy to balance nutrient cycles … move to living within the planetary boundaries, with regards to nutrient flows”. ESPP will underline in particular the need to work with the food & beverage industry to address dietary choices, the key driver for nutrient use, to support agricultural nutrient stewardship and nutrient recycling, including with fiscal and market tools and with nutrient recycling demonstration sites, and to address contaminants in secondary nutrient flows (sewage sludge, manure).
EU Assembly of Regional and Local Representatives, Written Stakeholder Consultation "New Circular Economy Action Plan" consultation open to 1st May 2020
Call for input: Nutrient technologies and climate change
ESPP (European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform) and SPA (Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance, America) are preparing several special issues of SCOPE Newsletter relating eutrophication, nutrient management and climate change. Circulation: 41000 emails worldwide, detected openings 11 – 14%. Issues will cover: eutrophication and methane emissions, climate change impacts on nutrient runoff, climate change and diet nutrition, and links between nutrient technologies and climate change.
We will include a selection of texts showing how products or technologies for nutrient recycling or eutrophication abatement can reduce greenhouse gas emissions or contribute to climate change mitigation. For example:
- greenhouse gas LCA analysis of nutrient recycling process
- technologies to mitigate impacts of nutrients and climate change on eutrophication
- addressing greenhouse gas emissions of fertiliser production
- reducing climate change impacts of nutrient use and management in agriculture
To include your technology, send us a text, by 15th May latest to
- Preference will be given to texts supported by data and/or references
- Links must be made to climate change
- Maximum 400 words plus 1-2 photos
- photos must be free of rights for web publication
- selection of texts by ESPP and SPA is final. We may propose to you to revise your text.
2020 BBI JU call for proposals open
The 2020 Bio-Based Industries Joint Undertaking call for proposals is open until 3 September. The call constitutes €102 million worth of funding for projects focusing on the upgrading and valorisation of biomass. The budget is divided between five Research and Innovation Actions (RIA), seven Innovation Actions (split between Demonstration Actions (DEMO) and Flagship Actions (FLAG)) and four Coordination and Support Actions (CSA), including €15 dedicated to FLAG projects under the topic of valorisation of organic fraction municipal solids waste through integrated biorefineries at commercial level.
https://www.bbi-europe.eu/news/over-%E2%82%AC100-million-available-advancing-european-bio-based-sector
New ESPP member
Prosumer feasibility study of P-recovery in Italy
Wastes from slaughterhouses and food processing industries are the third ‘waste stream’ containing phosphorus (P) in Europe, offering potential to recover and recycle phosphorus to fertilisers. Italy and particularly Emilia-Romagna Region have thousands of companies in this sector. The Prosumer project will assess and develop business models for the techno-economic feasibility of P recovery from waste streams in the Italian agri-food sector and its reuse in fertilizers. The project is coordinated by the University of Bologna with the support of Marche Polytechnic University and involves Italian companies in the agri-food sector (Pizzoli, Granarolo, Caviro Extra) and in fertiliser production (Puccioni) who will provide data for the model. The expected results, fitting with several ESPP objectives, include to (i) increase awareness about phosphorus and disseminate information; (ii) evaluate business risks and opportunities (iii) deliver decision support tools for financial instruments and regulatory framework.
Prosumer project: Techno-economic and environmental feasibility study of Phosphorus recovery and reuse in fertilizers applied to Italian Prosumers (producers and consumers of P). funded by EIT Climate-KIC (project n. 200103, 2020). Contact: Jessica Rossi
Communications
BBC features phosphorus recovery
BBC’s “People Fixing the World” has featured Ostara, recovering phosphorus as struvite, and SNB, incinerating sewage sludge and looking to recover phosphorus. A 3 minute BBC video provides an excellent summary of why phosphorus is important, and how struvite is recovered by Ostara at Amersfoort, The Netherlands, to produce a high quality fertiliser adapted to plant needs (non water soluble, so low leaching). SNB explain that sewage sludge ash is recycled in construction, but that they hope to develop P-recovery upstream of this end-use. A 30 minute podcast explains the importance of phosphorus, from its discovery to today, its different uses of phosphorus, the impacts of phosphorus losses and the need to develop the circular economy for phosphorus.
BBC News video, “People fixing the planet”, 3 minutes, 30th March 2020 and BBC World Service podcast, 30 minutes (sound), “The treasure in our toilet”, interviews of Robert Van Springelen, Ostara, and Silvester Bombeeck, SNB. Summary here.
Two new books on phosphorus
A 150 page new book by Alexandra Drizo presents an update of approaches and technologies for phosphorus removal and recovery, covering phosphorus management in sewage, agriculture and in lakes, including summaries of regulation for phosphorus removal and recovery The book covers: the challenges of eutrophication are summarised, water quality legislation, regulation of innovative phosphorus removal technologies and of phosphorus recycling, methods and technologies for removal of phosphorus from sewage, actions for mitigation of agricultural and stormwater phosphorus runoff, in-lake phosphorus treatment and phosphorus recovery and recycling technologies.
A 460 page book edited by Alan Steinman and Bryan Spears, with 24 chapters and 17 case studies, by over 60 experts worldwide, looks at “internal loading” of phosphorus to lakes and coastal lagoons, that is release of phosphorus from bottom sediments. It is feared that climate change will increase sediment P releases, because warming may lead to longer periods of stratification (periods where deep and shallow water layers do not mix) resulting in anoxia (no oxygen) conditions in sediments, and to increased decomposition of organic matter in sediments. The book analyses drivers of sediment phosphorus release and uptake, measurement techniques, management approaches including in-lake treatment techniques.
“Phosphorus Pollution Control: Policies and Strategies”, A. Drizo, 2020, ISBN: 978-1-118-82548-8
“Internal Phosphorus Loading in Lakes. Causes, Case Studies, and Management”, A. Steinman & B. Spears, January 2020, ISBN 978-1-60427-144-7
Atmospheric phosphorus deposition
Nutrient inputs to the Mediterranean
Malagó et al. have estimated total nutrient inputs to the Mediterranean at 1 900 ktN-total/year and 100 ktP-total/year phosphorus, based on modelling nutrient inputs from diffuse sources (i.e. mineral fertilisers and manure) and point sources (i.e. human settlements connected to sewers and industrial discharge). They used readily available global data and determined the relative importance of different sources identifying hotspot areas of higher pollution. The main contributor to nitrogen is agriculture, whereas for phosphorus the biggest sources are wastewater, soil erosion, and agriculture. However, the main source for soluble phosphorus (30 ktP-ortho/year) is wastewater.
Kanakidou et al. estimated, using modelling, atmospheric deposition to the Mediterranean at around 60 tP-soluble/year, (initial model result 4.3 ktP-soluble/year, multiplied by x14 for re-correlation), compared to 125 ktP-total/year from rivers and coastal cities. For nitrogen, these authors estimate atmospheric inputs at 1 281 ktN/y compared to around 1 360 ktN/y from rivers and cities, (for nitrogen, the model estimate corresponds approximately to other data without re-correlation).
In another paper, Violaki et al. estimate atmospheric deposition of soluble phosphorus (in rainwater and in dry deposition), based on sampling at two sites for 2 – 7 years. They conclude that total dissolved phosphorus from deposition, based on the sites with the higher results, is up to 2.2 mmolP/m2/year in the West Mediterranean and 1.5 mmolP/m2/year for the East that is c.140 ktP-soluble/year for the 2.5 million km2 of the whole Mediterranean. This is coherent with Koçak 2010 who estimated that, for the Eastern Mediterranean (Turkish coast), soluble phosphorus and soluble nitrogen DIN inputs were dominated by atmospheric deposition, whereas silicon input was dominate by river inflows.
Violaki et al. estimate that the atmospheric deposition might cause up to 7% of algal production in the North West Mediterranean, and up to 38% in oligotrophic areas of the East Mediterranean during stratified periods. Thus, the atmospheric P deposition may make some contribution to CO2 uptake at times the Mediterranean.
“Modelling nutrient fluxes into the Mediterranean Sea”, A. Malagó et al., Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies 22 (2019) 100592, DOI
“Organic phosphorus in atmospheric deposition over the Mediterranean Sea: An important missing piece of the phosphorus cycle” ,K; Violaki et al., Progress in Oceanography 163 (2018) 50–58, DOI
“Atmospheric inputs of nutrients to the Mediterranean Sea”, M. Kanakidou, et al., Deep-Sea Research Part II 171 (2020) 104606
“Atmospheric nutrient inputs to the northern levantine basin from a long-term observation: sources and comparison with riverine inputs”, M. Koçak et al., Biogeosciences, 7, 4037–4050, 2010 DOI
“Modeling the impacts of atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and desert dust–derived phosphorus on nutrients and biological budgets of the Mediterranean Sea”, C. Richon et al., 2017 Prog. Oceanogr Volume 163, April 2018, Pages 21-39
Global P flows from atmospheric deposition
For comparison to the above studies for the Mediterranean, Tipping (CEH UK) et al, 2014, collated data on atmospheric phosphorus deposition at c. 250 sites worldwide (with a recognised bias of >80% of sites in Europe and North America). They found a geometric mean deposition of 0.14 gTP/m2/year (total phosphorus), of which around 40% on average is soluble P and a further 20% is non filterable P (with significant variations between sites), that is around 60% of TP deposition is relatively available. This corresponds to a total global atmospheric deposition of around 3.7 MtP/y. For comparison: annual world beneficiated phosphate rock production is 17 – 24 MtP/y (see: ESPP Factsheet). Most of this atmospheric deposition is considered to come from natural sources, in particular dusts, especially from the Sahara, and also from pollen and other biogenic organic materials. Anthropogenic sources include burning of fossil fuels. Data showed considerable variation between sites, and at sites between years. The authors note that atmospheric deposition from fertiliser application can be significant locally, and may impact sensitive ecosystems near farmland, noting that this question requires further research, whereas long-range transport, which is important for oceans, is mainly from dust.
“Atmospheric deposition of phosphorus to land and freshwater”, E. Tippng et al., Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts, 2014, 16, 1608
ESPP members

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews042
Download as PDF
ESPP is making a comeback on social media. After a year of minimum activity, ESPP is now reactivating the presence
on Twitter https://twitter.com/phosphorusfacts. We are also launching a new LinkedIn page https://www.linkedin.com/company/european-sustainable-phorphorus-platform/ Please follow us there.
The existing ESPP LinkedIn group https://www.linkedin.com/groups/4783093/ will be kept as a forum for the moment.
Looking forward to seeing you online.
Postponement ESPC4 and PERM -> 31st May - 2nd June 2021
Given the development of the international corona virus situation, and after re-discussion with the venue hotel and the Belvedere Palace, Vienna, we have decided to postpone ESPC4 and PERM (4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference and European Phosphorus Research Meeting) from June 2020 to Vienna 31st May - 2nd June 2021
Public consultations
EU Industrial Emissions Directive (BAT BREFs)
EU aquaculture policy
Events
Postponement ESPC4 and PERM -> 31st May – 2nd June 2021
Workshop on iron phosphate chemistry applied to phosphorus stewardship
RAMIRAN 2020, Systemic, ESNI
Corona virus
COVID and sewage
Fertiliser industries working to feed the world
Policy
EU new Circular Economy Action Plan
Global fertiliser industry “committed to reducing P losses”
Prosumer cross-KIC meeting on perspectives for P-recovery
Call for 80% cut in meat eating
Science and research
National and global phosphorus footprints
Lack of data on global phosphorus cycles
AshDec P-recovery process new test data
Baltic region nutrient flows and management perspectives
Lessons from Asia’s nutrient footprints
Insect frass showed to be a good fertiliser
Nitrification inhibitor improves P uptake and yield
UBA report on pharmaceuticals in recycled phosphates
Erratum
Public consultations
EU Industrial Emissions Directive (BAT BREFs)
A public consultation is open to 21st April on the “Inception Impact Assessment” for the EU Industrial Emissions Directive (IED), which defines Best Available Technology (BAT BREFs), which are legally applicable to all installations in concerned industrial sectors across Europe. The roadmap suggests widening the scope of the IED to include cattle farms, “mixed farms” and aquaculture. ESPP supports this, because it is coherent with the inclusion already today of large pig and poultry farms. ESPP welcomes a proposed accent on Circular Economy. ESPP also proposes to streamline the BREF process, which today generates documents hundreds of pages long. The BAT specifications, which are relatively short and are legally constraining, could continue to be defined by the formal consultation and adoption process, but the examples and innovation texts, which are illustrative, could be more informal and so more frequently updated.
EU public consultation on the inception impact assessment for the Industrial Emissions Directive. Deadline = 21st April 2020 https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12306-EU-rules-on-industrial-emissions-revision
EU aquaculture policy
A public consultation is open to 21st April on the Roadmap for “Updated Guidelines” for the EU aquaculture. ESPP welcomes the reference to the Green Deal and the Farm to Fork Strategy. ESPP will input underlining the importance of improving the nutrient efficiency of aquaculture feed, including use of local crops or by-products, better uptake of plant forms of phosphorus in fish (especially salmon) and nutrient footprints, making the link to the nutrient strategy proposed in Horizon Europe. ESPP also underlines the need to reduce nutrient losses from both offshore and fresh water aquaculture, and to develop nutrient recycling, including integrating fish manure into the EU Fertilising Products Regulation
EU public consultation on EU fish farms (aquaculture) – updated guidelines.. Deadline = 21st April 2020 https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/12261-Strategic-Guidelines-for-EU-aquaculture-update
Events
Postponement ESPC4 and PERM -> 31st May - 2nd June 2021
Given the development of the international corona virus situation, and after re-discussion with the venue hotel and the Belvedere Palace, Vienna, we have decided to postpone ESPC4 and PERM (4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference and European Phosphorus Research Meeting) from June 2020 to Vienna 31st May - 2nd June 2021
https://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
Workshop on iron phosphate chemistry applied to phosphorus stewardship
This workshop remains fixed 13-14 July, 2020 either with a physical meeting in Utrecht, the Netherlands, or by webinar (in which case the programme will be organised differently). So: save the date! Themes will cover: Iron phosphorus interactions in sediments, in soils and engineered systems, Strategies for phosphorus release and P-recovery from iron phosphates, Iron - phosphate interactions in agriculture and Markets for recovered iron phosphate materials.
Contact:
Registration: here.
RAMIRAN 2020, Systemic, ESNI
The manure and organic resources recycling conference, RAMIRAN, remains fixed 14-17 September 2020, Cambridge, UK. The SYSTEMIC workshop on nutrient recovery from anaerobic digestion and ESNI (European Sustainable Nutrient Initiative) are rescheduled to 26 – 27 October 2020, Brussels
Ramiran: www.ramiran2020.org
ESNI and SYSTEMIC workshop on Eventbrite
Corona virus
COVID and sewage
Researchers at KWR Netherlands have found gene fragments of the Covid-19 virus in wastewater entering a sewage works, with repeated tests confirming the results. The virus gene fragments were not detected in the sewage works effluent (treated water), but only one site was tested, and sewage sludge was not tested. Although the tests do not discriminate between potentially active virus and inactive fragments, it is underlined that the results do not indicate that Covid-19 infection is possible from sewage. Workers in contact with wastewater should in any case use protective equipment, because of other health and safety risks in handling wastewater, and the water industry underlines that this should be reinforced. The World Health Organisation briefing on Covid-19 in water and sewage (19th March) can be summarised as follows: there is no proof for this the Covid-19 virus, but it has a fragile outer membrane and is likely to be more rapidly inactivated in sewage than other viruses which have been shown to survive for days to weeks in water or sewage (e.g. gastroenteritis, hepatitis). A new paper in Nature (published 1/4/20) found high virus RNA concentrations in faeces of nine Covid-19 patients, but no infectious virus in faeces, in urine nor in blood. The study concludes that there were indications of viral replication in the gut and that the absence of detected viable virus in faeces may be because the nine patients were mild cases, and none had diarrhoea (which occurs in maybe 2% of Covid-19 cases).
KWR press release “What we learn about the Corona virus through waste water research“ 24th March 2020
KWR Webinar “COVID-19: Significance and impact of the pandemic for the water sector”
WHO “Water, sanitation, hygiene, and waste management for the COVID-19 virus, Interim guidance” 19th March 2020
“Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019”, R. Wölfel et al., Nature, 1 April 2020
Fertiliser industries working to feed the world
The fertilisers industry is committed to continue to supply farmers, in order to maintain the world food supply. Fertilizers Europe states its commitment to continuing to deliver nutrients to farmers, in the crucial spring period when fertilisers are needed. The industry thanks the European Commission for citing agricultural production inputs as goods for which continuation of flow should be ensured in border management. IFA (International Fertilizers Association) underlines that >40% of fertiliser production is traded internationally, so that continuing movement is essential to enable supply, and that without mineral fertilisers world food production would be cut by around half. Both federations underline the need to ensure safety of workers handling and transporting fertilisers through enhanced hygiene measures and personal protective equipment.
Policy
EU new Circular Economy Action Plan
The revised Circular Economy Action Plan published by the new Commission on 1st March includes “Food, water and nutrients” as one of the seven key targeted value chains. Actions indicated are to “develop an Integrated Nutrient Management Plan with a view to ensuring more sustainable application of nutrients and stimulating the markets for recovered nutrients”, reduce food waste, facilitate water reuse, possible review of the wastewater and sewage sludge directives (including assessing natural nutrient recovery e.g. by algae), continuing the Bioeconomy Action Plan, a policy framework on compostable, biodegradable and bio-based plastics (ESPP note: important for digestates and composts) and a number of actions to address microplastics and to better understand their risk and occurrence. The Plan indicates the need to improve monitoring of resource recycling, proposing a “market observatory for key secondary materials”, a “Monitoring Framework for the Circular Economy” and “Indicators on resource use, including consumption and material footprints”. The Plan also aims to better integrate the circular economy into Member States fiscal policies, via the European Semester and at the global level to define a “Safe Operating Space” for natural resource use.
COM(2020)98 “A new Circular Economy Action Plan” 11th March 2020
Global fertiliser industry “committed to reducing P losses”
A 3-minute video from the International Fertilizer Association (IFA) promotes the need for phosphorus fertilisers to feed the world, stating that 32% of the world’s cropland and 43% of the pastures are phosphorus deficient and that world phosphate rock resources represent 1 000 years of consumption. The video underlines that eutrophication is a major problem, caused by fertiliser losses and other phosphorus releases, and that it is likely to worsen with climate change. The fertiliser industry states that it is promoting better fertiliser management, indicating that fertiliser use efficiency can reach 90% and losses of fertiliser P to surface waters can be reduced to 3%. IFA states that it supports recycling where appropriate, and is “committed to reducing phosphorus losses”.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QwOR0PzZENk&t=
Prosumer cross-KIC meeting on perspectives for P-recovery
The web-meeting “Sustainable strategies towards a phosphorus circular economy: Cross-KIC web-meeting” (26th March, 2020), organized by the Department of Industrial Engineering of the University of Bologna, brought together some 40 participants from research, industry and high-education around two projects funded by the EIT (the EU’s European Institute of Innovation and Technology) KIC (Knowledge & Innovation Communities) ‘Climate’ and ‘Raw Materials’, respectively Prosumer and InPhos projects. Other projects relevant to phosphorus funded by these KIC’s include raPHOsafe and Phosforce. The web-meeting covered different disciplines of phosphorus management. The company Puccioni, fertiliser producer, indicated that the company is working on the industrial-scale use of recovered struvite from the wastewater of another Italian company, Pizzoli, a potato processing plant, as input to triple super phosphate production. Both companies are stakeholders of the Prosumer project. The technological provider, Outotec, summarised state of the art of phosphorus recovery. Marche Polytechnic University explained the European and Italian legislative framework and the technical features of recovered P for reuse in agriculture.
The webcam discussed agricultural valorisation of sewage sludge. In Italy, this can contribute to soil carbon in Southern Italy where this is critical. The proposed new Italy sludge management regulation, currently under consultation, would enable continuing agricultural use limited to high quality sludge (metal and organic contaminant limits, nutrient value) and would fix a priority of P-recovery if sludge could not achieve these criteria and define End-of-Waste for appropriate recovered P products.
The Italy Phosphorus Platform (ENEA, under the aegis of the Environment Ministry) presented survey results showing that stakeholders see the three biggest obstacles to nutrient recycling to be End-of-Waste regulatory problems, need for regulatory drivers for recovery and lack of knowledge.
In the Baltic region, the InPhos project, coordinated by the Mineral and Energy Economy Research Institute, has identified priority recommendations for a common and shared strategy for a more sustainable P management and for the reduction of eutrophication. Proman presented results of a quantification of nutrient flows in the Baltic Sea Region, as first step to clearly monitor the situation and define effective solutions.
After the presentation of University of Bologna, discussion among all attenders confirmed the value of R&I projects in demonstrating the technical feasibility and assessing the economics and business models for nutrient recovery, as these are essential to facilitate movement by policy makers and industry.
InPhos Prosumer webinar 26th March 2020
See below summaries of Prosumer project, and of Outotec (AshDec update) and Proman (Baltic nutrient management) presentations.
Call for 80% cut in meat eating
Greenpeace says Europe neds to reduce average meat consumption by 80% (by 2050) to achieve the UN +1.5°C limit to hope to prevent climate breakdown. This corresponds to the 300 g of meat per week (the equivalent of two burgers) recommended by The Lancet for a balanced sustainable diet (see ESPP eNews n°30). Greenpeace calls on the European Commission to include targets for reductions in meat consumption in its Farm to Fork Strategy, to be presented soon as part of the Green Deal. Mark Driscoll, food consultant at Tasting the Future, suggests that a massive reduction in meat consumption is indeed necessary (he suggests -50% by 2030) to reduce both environmental and health damage of our diets, but he underlines that locally produced, regeneratively farmed meat can have sustainability advantages.
Greenpeace “EU climate diet: 71% less meat by 2030” 13th March 2020
Science and research
National and global phosphorus footprints
A study estimates the “Phosphorus Exceedance Footprint” (PEF) for different countries, assessing their contribution to the transgression of global planetary boundaries for phosphorus, particularly looking at international trade. Around 30% of planetary boundary exceedance for phosphorus is shown to be linked to international trade flows. Wealthier countries tend to reduce their domestic fertiliser use whilst increasing import of products containing embedded phosphorus footprints. The highest PEF per capita identified is for New Zealand (nearly 19 kgP/capita/year), presumably related to high levels of meat production. The highest absolute PEF is China (3.3 kgP/capita/year, but total 4.5 million tonnes P/year, that is 44% of total world PEF), followed by India, the USA and Brazil. France imports around 100% of its PEF, presumably corresponding mainly to imported animal feed, whereas Brazil and New Zealand export around 100% of their DPE (domestic P exceedance), presumably corresponding to exports of meat products. The authors consider that this work will facilitate devilment of planetary boundary benchmarking for countries, public policies, diets and food products.
“Towards meaningful consumption-based planetary boundary indicators: The phosphorus exceedance footprint”, M. Li et al., Global Environmental Change 54 (2019) 227–238 DOI
Lack of data on global phosphorus cycles
The only relatively recent paper attempting to estimated global phosphorus flows shows the need for a coherent assessment, in order to have reliable data to support policy making. Chen & Graedel 2016 (estimating flows for 2013) suggest that from 69 MtP/year in mined phosphate rock, only 31 Mt end up in beneficiated, marketable rock. This is reasonably close to Steiner et al. 2015 (see ESPP’s SCOPE Newsletter n°128). However, Chen & Graedel suggest that the non processed phosphate rock (tailings) ends up as water pollution, whereas in most mines this will be returned to the mining site with not significantly more loss to water than the rock before mining. This leads the paper to conclude that over half of annual P losses to water worldwide are from mining. The authors also conclude that globally soils are losing nearly 11 MtP/year to water (that is nearly half the annual P used in mineral fertiliser). This contradicts other authors who estimate global soil P accumulation (the reference indicated is incorrect, but may refer to Bouwman 2009, see SCOPE Newsletter n°88). These differences confirm the need for an up-to-date assessment of global phosphorus flows.
“A half-century of global phosphorus flows, stocks, production, consumption, recycling, and environmental impacts”, M. Chen, T. Graedel, Global Environmental Change 36 (2016) 139–152. For other data see ESPP Phosphorus Fact Sheet
AshDec P-recovery process new test data
Tanja Schaaf presented 26th March 2020, at the InPhos Prosumer workshop (see above) an update on the AshDec process for phosphate recovery from sewage sludge incineration ash and other ashes. A 20-25 kg/h input ash pilot has been operated continuously for 7 day, testing different additives and different temperatures. The choice of additive (sodium carbonate or sulphate) and operation with excess or depleted oxygen impact heavy metal removal and phosphorus solubility (plant availability) in the final product. Sodium carbonate showed to give a product with >80% P-NAC (neutral ammonium citrate) solubility, even down to 850°C. Significant removal of lead, arsenic and cadmium was achieved, improving at higher temperatures (even though cadmium was already very low in the sewage sludge incineration ash used). Copper and zinc were not significantly removed. Pot trials with spinach, soybean and rye grass at Bonn University show fertiliser effectiveness comparable to triple super phosphate.
Summary presented at the InPhos Prosumer webinar 26th March 2020
Baltic region nutrient flows and management perspectives
A study by Proman for HELCOM (the intergovernmental Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission) has developed substance flow analyses for phosphorus and nitrogen and identifies potentials for reducing losses to the Sea and for developing recycling. To calculate losses, nutrient use efficiency (NUE) is estimated at 90% for mineral fertilisers and at 70% for N and 77% for P in organic fertilisers (based on references below). Nitrogen balance per hectare (input minus estimated offtake, in harvest and in crop residues removed from the field) is highest in Russia (Baltic catchment) and Denmark, and phosphorus balance also highest for Russia. The biggest opportunities for nutrient recovery are in manure (combined with anaerobic digestion) and in sewage (largely in the treatment phase for N and in sludge management for P). Nutrient recycling could represent 500 – 900 KtN/y in the Baltic region, potentially replacing 55 – 69% of mineral N fertiliser use, and 31 – 122 KtP/y, replacing 17 – 50% of mineral P fertiliser use. Improving fertiliser use efficiency remains on the largest opportunities for reducing nutrient losses.
Summary presented at the InPhos Prosumer webinar 26th March 2020
References for Nutrient Use Efficiency: Gutser et al., 2005, Short-term and residual availability of nitrogen after long-term application of organic fertilisers on arable land. J. Plant Nutr. Soil. Sci 168, 439-446. DOI: 10.1002/jpln.200520510. Hamilton et al., 2017, Recycling potential of secondary phosphorus resources as assessed by integrating substance flow analysis and plant-availability, Science of the Total Environment 575, 1546-1555. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.056. Syers et al., 2010, A new perspective on the efficiency of phosphorus fertiliser use, 19th World Congress of Soil Science, Soil Solutions for a Changing World. 01.08.2010 – 06.08.2010, Brisbane, AU. Published on DVD.
Lessons from Asia’s nutrient footprints
A study estimates changes in the per capita nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) footprints of China, India and Japan from 1961 to 2013, using a comparable framework. Calculations derive nutrient use efficiencies and nutrient recycling ratios, calculated for each nutrient, each country, and each year. The ratios are based on IFA data, FAO data and literatures on inputs in food production, manure use, food losses, etc. The number used for meat vary from, e.g. 28 kgP-released per kgP in food intake for Japan in the 1960’s (up to 41 in the 1980’s) compared to 7.4 for India in the 1960’s (up to 8.4 in the 2010’s). For vegetables, the ratios are 6.4 (up to 12) for Japan compared to 0.01 (up to 0.9) for India. China’s footprints increased significantly from 1976: from c. 5 to 19 kgN and from 1.2 to 4.8 kgP (per person, per year). There were some cases of near zero new phosphorus use, due to use of P in soil by crops: the accounted P input was either less than or only a little more than the P in the final crop product. India’s footprints also increased from 1976, from 8.5 to 11 kgN and from 1 to 1.6 kgP. In Japan, the footprints increased until 1993, from 12 to 28 kgN and from 2.6 to 8 kgP, but then fell to 22 kgN and 6 kgP by 2013. This decrease in Japan, despite increasing meat consumption, is considered to be related to decreasing cereal consumption and improved agricultural nutrient use efficiency. The authors conclude that the N footprint is most sensitive to meat consumption, whereas the phosphorus footprint is most sensitive to consumption of vegetables, whereas improving nutrient use efficiency can significantly reduce the nutrient footprint for all foodstuffs and diets. They note that if footprints of 7.6 billion people in the high and middle income countries in 2030 increase to the 1993 levels of Japan’s footprints, even if the footprints of the other 1.0 billion people stay at the 1961 levels of China’s footprints, this would result in increases of +20% for the global nitrogen footprint and +90% for the global phosphorus footprint.
“Trends in the food nitrogen and phosphorus footprints for Asia's giants: China, India, and Japan”, A. Oita et al., Resources, Conservation & Recycling 157 (2020) 104752 DOI
Insect frass showed to be a good fertiliser
13-week pot trials with barley (Hordeum vulgare) compared insect frass to mineral NPK fertiliser. Insect frass is the waste generated from insect farming, a mixture of insect faeces and used substrate. In this case, the frass was from a mealworm farm operated by Ÿnsect, Paris, after hygienisation (60 minutes @ 70°C). At this industrial insect farm, the mealworms are fed with local agriculture by-products (wheat bran). Soil was from a cultivated field, with pH 7.8. Frass or mineral fertiliser was mixed into the soil two weeks before planting the barley seed, at a loading equivalent to 10 tonnes of frass per hectare (dry weight) or equivalent nutrients (as ammonium nitrate, potassium phosphate and potassium chloride) with four treatments: frass, 50% frass / 50% mineral fertiliser, mineral fertiliser, control. Biomass production and plant N, P and K concentrations were not significantly different between the frass and fertiliser treatments, and were significantly higher than the control (one third to one half higher). Soil incubation and Biolog EcoPlate tests showed that the frass has lower water-soluble nutrients than these mineral fertilisers (the authors indicate that this will reduce risk of nutrient leaching) and that the frass stimulates soil microbial activity, especially when combined with mineral fertiliser.
“Potential use of mealworm frass as a fertilizer: Impact on crop growth and soil properties”, D. Houben et al., Nature Research Scientific Reports, 2020, 10:4659, DOI
Nitrification inhibitor improves P uptake and yield
30-day pot trails with maize suggest that the nitrification inhibitor DMPP (3,4-Dimethylpyrazolphosphate) improved yield and phosphorus uptake with both soluble phosphorus fertiliser (TSP) and low plant availability P sources (phosphate rock, recovered phosphate: thermochemically magnesium treated sewage sludge ash SS-Mg). The trials used ammonium sulphate nitrate as N fertiliser. Controls showed that differences were not related to the P content of the DMPP. Analysis showed that the DMPP increased ammonium fixation in detectable hot-spots in the soil. The authors suggest that the slow release of plant available ammonium may decreases rhizosphere pH, due to H+ release in plant ammonium uptake, so increasing phosphorus availability. An earlier paper by some of the same authors showed that pyrolysis (400-500°C) of biological P-removal sewage sludge resulted in a product with good plant availability (NAC neutral ammonium citrate P solubility, maize pot trials), whereas pyrolysed chemical P-removal sludge had low plant availability. High temperature treatment of the chemical P-removal sludge with sodium additives resulted in high plant P availability (as calcium sodium phosphate).
“Effects of a nitrification inhibitor on nitrogen species in the soil and the yield and phosphorus uptake of maize”, C. Vogel et al., Science of the Total Environment 715 (2020) 136895, DOI 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136895
“Effect of various types of thermochemical processing of sewage sludges on phosphorus speciation, solubility, and fertilization performance”, D. Steckenmesser et al., Waste Management 62 (2017) 194–203 DOI 10.1016/j.wasman.2017.02.019
UBA report on pharmaceuticals in recycled phosphates
The German Environment Agency (UBA) has published results of analysis of pharmaceuticals in sewage sludge and in struvite, biochar/HTC and thermal process P-recovery products. 11 pharmaceuticals were analysed in sewage and recovered phosphates at 9 sites: four precipitated phosphate salt processes (AirPrex, Stuttgard, MSE, P-RoC), two thermal processes (AshDec, Mephrec), three pyrolysis/hydrothermal carbonisation processes (Pyreg, TCR, AVA Cleanphos). Results conclude, that the pharmaceuticals were no longer detectable after processing at 400 - 500°C whereas the AVA Cleanphos process at 210°C did reduce but not fully eliminate them. Some pharmaceuticals were detectable in the precipitated phosphate salts (highest: 1.1 mg/kg ciprofloxacin in Air-Prex struvite, precipitated upstream of sludge dewatering). The report concludes that further research is needed as to the possible risks of use as fertilisers of the recycled phosphate products containing traces of pharmaceuticals, as well as actions to reduce levels of pharmaceuticals in sewage.
“Arzneimittelrückstände in Rezyklaten der Phosphorrückgewinnung aus Klärschlämmen” (Pharmaceutical residues in recycled phosphates from sewage works), Umwelt Bundesamt 31/2019 ISSN 1862-4804
Erratum
In the article “Effectiveness of fertiliser and manure in long term field trial”, summarising Ning et al. 2020, in our last eNews (n°41), the numbers indicated for application, budget, crop uptake of phosphorus should be read as kg/ha total for the 20 years (and not as kg/ha/year as incorrectly indicated).

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews041
Download as PDF
Events
ESPC4 Full programme now online
4th European Phosphorus Research Meeting (PERM)
Workshop on iron phosphate chemistry applied to phosphorus stewardship
RAMIRAN 2020
Corona virus situation
ESPP members
Veolia and Yara to present Nutrient Upcycling Alliance
New ESPP member: Fertimanure project
Innovation
Eutrophication solution from down-under
Regulatory
EU consultation on “Farm to Fork” strategy: closes 16th March
EU “SafeManure”: not “end-of-manure”
European Commission announces STRUBIAS annexes for 2021
Danish assessment concludes sewage sludge safe for Organic Farming
ESPP requests withdrawal of EU-funded study on composts and digestates
The Green Deal and EU economic policy
Communications
The Baltic Sea of Opportunity
US Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance webinar on P and food
European Commission publishes conclusions on resource recovery
Circularity Gap Report 2020
Industrial Phosphorus Chemistry Symposium
IFA Forum on Plant Nutrition
IFA: potential disruptors of the mineral fertilisers market
Measures for better manure nutrient use presented for HELCOM
Review of fertiliser recycling from manure in Norway
EIP-Agri: new pig and poultry feed
Science and research
Review of P fertiliser performance of recycled nutrient products
Effectiveness of fertiliser and manure in long term field trial
Phosphorus flows in global aquaculture
ESPP members
Events
ESPC4 Full programme now online
This is the major event on phosphorus sustainability in Europe, taking place every 2-3 years. The full programme of speakers for the 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference, Vienna, 15-17 June 2020, is now published Registration is now open on Eventbrite). Sessions cover city and regional actions on nutrient stewardship, business case examples of phosphorus recycling, policy tools, research perspectives and new technologies for P-recovery from research to industrial implementation in Europe and worldwide
ESPC4 is jointly organised by the European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP) and Proman Consulting, with support of the City of Vienna (Municipal Department 48 (MA48); Waste Management, Street Cleaning and Vehicle Fleet) and of Borealis, EasyMining, WKU and LAT
Registration: Eventbrite
Conference programme, hotel lists, etc: http://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
See note below on Corona virus.
4th European Phosphorus Research Meeting (PERM)
The third day of ESPC4 (17th June, Vienna) will be the 4th European Phosphorus Research Meeting, showcasing R&D into phosphorus recycling and recycled products and new approaches to phosphorus stewardship. This is a unique opportunity to meet and exchange with other projects working on phosphorus, and to discuss research perspectives with the European Commission, industry and stakeholders. The meeting will be limited to around 100 participants, 20 project flash presentations and around 20 posters, in order to enable dialogue, discussion and networking. To participate: register as below and contact
Co-organised by ESPP, Biorefine Cluster Europe, TU Wien, Proman Consulting.
Registration with booking for ESPC4: Eventbrite
Conference programme, hotel lists, etc: http://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
See note below on Corona virus.
Workshop on iron phosphate chemistry applied to phosphorus stewardship
ESPP, with WETSUS, INCOPA, INRAE Rennes and the Horizon 2020 projects P-TRAP and SUSFERT, is organising a science and implementation workshop on iron phosphate chemistry in different systems (sediments, soil, agriculture, waste water and sewage sludge). The objective is to improve understanding of applied iron phosphate chemistry in these systems, to develop phosphorus recycling, eutrophication management and better agronomic use of secondary resources. The 1.5 day workshop will be held in Utrecht, the Netherlands 13-14 July, 2020 and include a networking dinner. The themes will cover: Iron phosphorus interactions in sediments, in soils and engineered systems, Strategies for phosphorus release and P-recovery from iron phosphates, Iron - phosphate interactions in agriculture and Markets for recovered iron phosphate materials. Proposals for posters, presentations or specific questions to address are welcome
Utrecht, the Netherlands 13-14 July, 2020. See note below on Corona virus.
Registration: Eventbrite
Contact:
RAMIRAN 2020
Europe’s leading manure and organic resources recycling conference, RAMIRAN, will take place in Cambridge, UK, 14-17 September 2020. The RAMIRAN network was established 25 years ago and the biennial conference attracts some 250 participants. This year’s RAMIRAN will look at “Managing Organic Resources in a Changing Environment”, including nutrient utilisation, soil quality, air and water, best practices, treatment technologies and policy. Abstract submission until 1st March 2019.
www.ramiran2020.org
Corona virus situation
ESPP is monitoring with concern the Corona virus development. For the events above planned by ESPP in June (ESPC4, PERM) and July (iron phosphorus workshop), in agreement with the City of Vienna for ESPC4 and PERM, it is not at present justified to postpone. However, if the developing situation does necessitate postponement of either of these events, then all registrations will be transferred to the new date to be fixed. If this is not possible for the registrant, then partial reimbursement will be made (minus non-recoverable costs). All registrants will be directly updated of developments by email.
ESPP members
Veolia and Yara to present Nutrient Upcycling Alliance
Global resource recovery company Veolia and leading crop nutrition company Yara, both members of ESPP, have launched a “Nutrient Upcycling Alliance”, to implement a sustainable and economically viable food system through hands-on, business driven projects. The Food initiative of the Ellen MacArthur Foundation has provided circular economy knowledge support to inform the strategy and policy objectives, which will be developed with companies in the food industry and with farmers. (The Ellen MacArthur Foundation published a report on “Cites and Circular Economy for Food” in 2019, see ESPP eNews n°31). The two companies are already working together on operational initiatives to launch new nutrient recovery installations in a number of major European cities and to transform the recovered nutrients into performance fertiliser products. They are developing actions to recover nutrients and recycle to quality mineral fertilisers, with Yara’s expertise, and to organo-mineral fertilisers, in combination with Veolia’s subsidiary Sede Angibaud. The objective is also to collect and process (non-edible) food waste in cities to recycle to agriculture. A first joint development is already operational in Oslo (VEAS), recovering ammonia from sewage sludge methane production and processing to nitrogen fertilisers. The Nutrient Upcycling Alliance (NUA) will be presented at the 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPC4).
“Veolia and Yara partner to propel European circular economy”
https://www.yara.com/corporate-releases/veolia-and-yara-partner-to-propel-european-circular-economy/
New ESPP member: Fertimanure project
The FERTIMANURE project (Innovative nutrient recovery from secondary sources: production of high-added value FERTilisers from animal MANURE, Horizon 2020, 2020-2023) is a new ESPP member, represented by project coordinator BETA Technological Center (UVIC-UCC, Vic, Spain). The project will examine innovative technologies for nutrient recovery and manure recycling, as well as the development of innovative nutrient management routes and circular economy business models. Five on-farm nutrient recovery pilot plants will be demonstrated in Belgium, France, Germany, The Netherlands and Spain. With different combinations of on-farm and centralised production and processing of manure and sub-products, eleven different bio-based fertilisers and twenty tailor-made fertilisers will be developed and assessed, including fertilising product adequacy tested in greenhouse and field, quality and safety, and sustainability. The project includes 21 partners from Belgium, Croatia, France, Germany, Italy, The Netherlands, Poland, Spain and Argentina, including Fertilizers Europe, Greenwin cluster Belgium, the French Chamber of Agriculture (APCA), and the European Landowners Association (ELO).
Contact: Laia Llenas Argelaguet (FERTIMANURE PI)
Innovation
Eutrophication solution from down-under
Australian innovation company Marine Easy Clean, manufacturers of The Water Cleanser (TWC) is looking to demonstrate in Europe its passive technology solution to address eutrophication in natural systems, fresh or saltwater, or to improve waste nutrient cycling in aquaculture. The TWC block restores natural bacterial balance without releasing chemicals. It contains very many microscopic capillaries, the size of which allow the proliferation of bacterial inhabitation and a non-soluble source of organic carbon (wax) which together enable rapid development of naturally present Bacillus bacteria. These release enzymes which break down organic matter in water, rendering bioavailable phosphorus and nitrogen. This enables “green” chloroplast and diatom algae to develop, providing food to crustaceans, shellfish and fish, rather than toxic Cycanobacteria (blue green algae) which develop when there is too much phosphorus and insufficient available nitrogen. The uptake of phosphorus by the “green” algae leads to low water phosphate levels, so reducing eutrophication symptoms and restoring natural ecosystem balance. In tank systems, this also improves aquaculture productivity. The Bacillus also decompose natural oils, which tend to accumulate in eutrophic waters and which can reduce surface oxygen exchange. Because the Bacillus largely function without oxygen, they do not generate oxygen depletion (dead zones). Published tests show the effectiveness of the TWC blocks in 100 litre tanks (using polluted water from the Rio de Janeiro lagoon), as well as in fish and crayfish production tanks. TWC is looking for research, industry or public partners to test the system in Europe, in restoration of eutrophied waters (fresh or salt) or in aquaculture (in tank systems, or to address ‘dead zones’ below open-water aquaculture pens).
https://www.marineeasyclean.com.au/
Regulatory
EU consultation on “Farm to Fork” strategy: closes 16th March
The European Commission has opened to 16th March 2020 a public consultation on the ‘Roadmap’ for an EU Sustainable Food (‘farm to fork’) strategy. The proposed roadmap underlines that globally, the food system generates 20-30% of greenhouse emissions, as well as to air, soil and water pollution and biodiversity loss, and that around 20% of EU food production is lost as waste whilst 7% of the EU population cannot “afford a quality meal every second day”, yet obesity and diet related disease and health costs are rising. Four objectives are defined for the strategy: sustainable primary food production, sustainable food processing and food services, sustainable food consummation and a “shift towards healthy, sustainable diets” and reducing food waste. The inclusion of diet in EU policy objectives is a significant landmark and it is stated that the Commission will propose actions to help consumers choose healthy and sustainable diets by providing better food information, including on “nutritional value”. Actions cited include to reduce the use of fertilisers and establishing Advisory Groups on the Food Chain and on Aquaculture.
For memory, the EU Regulation on Food Information 1169/2011 makes obligatory, for pre-packed foods, ‘front of pack’ information on content of calories, fat, saturates, carbohydrate, sugars, protein and salt. Other nutritional information, including levels of minerals (including phosphorus) is voluntary.
EU public consultation to 16th March 2020:
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/initiatives/ares-2020-941864_en
EU “SafeManure”: not “end-of-manure”
ESPP and the German Phosphorus Platform (DPP) participated at the expert & stakeholders meeting to input to the draft EU report “SafeManure: Developing criteria for safe use of processed manure in Nitrates Vulnerable Zones above the threshold established by the Nitrates Directive”, at JRC Seville, 28-30 January 2020. The meeting clarified that this proposal aims to facilitate, under specified conditions, the use of “processed” manure to replace mineral fertiliser in some regions with high livestock density, that is: authorisation of use at levels higher than the 170 kgN/ha general limit for manure and processed manure fixed by the Nitrates Directive, up to the higher limits regionally applicable for non-manure fertilisers. This concerns particularly the liquid fraction of solid/liquid separated manure, processed manure digestates, animal urine separated in the stable or process-separated and some “mineral concentrates” (a category which is poorly defined). The materials defined by the criteria, termed ‘ReNure’ materials, would continue to be classified as manures, and would not be given End of Waste status. The conditions for use would have to be specifically defined in Member State / Region ‘Nitrate Vulnerable Zone Action Programmes’, subject to case-by-case European Commission validation (the proposed ReNure criteria include requirements to define regional specifications on both ReNure and other fertiliser application, field management …). In discussion, the obligation was added to ensure appropriate management of phosphorus in Action Programmes where ReNure materials use derogations are included. ReNure status would thus be specific to a given region, would not be transferrable to another region, and would confer neither EU nor national fertiliser status (the materials remain “manure in a processed form”).
ESPP expressed regret that the European Commission has not so far been considered our submitted proposals to clarify “end of manure” status, for materials which are “mineral fertilisers”, referring to the definition in the EU Fertilising Product Regulation (FPR), that is < 1% organic carbon / DM. ESPP suggests that such materials, derived wholly or partly from manure, should be no longer treated as “processed manure” under the Nitrates Directive, without modification of regional Action Programmes. We suggest that this would respect the Nitrates Directive text, by limiting to products which clearly do not resemble manure or pose leaching or pollution risks. ESPP has written to the European Commission (DG Environment) request that this possibility be assessed.
JRC “interim” version of the SafeManure report, as discussed at the meeting, and now undergoing finalisation by JRC: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/regulatory
European Commission announces STRUBIAS annexes for 2021
The European Commission has published on its “Have your say” public website, a preliminary information (not dated) announcing an expected future public consultation (dates not announced) on the new criteria for use of ‘STRUBIAS’ materials as components for CE-Mark fertilisers (CMCs), under the EU Fertilising Products Regulation: struvite and precipitated phosphate salts, ashes and “thermal oxidation materials” and biochars, pyrolysis and gasification materials. These pages indicate expected adoption of these three criteria “First quarter 2021”, that is before the date of entry into application of the Fertilising Products Regulation in July 2022. The proposed criteria texts are not published here, but are (according to our information) essentially the same as those proposed in the JRC report (see ESPP eNews n°36) and are available on the ESPP website (under Activities -> Regulatory). It was expected to finalise discussion of these criteria at the EU Fertilisers Working Group planned end March 2020, but this meeting has been postponed due to Corona virus.
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say
Danish assessment concludes sewage sludge safe for Organic Farming
An assessment of risks related to use of sewage sludge and pig or cattle slurry has been published by Copenhagen University and the Danish National Food Institute (DTU). This follows from a 2017 report of the Danish Organic (Farming) Business Development Team which recommended that Organic Farmers should be allowed to use nutrients from treated municipal wastewater. The assessment finds that the main risks from pig and cattle slurry are copper and zinc, but that these will decrease with regulations prohibiting addition of these elements to pig feed in 2019 and 2022 respectively. Other contaminants showed no significant risk, with the summed risk of all organic contaminants (including antibiotic resistance) “low” for soil (but with a risk for oestrogen for farrowing pigs). For sewage sludge, the only contaminants with PEC/PNEC >1 (Predicted Environmental Concentration / Predicted No Effect Concentration) were phthalates and triclocarbon (but for triclcarbon there was no data for Danish sludge and estimates were based on US numbers). Organic contaminants in sewage sludge are not expected to accumulate in soil. Metal compounds would only reach PNEC after long periods of repeated sludge application: the most critical being zinc at 100 years. Veterinary medicine residues in sewage sludge are considered of “low concern” and the risk from antibiotic resistance is no higher than for manures and is likely to be not significant. Overall, sewage sludge is considered to not represent a higher risk to soil organisms than pig or cattle slurry.
“Assessment of risks related to agricultural use of sewage sludge, pig and cattle slurry”, K. Eggers Pedersen et al., University of Copenhagen and DTU Food, National Food Institute, Denmark, December 2019, ISBN 978-87-996274-2-4 https://plen.ku.dk/raadgivning/rapporter/Assessment_of_risks_related_to_agricultural_use_of_sewage_sludge_pig_and_cattle_slurry.pdf
ESPP requests withdrawal of EU-funded study on composts and digestates
As indicated in ESPP eNews n°37, the European Commission has published a study on contaminants in composts and digestates, proposing possible EU-wide restrictions, using “Risk Management” measures under EU chemical regulation REACH. Despite both compost and digestate being exempted from REACH “Registration”, REACH can still be used to impose bans or restrictions.
ESPP’s comments were elaborated with the European Compost Network (ECN), the European Biogas Association (EBA), Growing Media Europe and the water industry (Eureau). ESPP underlines that the report fails to consider reduction of contaminants at source as a priority, does not offer a science-based risk assessment, ignores existing risk assessments, is not coherent with the EU Fertilising Products Regulation and contains no assessment of cost/benefit nor of overall life cycle impacts. For example, key conclusions on pharmaceuticals seem to be based on the “opinion” of just one “expert”. A proposed ban of compost and digestate with sewage sludge as an input (contrary to authorisation under several Member States’ national fertiliser legislation) seems to be based on this one “opinion” on pharmaceuticals, on dioxins and furans (which are not a particularly relevant contaminant in sewage sludge, and are decreasing) and on copper and zinc (which are micro-nutrients, c.f. their treatment under the EU Fertilising Products Regulation). Incoherent and unrealistic contaminant limits are proposed for various other substances, including nickel and mercury. Indeed, the study does not even define which “composts” and “digestates” are covered, seeming to include a wide range of waste inputs which may not be relevant.
ESPP comments on the AMEC study: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/regulatory
AMEC study: “Digestate and compost as fertilisers: Risk assessment and risk management options. Final Report” Ramboll – Peter Fisk – WOOD (ref. 40039CL00313, 8th February 2019
The Green Deal and EU economic policy
IEEP (Institute for European Environment Policy) has published a paper proposing to reform the European Semester to implement the Commission’s Green Deal and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The Semester was adopted by Council in 2010 as a tool for economic and fiscal coordination in the EU, with objectives of convergence, stability and economic growth, and coordinates in a six month cycle Member States’ policies including structural reforms, fiscality and macroeconomic balances. A social element was added to the Semester in 2013, but environment is still largely absent: 21 green growth indicators are mostly on energy and DG ENVI is not involved in the process (led by GROW, ECFIN, EMPL, FISMA). However, in December 2019, the Commission published an “Annual Sustainable Growth Strategy”, replacing the previous years’ “Annual Growth Survey”. This refers to the importance of material resources and ecosystem services. IEEP suggest this should be implemented by introducing sustainability and wellbeing into the European Semester process. IEEP propose 8 sustainability dimensions, including green economy, green taxes and incentives, green R&D and innovation and sustainable industry. IEEP propose to use 15 existing indicators as an environmental sustainability scoreboard, including % of water bodies in Good Ecological Status, soil sealing, eco-innovation index, greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, material consumption per capita and years of life lost due to particulate air pollution.
“Delivering the Green Deal: the role of a reformed European Semester within a new sustainable economy strategy”, IEEP, C. Charveriat & E. Bodin, 2020
Communications
The Baltic Sea of Opportunity
An 18 minute film from the Baltic BONUS RETURN project explains visually, for a general public audience, that phosphorus can be transformed from a problematic pollutant to an economic resource. Phosphorus is essential for life, agriculture and global food security. But losses are the biggest cause of eutrophication, devastating the Baltic. Jakob Granit, Swedish Agency for Marine and Water Management, explains the need to reduce nutrient loads into agriculture and to take nutrients, accumulated in the past, out of water and from sediments. Solutions exist to transform phosphorus waste into a sustainable resource. Examples presented include Wodociagi Slupsk, Poland, producing compost from sewage sludge which is then sold as a fertiliser in Poland. Jon Wessling, LRF (Federation of Swedish Farmers) explains that they recommend the use of sewage sludge in agriculture. Innovations tested in the BONUS RETURN project are presented. BioPhree Aquacare (see ESPP eNews n°29) is tested at Knivsta, Sweden, on a sewage works discharge stream. This process uses adsorbents to remove phosphorus from dilute streams, such as surface waters, which then can be regenerated to recover phosphorus. The Ravita (Helsinki HSY) P-removal and recovery process is tested in Finland (see SCOPE Newsletter n°132). TerraNova, a continuous hydrothermal hydrolysis carbonisation process (see SCOPE Newsletter n°132) will be tested on sewage sludge in Gävle, Sweden, producing a biochar-type fertiliser. The film underlines the challenges of regulatory obstacles to nutrient recycling and the opportunities of the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation.
The Baltic Sea of Opportunity https://www.bonusreturn.eu/sea-of-opportunity-film/
US Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance webinar on P and food
The 9th webinar organised by the US Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance, 18th February and can be watched here discussed phosphorus and food. Jaime Uribarri’s presentation suggested that US food phosphorus levels are considerably higher than the RDA (recommended daily allowance = recommended minimum dietary intake) and that there is evidence that increased phosphorus levels in blood are linked to risk of arterial calcification, and so cardiovascular disease. However, most of the papers referenced only show a link with diet for kidney disease patients, not for the general population. He emphasised the absence of information about levels of phosphate food additives in different foods, which can be important because these additives are absorbed into the body more than phosphorus in plant materials in foods. Jim Elser underlined that the world’s phosphorus footprint (mined phosphorus per capita) has increased nearly 40% since the 1960s and that the key cause is increasing meat content of diets. David Vaccari presented an analysis of possible routes to reduce phosphorus consumption, showing that important action points are reducing food waste, improving fertiliser and improving the use efficiency of phosphorus in livestock production (in particular, better use of manure). With current practices, he estimates that without fertilisers from rock phosphate, only a world population of around 2.5 billion could be fed, but that this could be increased to over 10 billion by significant improvements in these action points, and to 15 billion if this were combined with a reduction in meat in diet.
Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance videos and webinars:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCNFDQTfeT7mGsMY_YOgMonA
European Commission publishes conclusions on resource recovery
The conclusions on resource recovery from wastewater, from the workshop organised by four Horizon 2020 projects (SMART-Plant, nextGen, Hydrousa and Project-O) and the European Commission (EASME) at the 2019 IWA Resource Recovery conference, have now been published by the European Commission. The workshop agreed the following recommendations to further nutrient recovery and recycling: promote a positive image for recycling nutrients; need for stable regulatory support; importance of networking of competence, platforms and data benchmarking; difficulties posed by disparate implementation of End-of-Waste in different Member States and regions. The workshop recommended to promote and support nutrient recycling in Horizon Europe, and to develop better coordination of End-of-Waste, Water Policy and Circular Economy policies between Member States.
Report. Post-Conference workshop @IWARR2019. “H2020 Water Innovations for Sustainable Impacts in Industries and Utilities” here.
Circularity Gap Report 2020
The Circle Economy report 2020 indicates that global circularity has fallen from 9.1% (% of recycled materials in total resource consumption) to 8.6% from 2018 to 2020. The report underlines that circularity is key to achieving climate objectives. Nutrition is the second biggest user of resources, after housing/infrastructure, and consumes 21 billion tonnes of resources per year worldwide, out of a total of around 100 billion t/y entering the global economy (of which 92 bt extracted, just over 8 bt recycled). The report notes the need for better data and monitoring, including on the quality and composition of materials recycled. Sophisticated infographics illustrate global flows and country circularity levels. This suggests that companies closest to circularity include Sri Lanka, Georgia, Cuba, Jamaica. The least circular countries include the UAE, Burkina Faso and Luxembourg, with Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Latvia and Sweden classed in the next-to-worst. Company CEOs cited as supporting the report include DSM and Royal Philips.
The Circularity Gap Report 2020, Circle Economy, CGRi, Platform for Accelerating the Circular Economy (PACE).
Industrial Phosphorus Chemistry Symposium
The first Industrial Phosphorus Chemistry Symposium (IndPhos) took place in April 2019 back-to-back with the 16th European Workshop on Phosphorus Chemistry (EWPC). Willem Schipper, Schipper Consulting, focussed on options to make industrial uses of phosphorus more sustainable and more circular. Chris Harris, Solvay, showcased a wide range of applications of organophosphorus chemistry, including as flame retardants, in mining, scale and corrosion control in water treatment, agriculture, medicine and as ligands for catalysts in industrial applications. Thomas Schaub, BASF presented new phosphorus-containing catalysts for the hydrogenation of esters and for the synthesis of sodium acrylate based on CO2 and ethylene. Jan-Gerd Hansel, Lanxess, discussed the development of halogen-free flame retardants, in particular new poly(alkylene phosphate) esters as flame retardants in polyurethane foams. Steven van Zutphen, Italmatch, explained the industrial, regulatory and health and safety issues in scale-up of new chemistries from bench to multi-ton reactor scale. Reinhard Sommerlade, independent process design chemist, presented industrial uses of phosphorus-based photo-initiators, such as bis(acyl)phosphine oxides (BAPOs). Irradiation breaks the phosphorus - acyl carbon bond in these compounds, initiating emission-free polymerization of monomeric or oligomeric polymer precursors for various applications. Hansjörg Grützmacher, ETH, Zurich, discussed synthesis and application of new and sustainable building blocks in phosphorus chemistry, emphasising the need to combine innovation with recyclability and industrial feasibility.
Indphos was organised by Chris Slootweg, University of Amsterdam, with support from Solvay, OCP, Lanxess, Magritek, Strem, Glindemann, Springer, the Royal Society of Chemistry and the European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry
https://ewpc16.com/indphos/
IFA Forum on Plant Nutrition
The “High-level Forum on Sustainable Plant Nutrition”, Versailles, France, November 2019, was chaired by David Nabarro, 4SD, 2018 World Food Prize laureate, and brought together the fertiliser industry, fertiliser industry stakeholders, funding and policy organisations and scientists. Prefacing the forum conclusions, Mostafa Terrab, OCP and IFA Chair, underlined that mineral fertilisers underpin around half of global food production, and that fertilisers will continue to be vital to feed the world, with improved soil health, water management and crop genetics. The forum addressed five challenges to global agricultural systems, and defined five recommendations to the fertilisers industry. The challenges to agriculture are: producing more with lower inputs, whilst improving nutritional quality; balancing productivity and environment; preserving natural resources; reducing climate emissions, including by improving nutrient use efficiency (NUE); training and empowering farmers. World hunger has increased for the last three years to 2019, today impacting over 800 million people. Some 2 billion people suffer from micronutrient malnutrition, impairing physical and mental development and the immune system. Whereas in some communities over-consumption of animal protein damages health. Recommendations to the fertiliser business are: new business models, including “from volume to value-added”, energy efficiency and circularity, including externalities in true cost accounting; building partnerships from farmers to consumers; collecting and using big data; technology innovation, such as micronutrient fertilisers, nutrient delivery efficient fertilisers, bio-stimulants, precision agriculture; promoting public policies which support human nutrition, carbon sequestration and reduced nutrient pollution.
IFA High Level Forum on Sustainable Plant Nutrition “Toward a new paradigm for sustainable plant nutrition”, 18-20 November 2019, Versailles, France https://www.highlevelforum.org
IFA: potential disruptors of the mineral fertilisers market
The IFA (International Fertilizer Association, the world fertiliser industry federation) marketing conference, Dubai, March 2020, included a session on potential disruptors of conventional mineral fertiliser markets. Armelle Gruère, IFA, listed potential market disruptors identified by IFA: increasing nutrient recycling, bio-stimulants, crop strains requiring less nutrients (e.g. nitrogen fixing), new fertiliser types, policies (regulation, subsidies), agriculture system changes in particular IT and big data, biofuels, diet changes. Derek Oliphant, Agbio Investor, noted that the global market for agriculture intrants is 250 billion US$, of which around 60 bn$ fertilisers and around 2 bn$ bio-stimulants. The bio-stimulants market is growing at >10%/year, and the EU is 40% of the world market. Development of crop strains (seeds) with improved nutrient use efficiency is today less of an industry priority than pest resistance. Ravinda Shrotriya, presented production of vegetables in urban hydroponics. Using artificial light, around 8 kWh energy is needed per kg vegetables, but water and intrant use efficiency are very high. Marina Simonova, IFA, indicated that world greenhouse area is growing +5%/year, generating demand for water-soluble fertilisers (e.g. MAP). Together, speciality fertilisers (water soluble, coated, slow or controlled release, nitrogen-stabilised / eutrophication inhibited) are growing at 4%/year and today represent 10% in value of world mineral fertiliser sales. Chris Thornton, ESPP, explained that the potential for nutrient recycling is significant, but that data is lacking. The quantity of phosphorus in manures in Europe is of the same order as that used in mineral fertilisers, and the quantity in sewage, organic solid wastes and animal by-products is a further one third of mineral fertilisers. There is a lack of data as to how much of these secondary nutrients is today recycled, and are really potentially recyclable, both at the global level (no reliable phosphorus flow study) and at the EU level (no monitoring, no update since Kimo Van Dijk’s 2015 paper (2005 data). ESPP presented examples of companies operating or building full-scale nutrient recycling today, either in organic (composts, organic fertilisers) or mineral forms (recovered ammonia, phosphorus), with large industrial operators (Veolia, Suez, ICL, Borealis, Fertiberia, Outotec, Ragn-Sells/EasyMining, …), SMEs (Ostara, NuReSys, N2-Applied …) and cities/regions (Kanton Zurich, Vienna …).
IFA Marketing Conference Dubai 3-5 March 2020
Measures for better manure nutrient use presented for HELCOM
The Baltic Sea Interreg platform project SuMaNu (Sustainable Manure and Nutrient Management for Reduction of Nutrient Loss in the Baltic Sea Region) compiles best practises in organic fertilizer use, manure management and processing. It will deliver recommendations to help implement the forthcoming Regional Nutrient Recycling Strategy for the Baltic Sea riparian countries prepared in HELCOM. Preliminary (draft) recommendations were presented for discussion at a workshop on nutrient recycling measures arranged on 4-5 February in Helsinki, Finland, with HELCOM, the Finland Ministries of the Environment and of Agriculture of Finland as well as key coordinating actors of the EU Strategy for the Baltic Sea Region. The SuMaNu platform draft recommendations address the importance of optimised fertilisation planning, manure management, measures to address regional nutrient surpluses, management of safety and hygienic risks with respect to trace elements and organic contaminants; and knowledge transfer.
More information on the workshop and the HELCOM Regional Nutrient Recycling Strategy here
Follow progress of the SuMaNu platform here: balticsumanu.eu
Review of fertiliser recycling from manure in Norway
NIBIO (Norwegian Institute of Bioeconomy Research) has published a literature review and assessment of manure treatment technologies and recycled fertilisers from manure. In Norway, around 8 400 tP/y of mineral fertiliser are applied, as well as some 12 000 tP/y in manure, resulting in an annual soil P accumulation of around 12 000 tP/y, probably mainly due to over-application of manure in livestock intense regions. Livestock production in Norway is concentrated in the South-West (especially in Rogaland county). A currently ongoing revision of national fertiliser regulations is expected to reduce phosphorus application rates, and so lead to manure treatment and transport. Manure treatment technologies summarised are solid/liquid separation (sedimentation, centrifuge, filtration with or without pressure); upgrading of solid or liquid fractions (drying and pelletising, composting, combustion, pyrolysis, precipitation, concentration); anaerobic digestion; acidification. Literature shows that most pig and cattle manure separated fractions showed similar plant phosphorus uptake to mineral fertilisers, including when polymer flocculants were used to improve separation. Thermal treatments (drying, pyrolysis, combustion), however, tend to reduce phosphorus availability, especially at higher temperatures. The plant availability of inorganic chemicals recovered from manure depends on their chemical and physical characteristics. The effects of anaerobic digestion on manure plant availability are considered not clear from the limited data available. Composting may reduce plant P availability. Acidification tends to improve plant P availability, but also reduces separation efficiencies. NIBIO concludes that manure processing technologies are available which can improve phosphorus management and increase recycling, and which ensure good plant P availability.
“Manure-based recycling fertilisers. A literature review of treatment technologies and their effect on phosphorus fertilisation effects”, E. Brod, NIBIO report vol.4, n°91, 2018
EIP-Agri: new pig and poultry feed
The EU-funded “EIP-Agri” (European Innovation Partnership) has published conclusions on “New feed for pigs and poultry” assessing new feed sources and feeding strategies. Based on costs, nutritional value and sustainability, five priority feed sources are identified: bakery products (food industry waste bread or biscuits), protein extracted from green biomass such as grass or clover, insects, micro-algae (e.g. harvested seaweed such as kelp, or algae grown on waste streams such as digestate) and single-cell protein (e.g. from bacteria cultured on wastes). Some of these products offer pro-biotic benefits as well as feed value. Identified challenges include ensuring consistent nutritional characteristics; risks of contamination by e.g. packaging (bakery products) or toxins (algae, bacteria); logistics of production, processing, storage and transport; public acceptance and integration into Organic Farming. Further research is necessary into improving fat / protein / micronutrient balances in different materials, processing, digestibility and into analysis techniques.
EIP-Agri Focus Group “New feed for pigs and poultry”, final report, January 2020
Science and research
Review of P fertiliser performance of recycled nutrient products
200 published studies testing the phosphate fertilisation effect of a wide range of different recycled nutrient materials are reviewed, covering recovered minerals (calcium phosphates, struvite, etc), various treated and untreated ashes, pyrolysis products, sewage sludges, digestates. The authors conclude that some recycled products offer phosphate fertiliser effectiveness comparable to commercial, water-soluble, mineral fertilisers, but that plant growth tests show widely varying results. Plant availability in some recycled nutrient products can depend considerably on conditions in the production process, and on levels of iron, aluminium and calcium, in particular of iron. Plant availability will also depend on the physical form of the material, e.g. crystal structure and particle size. Variability also results from the lack of standardisation between testing methods. The authors consider that standard chemical extraction methods (water solubility, NAC neutral ammonium citrate, citric acid, formic acid) do not provide good indications of plant availability. They consider that NAC can dissolve iron and aluminium phosphates (e.g. in sewage sludge) or complex calcium phosphates (eg. Whitlockite) which are poorly plant available. Citric acid P solubility can be affected by calcite or dolomite which bind to citrate ligands. The authors suggest that alternative methods such as sequential fractionation, soil incubation or soil P sink methods should be developed.
“Agronomic performance of P recycling fertilizers and methods to predict it: a review”, S. Kratz, C. Vogel, C. Adam, Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst, 115, pages1–39 (2019) DOI
Effectiveness of fertiliser and manure in long term field trial
Data is presented of a 20 year field trial testing eight combinations of mineral fertilisers and composted pig manure applied in Spring (control, manure only, N, NP and NPK with or without manure) on maize and soybean in Liaoning Province, China. Where crops received fertiliser plus manure, this was additive: e.g. P in mineral fertiliser when applied was always c. 23 kgP/ha/y, with additional c. 10 kgP/ha/y when manure was also applied. In this scenario, mineral fertilisers were the principal route to ensure phosphorus budgets and increase soil available P, enabling improved and more reliable crop yield and nutrient use efficiency (NUE). The authors conclude that long term application of mineral fertiliser and manure together considerably increase the conversion of residual fertiliser P (the P not taken up by the crop) to soil available P. However, the data also suggests that fertiliser plus manure resulted in excess P application (total P input 36 vs. P uptake in crops 22 kgP/ha/y) whereas mineral fertiliser corresponded to a nearly balanced P budget (NPK: P input 23, crop offtake 20 kgP/ha/y) and manure only to a P deficit (input 9, offtake 15 kgP/ha/y). In most years, Phosphorus Use Efficiency (PUE) was significantly higher with manure application only (note: this may be the result of the P deficit) but was similar for NPK+manure compared to NPK, despite the P over-application, suggesting that manure does improve overall Phosphorus Use Efficiency.
“Mineral fertilizers with recycled manure boost crop yield and P balance in a long-term field trial”, C. Ning et al., Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 2020 DOI
Phosphorus flows in global aquaculture
An assessment of phosphorus flows in global aquaculture and fish harvesting suggests that around 10% of world phosphate production is used in aquaculture: estimate of 2.04 MtP/y used in aquaculture, compared to world P production from phosphate rock of around 20 MtP/y (see ESPP Factsheet). This compares to FAO (2016, p4) estimate that fish (only) accounts for 6.7%of world diet protein. The authors estimate total harvest of P in fish and seafood at 1.1 MtP/y, with around 60% from captured fish and seafood and around 40% from aquaculture production. This means that around 1.6 MtP/y is net lost in aquaculture (input P minus harvested P), mainly to aquatic systems. The authors estimate that the total harvested P in fish and seafood was 0.21 MtP/y in 1950 and the input to aquaculture then only 0.1 mtP/y, so that the overall P budget has changed from net positive to negative. These estimates of P use in aquaculture are calculated by multiplying production of different species by estimated Phosphorus Use Efficiencies, inferred from farm-level data for different species. The result is nearly two times higher than that obtained (2.04 vs 1.11 MtP/y) by multiplying estimated aquaculture farm area by World Fish database nutrient input/surface data. This P input to agriculture includes both P fed directly to the fish or crustaceans (in fish meal or in plant materials used in feed) and also fertilisers (both mineral or organic, such as manures) input to aquaculture systems to grow vegetation to feed fish (but not fertilisers used to grow crops used to make fish feed).
“The shift of phosphorus transfers in global fisheries and aquaculture”, Y. Huang et al., Nature Communications (2020) 11:355 DOI
ESPP members

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews040
Download as PDF
Events
European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference (ESPC4)
CRU Phosphates 2020
RAMIRAN 2020
Regulatory
Sweden Enquiry recommends use of sewage sludge on crops
Regulatory status of insect “manure” as fertiliser
Nutrient recycling
ESPP – NNP - DPP phosphorus recovery technology catalogue
Italmatch acquires RecoPhos P4 production technology
AquaGreen pyrolysis of sewage sludge & fish manure
Food systems
Future of food and food production
Towards a radical move away from animal protein?
Sustainable Development in the Food and Beverage Industry
Food waste losses 16% of China’s fertiliser P use
Studies and research
Nutrient balances and recycled nutrients in organic farming
Plant availability of thermochemically recovered phosphorus
Recycling flame retardant boron from insulation to fertiliser
EC scientists conclude benefits of P-recovery
Global map of phosphorus recycling potential
European topsoil maps for P, N, K and C/N
ESPP members
Events
European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference (ESPC4)
Registration is now open (on Eventbrite) for the 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference, Vienna, 15-17 June 2020. This 4th ESPC will centre in plenary on business models, company success stories and city and regional actions towards nutrient circularity. Parallel sessions will mix research with application (see below, call for papers). The third day (17th June) will be the 4th European phosphorus R&D day, showcasing R&D into phosphorus recycling and recycled products and new approaches.
Registration: Eventbrite
Full details www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
CRU Phosphates 2020
The full speaker agenda is now published for the 13th CRU Phosphates Conference, 8-10 March 2020 Paris. This is the world’s leading phosphate industry meeting, with over 400 industry participants from 40 countries annually. Sessions include technical showcases, market outlooks worldwide and by major region, fertiliser regulation update and phosphorus recycling, new developments (biostimulants, crystalline and soluble fertilisers), animal feed phosphates, phosphate chemical processing. See summary of the 12th CRU Phosphates Conference (Florida, 2019) in ESPP eNews n°33. 10% fee discount for ESPP members.
CRU Phosphates 2020, 8-10 March Paris - https://events.crugroup.com/phosphates
RAMIRAN 2020
Europe’s leading manure and organic resources recycling conference, RAMIRAN, will take place in Cambridge, UK, 14-17 September 2020. The RAMIRAN network was established 25 years ago and the biennial conference attracts some 250 participants. This year’s RAMIRAN will look at “Managing Organic Resources in a Changing Environment”, including nutrient utilisation, soil quality, air and water, best practices, treatment technologies and policy. Abstract submission until 1st March 2019.
www.ramiran2020.org
Regulatory
Sweden Enquiry recommends use of sewage sludge on crops
The Sweden Government enquiry into phosphorus recycling and sewage sludge published its conclusions on 17th January 2020. The report recommends that regulation should require at least 60% recycling of phosphorus from sewage works > 20 000 p.e., that specifications should be developed for other organic-carbon containing fertilisers (in particular sewage sludge biochars) and proposes two options concerning use of sewage sludge in agriculture: either (1) a ban with “very few exceptions” (e.g. individual households), including a ban on use of separated urine, or (2) continuing use of “sanitised and quality-assured sludge” with demanding quality requirements (to be defined within 2-3 years) and reevaluation over coming years to decide whether further restrictions or requirements should be implemented. The report strongly recommends option 2, that is continuing use of sewage sludge in agriculture, with demanding quality requirements (in the Swedish text, not in the English summary). In this case, the 60% P-recycling requirement would include sludge use on crops. For both options, the report recommends to ban use of sewage sludge for non-agricultural applications, such as landscaping, where phosphorus is not valorised (such use is currently 2/3 of Sweden’s sewage sludge spreading). The report states that “current research on the spreading of sewage sludge has not yet shown adverse effects on health and the environment … with the quality requirements applied for use in Swedish agriculture” and underlines that sludge use in agriculture enables recycling not only of phosphorus, but also of nitrogen and organic carbon. The report concludes that a complete ban on sewage sludge use is not supported by risk assessment, whereas “there is clear evidence that sludge fertiliser application supplies plant nutrients and humus that agriculture demands”. An update of Sweden’s sewage and sludge regulations is recommended, with a strengthening of the role of the EPA in addressing sewage contaminants at source. It is also recommended that national objectives be developed for recycling of other resources in wastewater (nitrogen, potassium, carbon). The report notes that the market value of potentially recovered phosphorus in Sweden (c. 5 million €/y) is significantly lower than sludge mono-incineration and P-recovery technology costs (10-15 million €/y or higher).
Conclusions report of Sweden Government Inquiry into phosphorus recycling and sewage sludge use in agriculture, including 12-page detailed English summary pages 31-43 - Report of the Inquiry into a non-toxic and circular recycling of phosphorus from sewage sludge “Hållbar slamhantering”, published 17th January 2020
Stockholm Environment Institute workshop on the Inquiry conclusions: 30th January 15h30-17h00
Regulatory status of insect “manure” as fertiliser
The European federation of producers of insects for human and animal foods (IPIFF) has published a position paper on the use of insect larvae faeces (“insect frass”) as a fertiliser. In addition to their main outputs (whole insects, proteins, fats), insect farms produce “frass” - a secondary material which has potential to be upcycled as a fertilising product in agriculture. EU frass production in 2019 was circa ten thousand tonnes (of which 80-90% dry matter) forecasted to reach nine million tonnes/year by 2030. Its characteristics vary depending on the insect species and production method (e.g. the substrates used in insect farming). NPK values are similar to compost with values around 4:3:3 (4%N, 1.3%P, 2.5%K). In addition to nutrients, frass can contain bacteria which stimulate plant growth and health. At present, some EU countries authorise the use of insect frass under national fertilisers regulation, with varying requirements for sterilisation. This fragmented and unclear regulatory context is an obstacle to the development of appropriate processing of frass, and so to its commercialisation and the reintroduction of valuable nutrients in agriculture. IPIFF recommends: (1) the development of a specific EU regulatory definition of insect frass and its integration into the EU Fertilising Products Regulation; (2) that the status of insect frass be clearly aligned, across Europe, to standards and requirements for animal manure under the EU Animal By-Products Regulations (ABP); and (3) that an ABP Regulation endpoint be defined for direct use of non-sterilised insect frass on land (criteria on sieving/treatment to ensure absence of live insect larvae and microbiological and chemical safety).
“IPIFF Contribution Paper on the application of insect frass as fertilising product in agriculture”, 19th September 2019 International Platform of Insects for Food and Feed www.ipiff.org
Nutrient recycling
ESPP – NNP - DPP phosphorus recovery technology catalogue
A “catalogue” of technologies for P-recovery, particularly targeting operational information on processes today operating full-scale for P-recovery from sewage, is published online by the three nutrient platforms currently operational in Europe (ESPP European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform, DPP German Phosphorus Platform and NNP Netherlands Nutrient Platform). Ten processes for P-recovery from sewage (from sludge or sludge incineration ash), operating today full scale or under construction, are summarised, as well as a further c. 20 processes which concern P-recovery from manure (full scale), nitrogen recovery (full scale) or R&D scale P-recovery from sewage. The catalogue specifies the input materials for each process, output products, fate of iron/aluminium and of heavy metals or other contaminants, a summary of the process steps, current operating status (full-scale or pilot operation at how many sites, capacity and duration of operation) and websites of technology suppliers.
ESPP – DPP – NPP Phosphorus Recovery Technology Catalogue: http://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/p-recovery-technology-inventory
Italmatch acquires RecoPhos P4 production technology
The Italian chemicals group, Italmatch, specialist in phosphorus-based products for fire safety, energy storage applications, water treatment, oil & gas, lubricants and plastics, has acquired (from ICL) the RecoPhos thermal technology (see SCOPE Newsletter n°120) for production of P4 (elemental or “white” phosphorus) from secondary raw materials, in particular sewage sludge incineration ashes. P4 is specifically identified as one of the 27 EU “Critical Raw Materials”, separately and in addition to “phosphate rock”, because it is essential for a wide range of applications (see SCOPE Newsletter n°123), including fire protection, batteries, water treatment, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals …and because Europe is currently completely dependent on imports (essentially from Vietnam and Kazakhstan). There is today no EU producer of P4. The RecoPhos technology uses electro-magnetically induced heating of a reactor bed consisting of coke or graphite, and should enable P4 production with an improved energy efficiency profile compared to current industrial processes. It also aims to enable phosphorus recovery from ashes containing iron and to allow decentralised production units to be potentially viable. Because of its hazardous characteristics, P4 or its derivatives require very specific competence and organisation for production, handling and transport, and Italmatch has this industrial competence. A pilot RecoPhos plant was tested in Leoben, Austria, in 2015, treating around 10 kg/h of dry input material.
Italmatch press release, 16th January 2020 http://www.italmatch.com/italmatch-chemicals-group-acquires-the-recophos-project-technology/
AquaGreen pyrolysis of sewage sludge & fish manure
DANVA, the Danish Water and Wastewater Association, has launched a “PCP” (Pre-Commercial Procurement) project, funded by the Danish Market Development Fund to treat and recycle sewage sludge by use of superheated steam drying and pyrolysis. The technology is developed by the Danish start-up company AquaGreen ApS in corporation with the Danish Technical University (DTU) and Norwegian Akvaplan Niva, funded by the Horizon 2020 Eurostar program. A pilot plant with a capacity of 2.5 tons sewage wet weight sludge per day, at 25% DM, was installed and successfully demonstrated in 2018 at VandCenter Syd A/S, Odense Municipal Waste Water Treatment plant. In 2019, authorisation was given to AquaGreen and Nordlaks Smolten AS to test the system for treatment of fish manure from land based salmon farms in Norway. The dried sludge is pyrolyzed at 650 °C, and the flue gas provides the thermal energy for the superheated steam drying. The resulting biochar is rich on phosphorus (6-8% Vol.) and the plant availability has been proven and documented in field-trials performed by SEGES and green-house trials performed by Copenhagen University, Department of Plant and Environmental Sciences.
https://www.aquagreen.dk/
Food systems
Future of food and food production
A report from the Swiss investment bank UBS gives perspectives for future food production, looking at societal tendencies and industrial opportunities. The bank identifies as key drivers: scarcity (water, land, nutrients …), sustainability, new consumer attitudes, wellness (obesity, health inducing molecules), and digitalisation. Replacement of animal products by plant, algae or cell cultured foodstuffs is expected to develop strongly, for resource, environment and health reasons. ESPP notes that phosphorus will remain essential for all such production, opening opportunities for new recycling routes and efficient use. USB see major opportunities in technologies (e.g. drones) and data management to develop precision farming (connectivity, big data, satellite data …) and reduce food waste (internet of things). Challenges include consumer attitudes (traditional preferences), political defence of existing production systems and consumer attitudes to new products and bio-technologies (e.g. gene editing).
“The food revolution. The future of food and the challenges we face”. UBS Chief Investment Office, July 2019. UBS
“Plant-based protein is disrupting meat markets” UBS Investment Insights, 24 July 2019
Towards a radical move away from animal protein?
A report from an independent thinktank on disruption predicts that non-animal derived proteins will be five times cheaper than animal proteins by 2030, as well as healthier, better tasting and more convenient, leading to a halving of the number of cattle in the USA by 2030 and making the cattle farming industry “all but bankrupt” (disruption of only a third of the industry’s revenues would be sufficient to push it to bankruptcy), leading to a 40-80% fall in farm land prices and a 45% reduction in agriculture’s greenhouse emissions. The key driver will be precision fermentation, enabling micro-organisms to produce almost any organic molecule on demand. Food engineers will then be able to personalise recipes, to develop new products, target consumer tastes or nutrition and health needs. Precision fermentation will be supported by gene sequencing and genetic engineering of micro-organisms, artificial intelligence and robotics, enabling local production. Precision fermentation is already today used to produce e.g. insulin (medicine), human collagen (cosmetics) and artificial sweeteners (food). The report notes that a relatively small substitution can disrupt an existing market (e.g. only 3.3% wet weight of milk is protein) and predicts reductions in the (US) market for beef steak of -30% by 2030, ground beef -70% and milk -90%. The resulting job losses in cattle production and processing (1 million job losses in the USA) would be of a similar order to job creation in precision fermentation. The report suggests that the fertiliser industry would be negatively impacted by the move away from livestock production (-50% fertiliser consumption predicted). ESPP notes however that this assumes that land is not converted to plant production for food or biofuels/biomaterials. The report suggests that precision fermentation is 10-25x more “feedstock efficient” (presumably covering both energy and nutrients) than animal farming, and notes that it will generate wastewater and spent micro-organism biomass, which it suggests could be recycled as fertiliser.
“Rethinking Food and Agriculture 2020-2030. The Second Domestication of Plants and Animals, the Disruption of the Cow, and the Collapse of Industrial Livestock Farming”, RethinkX, C. Tubb, T. Seba, September 2019, 76 pages.
Sustainable Development in the Food and Beverage Industry
ESPP participated at the ENG SDF&B (Sustainable Development in the Food & Beverage Industry) conference, Düsseldorf, 14-15 January 2020, chairing the second day and leading a round table on “The phosphorus challenge” for food and agriculture. Participants at the conference included leading food companies, agri-food suppliers and supermarkets, including Mars, Coca Cola, Nestlé, Brau Union (Heineken), Metro, Migros, Delhaize Group, Tchibo, Bunge, Friesland Campina, HK Scan …) and the conference was sponsored by the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD). Presentations and discussions included innovation replacing animal products (e.g. Oatly, oat based “milk” replacement; Protifarm, food ingredients from insect production, Proveg, non-meat product incubator …); linking technology and data to sustainability enablement; sustainability from farm to fork, food prices and a living wage for farmers; identifying and reducing sustainability risks in supply chains; and the need for cross-industry cooperation and regulation to move the whole market to sustainability progress. Aquaculture was discussed, as an environmentally efficient source of healthy protein, with ongoing development of increasingly efficient, mainly plant based feed recipes (Mowi, Biomar).
http://www.engevents.com/sustainable2020
Food waste losses 16% of China’s fertiliser P use
A study estimating the phosphorus footprint of food waste in China estimates that over 83 000 tP/y are contained in at-table (commercial and home) food waste in China, with a total P footprint of over 420 000 tP/y including related crop or livestock production and food processing. This is over 16% of China’s annual consumption of mineral P fertiliser. The study is based on a modelling quantification of food waste, calculated per Chinese region, verified against data from several studies and statistics sources, concluding total at-table food waste of nearly 54 million tonnes/year in China (over 39 kg/person/year). This is then multiplied by “loss factors” for different production and processing systems (cultivated land, animal farming, crop processing …), from other papers by the same author. This may however over estimate animal production losses, because these calculations assume that all phosphorus not transferred into food products is lost, in particular that all manure P is lost and none recycled back to land.
“Food waste and the embedded phosphorus footprint in China”, B. Li et al., Journal of Cleaner Production 252 (2020) 119909 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119909
Studies and research
Nutrient balances and recycled nutrients in organic farming
The EU Horizon 2020 project RELACS (Replacing Contentious Inputs in Organic Farming Systems, or Improving Inputs for Organic Farming) has published preliminary results of a major ongoing study into need and use of nutrients, and of organic farmers’ attitudes to recycled nutrients. The study is based on interviews with a total of 79 organic farmers in seven European countries (Germany, Italy, Estonia, UK, Denmark, Switzerland, Hungary). The farms showed, on average, surpluses for nitrogen (average +28 kgN/ha) but near balance for phosphorus (average -1 kgP/ha) and potassium (average +2 kgK/ha), However, nutrient balances varied widely between farms (e.g. -15 to +40 kgP/ha for phosphorus). Farms with externally sourced nitrogen inputs tended to show surpluses of all three nutrients, while increasing reliance on biological nitrogen fixation induced more negative budgets of P and K. Nearly all farmers interviewed were open to using recycled fertilisers, including from urban waste streams, in order to close the nutrient cycle. Yet many farmers raised concerns about contaminants, in particular micro-plastics, as well as about consumer acceptance of use of sewage-derived products.
Jakob Magid, Copenhagen University, one of the RELACS project partners, has commented to SEGES : RELACS’ preliminary data suggests that organic farms relying mainly on nitrogen inputs from plants, with few or no external inputs, have a much lower output productivity than farms with a higher ratio of external inputs. Around half of the organic farms examined in RELACS had outputs of less or much less than 60 kgN/ha in their produce, corresponding to c. 3 tons grain per hectare. Most of the 71 farms examined had few or no animals, and their output was estimated by using farmgate balances of nitrogen in various products or manure. The farms that had higher outputs used substantial amounts of different inputs. The farms that rely heavily on biological nitrogen fixation tended to use few or no external inputs at all, which could be due to low accessibility, and limited economy. If organic farmers want to be able to supply a much larger part of the future European market with organic products, they will have to use the organic farmland as efficiently as possible, Jakob Magid says.
“Reducing the use of external fertilisers in organic agriculture”, 11th July 2019, RELACS (Replacing Contentious Inputs in Organic Farming Systems, or Improving Inputs for Organic Farming) www.relacs-project.eu
Plant availability of thermochemically recovered phosphorus
Greenhouse container trials tested the plant availability of phosphorus in thermochemically treated sewage sludge: 170 kg soil, 1 ½ years, barley, spinach, rye grass, maize. The sludge was from a sewage works using iron salts for chemical P-removal, after anaerobic digestion. It was first dried to >93% DM, then pyrolyzed at 550°C (Pyreg) and finally reacted at 950°C with a reducing agent (lignite) and sodium sulphate or chloride (HCl) + sodium sulphate. The resulting ash contained 10-11%P and around 15% iron (Fe), 10% aluminium (Al), 12% calcium (Ca) and 13-14% magnesium (Mg). NAC phosphorus solubility was over 93% for the sewage sludge, dropping to 88% after pyrolysis and to 63 or 87% after the thermochemical treatment (the higher solubility was when chloride was added in the process). Dry matter yield in the container trials was significantly lower than for triple super phosphate for the pyrolyzed sludge and thermochemical ash for both barley and rape and marginally lower for rye grass (for spinach there were no significant differences from the control: no added P). The authors suggest that the container-scale crop trials can simulate real field conditions (significant root development) and that the results show “adequate” long-term plant availability of P in the thermochemical ash materials, but low short-term plant P availability. They suggest that this is because the thermochemical ash contains calcium sodium phosphate and calcium magnesium sodium phosphate (CaNaPO4 and Ca13Mg5Na18(PO4)18.
“Medium-scale Plant Experiment of Sewage Sludge- based Phosphorus Fertilizers from Large-scale Thermal Processing”, D. Steckenmesser, C. Vogel & D. Steffens, Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 2019.
Recycling flame retardant boron from insulation to fertiliser
A R&D trial tested pyrolysed (600°C, biochar) produced from boric acid flame retardant treated cellulosic insulation material (produced from recycled paper, Isocell Austria) as a boron fertiliser in pot trials with rape and sunflower. Such boron-treated flame retardant cellulose can be recycled as building insulation material only a few times because of deterioration in fibre length. The pyrolysis reduces the solubility of the boric acid, which is important because boron is a necessary micronutrient for plants, but is toxic if released too rapidly. Challenges to possible industrial implementation include collection of spent insulation material without contamination, PAH (naphthalene) levels in the biochar and regulatory status of the product (end-of-waste, fertiliser authorisation).
“Functional recycling of biobased, borate-stabilized insulation materials as B fertilizer”, O. Duboc, J. Santner et al., Environ. Sci. Technol 2019, 53, 24, 14620-14629, 2019
EC scientists conclude benefits of P-recovery
A study by three European Commission (JRC) scientists concludes that environment and health impacts of phosphorus recycling are “often lower” than for phosphate rock derived fertilisers, even without taking into account phosphate rock reserve depletion. The study models impacts of struvite recovery from biological P-removal sewage treatment, direct use of poultry litter incineration ash as fertiliser, pyrolysis of pig manure, and thermochemical treatment of sewage sludge or meat and bone meal, comparing impacts per kg bioavailable P compared to fertilisers produced from phosphate rock (via the “wet acid” route). The study assumes that, in regions with high livestock or population density, the secondary materials are currently either not recycled (co-incineration) or are used inefficiently (application up to Nitrates Vulnerable Zone maximum levels for manure nitrogen, resulting in over-application of phosphorus): phosphorus recycling is estimated to substitute more than twice as much phosphate rock in high density compared to low density regions (where the secondary materials are assumed to be spread appropriately on farmland as fertilising materials). This assumption “improves” results for regions of high livestock/population density, because the current management routes are thus calculated to have higher emissions and poorer use of P (i.e. more “burdens” in life cycle analysis) than if current use is assumed to be appropriate use on agricultural land. Consequently, their estimated “net” emissions (P-recycling minus current disposal route) are improved. With this calculation, most of the P-recycling materials/routes considered show lower overall emissions to air, water and/or soil than production and use of phosphate rock derived fertiliser. Overall the authors conclude that net societal costs for P-recycling products, for the materials/routes and scenarios considered, are 81%, 50% and 10% lower for sewage sludge, manure and meat and bone meal, compared to use of phosphate rock derived fertilisers (even without accounting for the societal benefits of reducing phosphate rock reserve depletion).
“Environmental and health co-benefits for advanced phosphorus recovery”, D. Tonini, H. Saveyn, D. Huygens, European Commission JRC Seville, Nature Sustainability, vol. 2, Nov. 2019, 1051-1061
Global map of phosphorus recycling potential
As an outcome of the P-RCN (Phosphorus Research Coordination Network, see ESPP Scope Newsletter n°125), scientists have mapped across the world, on a c. 18x11 km grid scale, livestock density and human population, so identifying regions with significant local secondary phosphorus. These are then compared to likely crop fertiliser demand, based on cropland (local % land use under crops) and national phosphorus import and fertiliser use tendencies, to identify zones with phosphorus recycling potential. The modelling concludes that most zones with high manure or sewage phosphorus, in India, China, South East Asia, Europe, North and South America, are close to cropland likely to have significant phosphorus demand. The study aims to enable identification, at a global scale of “hotspots” for phosphorus recycling potential.
“Global Opportunities to Increase Agricultural Independence Through Phosphorus Recycling” Earth's Future, 7, 370–383., 2019
European topsoil maps for P, N, K and C/N
European Commission (JRC) scientists (with University of Basel) have published maps of topsoil properties for Europe, presenting phosphorus, nitrogen, potassium, carbon/nitrogen ratio, pH and cation exchange capacity (CEC), an output of the EU FP7 RECARE project. The maps are based on over 20 000 soil sample tests, from 2009 and 2012 combined with 270 000 data points for land use and land cover and modelling (Gaussian Process Regression), leading to mapping with 250m resolution. Prediction was highest for C/N (R2>0.9) and reasonable for the other properties (R2>0.6) except CEC (R2=0.35). The authors conclude that land use seems to be the main driver for topsoil phosphorus levels, with fertiliser use leading to higher levels in agricultural areas, whereas soil nitrogen is dependent on soil organic carbon, vegetation, climate and soil texture. The results do not aim to replace local monitoring data, but to provide a European level overview. Maps for phosphorus and nitrogen are reproduced below with permission – see the cited publication for the other maps and full details.
“Mapping LUCAS topsoil chemical properties at European scale using Gaussian process regression”, C. Ballabio, P. Panagos et al., Geoderma 355 (2019) 113912
See maps for nitrogen and phosphorus in a published paper or pdf version of this ESPP eNews.
ESPP members
Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews039
Download as PDF
Events
European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference (ESPC4)
CRU Phosphates 2020
RAMIRAN 2020
Calls for papers
Call for texts: phosphorus stewardship and climate change
Public consultations
EU consultation on new Circular Economy policy
EU consultation on new “Soil Health & Food”
Regulatory
EU Green Deal
EU Water Framework Directive objectives confirmed
EU Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive assessment conclusions
Potential for reducing phosphorus pollution in Europe
Food, Drink & Milk BREF published
Nutrient recycling
ICL phosphate recycling to fertiliser
Atria Baltic Sea Commitment on sustainable livestock
Carbon and nitrogen capture
Microalgae from wastewater treatment as organic fertiliser
H2020 water innovation workshop recommendations on nutrient recycling
Experimental production of P4 (elemental P) from phosphoric acid
Studies and research
European Environment Agency calls for end of growth
Financing the circular economy
Nutrients, ocean deoxygenation and climate change
Scientists’ call for action on nitrogen
Review of possible nutrient recovery technologies
Events
European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference (ESPC4)
Registration is now open (on Eventbrite) for the 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference, Vienna, 15-17 June 2020. This 4th ESPC will centre in plenary on business models, company success stories and city and regional actions towards nutrient circularity. Parallel sessions will mix research with application (see below, call for papers). The third day (17th June) will be the 4th European phosphorus R&D day, showcasing R&D into phosphorus recycling and recycled products and new approaches.
Deadline for submission of presentations, success stories, posters is extended to 31st January 2020 (as several authors requested more time). Fifty presentations are already registered, but some opportunities remain.
Hotels are beginning to fill up in Vienna. Register and book now to get better prices!
Registration: Eventbrite
Full details www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
CRU Phosphates 2020
Registration is now open for the 13th CRU Phosphates Conference, 8-10 March 2020 Paris. This is the world’s leading phosphate industry meeting, with over 400 industry participants from 40 countries expected, covering supply, market trends and industry processes and technologies for phosphate rock, fertilisers, animal feed and industrial phosphorus applications. The conference includes outlook presentations by executives of the world’s leading phosphates companies; supply, demand and market trends; new phosphate processing technologies and operating experience. See summary of the 12th CRU Phosphates Conference (Florida, 2019) in ESPP eNews n°33. 10% registration fee discount for ESPP members.
CRU Phosphates 2020, 8-10 March Paris - https://events.crugroup.com/phosphates
RAMIRAN 2020
Europe’s leading manure and organic resources recycling conference, RAMIRAN, will take place in Cambridge, UK, 14-17 September 2020. The RAMIRAN network was established 25 years ago and the biennial conference attracts some 250 participants. This year’s RAMIRAN will look at “Managing Organic Resources in a Changing Environment”, including nutrient utilisation, soil quality, air and water, best practices, treatment technologies and policy. Abstract submission until 1st March 2019.
www.ramiran2020.org
See more upcoming events at www.phosphorusplatform.eu/upcoming-events
Calls for papers
Call for texts: phosphorus stewardship and climate change
ESPP (European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform) and the Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance (North America) are preparing a special SCOPE Newsletter edition on “Nutrients and Climate Change”. This will consist of selected short texts presenting expert perspectives on how climate change will impact nutrient emissions and eutrophication as well as actions to mitigate this. Proposed texts are invited from researchers, companies, stakeholders and any interested party. Around twenty texts will be selected for publication by an editorial committee chaired by Jessica Stubenrauch, Beatrice Garske (FNK Leipzig & University of Rostock), Anders Nättorp (FHNW Switzerland) and Jim Elser (University of Montana). The SCOPE Newsletter is circulated worldwide to 41 000 companies, stakeholders, regulators and media interested in nutrient management, with a detected opening rate of 12-14%, and is published on the ESPP website www.phosphorusplatform.eu Submit your text to be included!
Send us your ideas for action for on nutrients and climate change to appear with the world’s leading experts.
Maximum 600 words. Deadline 29/2/2020 latest.
Call details and instructions here: https://phosphorusplatform.eu/callfortexts
Public consultations
EU consultation on new Circular Economy policy
The European Commission has opened a public consultation, to 20th January 2020, on the Roadmap for a New Circular Economy Action Plan. The proposed Roadmap underlines the economic potential of the Circular Economy, which employs 4 million people with a 6% increase since 2012. Reducing dependency on raw materials, and reducing waste are cited as key objectives, in particular reducing landfill and incineration of municipal waste. Objectives indicated include developing the market for recycled materials, developing skills and investments, improving legal certainty. Actions to be considered include supporting design for recycling and preventing environmentally harmful products, regulating green claims and information on sustainability. The Roadmap cites as priority sectors “opportunities for closing loops for biological materials”, textiles, construction, electronics, plastics and packaging.
EU public consultation on the Roadmap for a New Circular Economy Action Plant, open to 20th January 2020
https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/initiatives/ares-2019-7907872
EU consultation on new “Soil Health & Food”
The EU has opened a public survey, to 19th January 2020, on the Horizon Europe ‘Mission’ on “Soil Health and Food”. This consultation targets mainly individuals or organisations for a simple opinion (around 15 rapid-to-answer questions) on what are key issues around soil health. ESPP will submit input underlining the importance of nutrients and of soil carbon, and the links between soil quality and nutritional value and safety of food.
EU survey on “Soil Health and Food” Horizon Europe Mission, open to 19th January 2020
https://ec.europa.eu/eusurvey/runner/mission-soil-health-and-food
Regulatory
EU Green Deal
The new European Commission published its “Green Deal” on 11th December 2019, a 24-page outline of political objectives plus a 4-page “Roadmap” (list of policy actions with dates). The Green Deal is now submitted to the European Parliament and Council (Member States). Key elements are an objective of zero net greenhouse emissions by 2050, implemented by a European Climate Law, a resource-efficient economy and a Sustainable Europe Investment Plan. The Green Deal also aims for “zero pollution”, restoring biodiversity, sustainable mobility and “farm to fork: fair, healthy and environmentally friendly food system”. A Climate Pact will be launched in March 2020 to engage citizens and give them a voice. A “clean circular economy” is one of the seven themes of the Green Deal, with a new EU “circular economy action plan” for March 2020. This may include “legal requirements to boost the market for secondary raw materials, with mandatory recycled content” and an “EU model for separate waste collection”. Nutrients are not, however, in the priority sectors listed (packaging, plastics, batteries, vehicles, construction materials, electronics, textiles). Nutrient management and the circular economy are however cited as an objective of the “farm to fork” objectives, where the roadmap includes “Measures, including legislative, to significantly reduce the use and risk of … fertilisers” (2020-2021). The objective to “reduce pollution from excess nutrients” is also cited under the zero pollution objective (action: zero pollution for water, air and soil: 2021).
European Commission press release, IP/19/6691, 11th December 2019 “The European Green Deal sets out how to make Europe the first climate neutral continent by 2050, boosting the economy, improving people's health and quality of life, caring for nature, and leaving no one behind”
European Commission Communication Brussels, COM(2019) 640 final, 11th December 2019 “The European Green Deal” (28 pages)
EU Water Framework Directive objectives confirmed
The European Commission has published (10th December 2019) the “Fitness Check” of the EU Water Framework Directive (with the Environmental Quality Standards, Groundwater and Floods Directives). The Commission’s conclusions maintain and confirm the Water Framework Directive’s objectives, in particular the 2027 deadline, by when Member States must ensure that all water bodies (lakes, rivers and groundwater) achieve ecological quality standards (“good” status). These conclusions have been welcomed with relief by NGOs and scientists, who had feared that the WFD deadlines might be delayed, and are coherent with the ambitious objectives of the new European Commission’s “Green Deal”. The public enquiry for this Fitness Check received an exceptionally high 370 000 responses. The Commission underlines that no substantial progress has been made over recent years in water bodies’ overall quality status, and that only half of water bodies had achieved good quality by 2015. The Commission notes that achieving quality objectives will requires reducing pressures, restoration (e.g. morphological), full implementation of the Nitrates Directive and of the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive and better integration of action in agriculture and transport. Diffuse pollution of nutrients (phosphorus, nitrogen) from agriculture are identified as a major challenge: “Around 38% of the EU’s surface water bodies are under pressure from diffuse pollution (of which agricultural production is a major source (25%))”. Failure to achieve the WFD’s objectives is considered to be due to insufficient funding, slow Member State implementation and insufficient integration of environment into other sectoral policies. Actions to address these should include working on best practices for cost-recovery, reduction of pollutants at source and green infrastructure.
SWD(2019) 440 European Commission summary of the Fitness Check of the Water Framework Directive (and other Directives) 10th December 2019 (4 pages)
SWD(2019)439 Water Fitness Check, full 10th December 2019 (184 pages)
EU Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive assessment conclusions
The European Commission has published conclusions of the “Assessment” of the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive (UWWTD 1991/271), an assessment carried out independently from the water policy REFIT (see above) and based on an in-depth JRC and OECD study and specific public consultations. The UWWTD assessment concludes that the Directive has been effective, largely because of the “clarity and simplicity of its requirements”, that benefits outweigh costs, that administrative costs are negligible compared to costs and benefits, that it is coherent with other water policy and that there is widespread recognition that the Directive is still needed and that withdrawing it would have negative impacts. The Directive is estimated to have been successful in reducing pollution, with wastewater BOD (biochemical oxygen demand), nitrogen and phosphorus reduced by 61%, 32% and 44% from 1990 to 2014. However, full compliance is still not achieved in a number of Member States: full compliance for phosphorus would reduce current total emissions to surface waters by over 13.5%. A further 250 billion € needs to spent in the EU to 2030 to maintain and achieve full UWWTD compliance. Nonetheless, the Directive is assessed to be cost effective, with total EU annual capital and operating costs at 18 bn€/y compared to benefits or nearly 30 bn€/y. Challenges which should be assessed are identified as: improving cost-recovery (water tariffs), better collection and treatment of stormwater overflows and urban runoff, emerging contaminants (pharmaceuticals, microplastics), more coherent definition of eutrophication ‘Sensitive Areas’ by Member States, Circular Economy potentials (control at source of pollutants to facilitate agricultural use of sludge and water reuse) and improving treatment wastewater from smaller agglomerations and non-connected households (these place significant pressure on over 10% of Europe’s water bodies). The assessment concludes that the Directive has led to innovation so that today eight of the world’s top fifteen water businesses are EU-based.
“Evaluation of the Council Directive 91/271/EEC of 21 May 1991, concerning urban waste-water Treatment”, SWD(2019) 700 final, 13th December 2019 (186 pages)
Potential for reducing phosphorus pollution in Europe
The JRC study (Pistocchi et al. 2019) accompanying the European Commission’s assessment of the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive (UWWTD), see above, provides an estimate (fig. 67, p86) of reductions in loads to the environment of phosphorus, nitrogen, BOD and coliforms which would result from full enforcement of the UWWT Directive. For phosphorus, this avoidable load is estimated to be just over 50 million p.e. (person equivalent), broken down as 20 M p.e. from non compliant agglomerations, around 15 M from small agglomerations and scattered dwellings, around 10 M from combined storm overflows (CSOs) and around 5 M p.e. from urban runoff. It is emphasised that the UWWTD only addresses loads from municipal wastewater. Estimates are given (from Vigiak 2019) for total 2019 loads of BOD to EU water bodies, suggesting 34% from livestock, 31% from sewage works and scattered dwellings and 20% from urban runoff (rest: industry, forestry). A comparable estimate is not provided for phosphorus or nitrogen.
“Water quality in Europe. Effects of the urban wastewater treatment directive: a retrospective and scenario analysis of Dir. 91/271/EEC”, Pistocchi et al. (JRC), 2019, study
“Predicting biochemical oxygen demand in European freshwater bodies”, Vigiak et al. (JRC), Science of The Total Environment, vol. 666, pp. 1089-1105, 2019
Food, Drink & Milk BREF published
The finalised BAT BREF for the “Food, Drink and Milk” industries (FDM) has now been published on the EU JRC website. Under the Industrial Emissions Directive, the BAT specifications in this document now become obligatory for all concerned FDM production sites. During the preparation discussions, ESPP underlined the importance of phosphorus stewardship, see ESPP eNews n°28. Under 17.1.6 (Resource efficiency) BAT 10, it is specified that “Phosphorus recovery as struvite” is BAT for “waste water streams with … high total phosphorus content (e.g. above 50 mg/l) and a significant flow”. Other BAT techniques indicated are anaerobic digestion, appropriate use of residues in animal feed, appropriate use of wastewater in agriculture to valorise nutrients and/or water.
BAT BREF for the “Food, Drink and Milk” industries (FDM) 2019
Nutrient recycling
ICL phosphate recycling to fertiliser
ICL Fertilizers, Amsterdam, has published a video presenting the new installations enabling use of sewage sludge incineration ash and bone meal ash as input materials for phosphate mineral fertiliser production. The phosphate recycling unit includes three new silos and input systems, enabling mixing of the ashes with phosphate rock in the chemical reaction phase with sulfuric and phosphoric acid, in the factory’s existing 550 000 t/y phosphate fertiliser production process. As well as reducing dependency on non-renewable phosphate rock resources, recycling of secondary phosphate-containing materials enables reduced transport and so reduced carbon footprint. ICL states as its objectives to be a frontrunner in phosphate recycling, with the ultimate goal of reaching a fully closed phosphorus loop.
ICL P-recycling video, 3’20’’ YouTube
Atria Baltic Sea Commitment on sustainable livestock
Atria, Finland, is a leading Nordic food company, with nearly 5 000 staff and a range of fresh and processed meat products. The company, with its A-Rehu contract farmers and contract producers, aims to achieve carbon neutrality by 2035. Atria has now also made a five year Commitment with the Baltic Sea Action Group (BSAG) as part of its sustainability and circular economy objectives. The Commitment aims to reduce the environmental impact of livestock production by, e.g. optimisation of feeding, recycling of food industry by-products as feed, nutrient recycling. Cooperation with arable farmers supplying animal feeds will aim to improve manure application and crop rotation and to increase land use efficiency and domestic protein crop production (to reduce the carbon footprint of imported soya). Conservation agriculture and other practices will be developed to improve soil health and carbon sequestration, by training of Atria’s own experts, sharing of best practices and communication of research results.
Press release “Atria and BSAG to cooperate”, 17 December 2019
Carbon and nitrogen capture
The benefits for soil, plant and soil microbes of an organic fertilising material produced by carbon and nitrogen capture technology were tested. The CCU (carbon capture and utilisation) technology developed by CCm is presented in ESPP’s SCOPE Newsletter n°134. Ammonia solution (recycling of nitrogen by stripping from e.g. digesters) is reacted with calcium nitrate, then with CO2 and a secondary organic (cellulosic substrate), producing calcium carbonate which acts as a binder, (as well as being a plant nutrient) enabling production of pellets containing nitrogen and organic carbon. The resulting product was tested using two different soils (peat compost, mineral soil), measuring soil characteristics, plant growth (30 day pot trials with wheat with CCm product dosed at 0 – 7 g/l soil) and soil microbial development (after soil sterilisation). Results showed that soil water retention was doubled in the peat compost with 25g CCm/l soil and soil matric potential was significantly improved (soil plant water availability: the force with which water is held by the soil matrix, as measured by a tensiometer). Wheat plant biomass showed c. 40% increase at 3 gCCm/l-soil (statistically significant), but with not such a large increase at 6 g/l (but still higher than without CCm): this is probably related to the nitrogen content of the CCm and possibly other nutrients (in the recycled organic substrate) as well as to improved soil properties. The CCm process shows interesting potential to valorize to soil both carbon and nutrients in organic wastes, whilst fixing further atmospheric nitrogen and providing a soil sink for industrial CO2.
“Sustainable soil improvement and water use in agriculture: CCU enabling technologies afford an innovative approach”, J. Lake et al., Journal of CO₂ Utilization 32 (2019) 21–30
Microalgae from wastewater treatment as organic fertiliser
Microalgae biomass of two different origins, after simple drying, was tested as an organic fertiliser for container-grown tomatoes in a greenhouse test (3 months), looking at tomato plant growth, fruit harvest quantity and quality. The microalgae biomass came from (a) flocs harvested from an outdoor raceway pond operated for batch treatment of wastewater from a freshwater fish cultivation aquaculture system and (b) production in outdoor photoreactors using marine water and flue gas CO2 and residual heat from landfill biogas combustion The dried microalgae biomass contained 0.6 and 1.3 %P (a and b), 2.4 and 8% N, 0.2 and 1.4 %K, 20 and 0.2% calcium and various microelements. Fertiliser effectiveness was compared to a liquid inorganic fertiliser adapted to tomatoes and a blend of two solid organic commercial fertilisers (Frayssinet, France) with potassium, magnesium and sulphate added to ensure comparable macronutrient ratios. The microalgae were applied assuming a 33% N mineralisation rate. The four treatments gave similar plant growth, but a lower fruit yield (wet weight) with the organic fertiliser, and very much lower still (< 50%) with the microalgae. Tomato quality (sugar and carotenoid content) were significantly higher with the organic fertiliser and the microalgae. The authors suggest that the significantly lower tomato productivity may be related to increased salinity with the organic fertilisers and microalgae.
“The use of microalgae as a high-value organic slow-release fertilizer results in tomatoes with increased carotenoid and sugar levels”, J. Coppens, J Appl Phycol 2015
H2020 water innovation workshop recommendations on nutrient recycling
A workshop on water innovation, organised by four Horizon 2020 projects (SMART-Plant, nextGen, Hydrousa and Project-O) and the European Commission (EASME), see ESPP SCOPE Newsletter n°132, discussed opportunities and challenges for resource recycling from wastewater. The workshop agreed the following recommendations to further nutrient recovery and recycling: promote a positive image for recycling nutrients; need for stable regulatory support; importance of networking of competence, platforms and data benchmarking; difficulties posed by disparate implementation of End-of-Waste in different Member States and regions. The workshop recommended to promote and support nutrient recycling in Horizon Europe, and to develop better coordination of End-of-Waste, Water Policy and Circular Economy policies between Member States.
Report. Post-Conference workshop @IWARR2019. “H2020 Water Innovations for Sustainable Impacts in Industries and Utilities”, SMART-Plant website.
Experimental production of P4 (elemental P) from phosphoric acid
A laboratory-scale study in Japan suggests that elemental phosphorus (P4, also known as “white” or “yellow phosphorus”) can possibly be produced from phosphoric acid using less energy than production directly from phosphate rock. Existing technologies are estimated to consume around 1 500 kWh electricity per tonne P4 produced, operating at around 1400°C. A 32 mm internal diameter, 1.2 m high quartz reactor furnace, heated electrically, was tested, mixing phosphoric acid with activated carbon as substrate (P-source and reducing agent). The furnace was heated to 1000°C in the activated carbon (reducing) zone, with a second reaction zone at 700°C. The authors suggest that phosphoric acid recovered from secondary materials, for example phosphoric acid recovered from steel slag, for which several experimental studies have been published in Japan (see e.g. Iwama et al. 2019).
“Carbothermic Reduction of Phosphoric Acid Extracted from Dephosphorization Slags to Produce Yellow Phosphorus”, R. Yoshida et al., International Journal of Materials and Metallurgical Engineering, Vol:13, No:11, 2019
“Extraction of Phosphorus and Recovery of Phosphate from Steelmaking Slag by Selective Leaching”, T. Iwama et al., ISIJ, 2019
Studies and research
European Environment Agency calls for end of growth
The EEA (European Environment Agency) “State of the Environment 2020” report says “change of direction (is) urgently needed to face climate change challenges, reverse degradation and ensure future prosperity” and that “Europe will not achieve its sustainability vision … by continuing to promote economic growth and seeking to manage the environmental and social impacts”. The new European Commission Vice-President, Frans Timmermans, responded that the EU needed an urgent paradigm shift, and the new Environment Commissioner, Virginijus Sinkevicius, indicated that priorities are biodiversity, the circular economy and zero pollution. The EEA report points to phosphorus and nitrogen cycles as both exceeding Planetary Boundaries, underlining that diffuse emissions of both P and N to water remain a problem (62% of EU ecosystems are exposed to levels of nitrogen beyond safe tolerance) and that this requires more coherent policies for agriculture, transport, industry and waste water treatment, including a wider food system perspective
See: ENDS 4/12/2019 and EEA “State of the Environment 2020”
Financing the circular economy
The European Commission has published an Expert Group report on circular economy (CE) financing, concluding that risk, and perception and assessment of risk, are the main challenge to finance of CE projects. The report develops recommendations for financial institutions, for project promoters and for policy makers. These are based on the following general conclusions: level playing field, value chain collaboration and participation of end-users, economic integration of externality costs and product longevity, financing knowledge and innovative first-movers. Recommendations to the financial sector are to define definitions, taxonomy and tools to measure circularity, risk analysis of linear models, financial risk sharing and increasing awareness. Project promoters should identify circular sources of revenues, collaborate with other circular economy communities, disclose environmental and social benefits and develop staff training and knowledge. Recommendations to financial decision makers are to develop reporting standards for risks of linear business models, define definitions and taxonomy of circularity, establish technical and financial advisory services to support circular economy projects and to prioritise circular economy projects within the InvestEU fund. Recommendations to policy makers are to create a framework favorable to and facilitate the circular economy, including: define metrics, develop national and regional circular economy strategies linked to other policies, set CE targets, create collaborative platforms, remove subsidies to linear systems, implement EPR extended producer responsibility, fix sunset dates for landfill, provide fiscal incentives, and create markets via public procurement.
“Accelerating the transition to the circular economy. Improving access to finance for circular economy projects”, European Commission, DG Research and Innovation, March 2019 (56 pages) ISBN 978-92-79-99324-4
Nutrients, ocean deoxygenation and climate change
A 580 page report by IUCN (International Union for Nature Conservation) assesses evidence for ocean deoxygenation across the world, links to eutrophication, to climate change and ocean warming and to algal blooms, impacts on ecological systems, fisheries and on people, perspectives and actions needed. Water oxygen concentrations are critical to fish and marine life, because it is much more difficult to breath in water than in air (there is much less oxygen in a given volume of water). Global ocean oxygen content is estimated to have fallen 1-2% since the mid twentieth century. The number of low oxygen ocean sites has increased to over 500 over recent decades, and climate warming is expected to exacerbate this. Ocean deoxygenation can be attributed to two causes: climate change and ocean warming, which lead to an overall slowdown in marine circulation and so lower uptake of oxygen to seawater from the atmosphere; and nutrient inputs, from atmospheric nitrogen deposition and land runoff of nitrogen and phosphorus (eutrophication) in coastal areas world-wide, leading to oxygen consumption by algae and then to oxygen deficiencies near the sea bed. Remobilisation of phosphorus and iron from sediment particles in low oxygen conditions can further accelerate the process (feedback loops). Impacts of ocean deoxygenation are regionally very variable, and are highly critical in semi-enclosed seas (e.g. Baltic, Black Sea, Gulf of Mexico) and the EBUS (Eastern Boundary Upwelling Systems (equatorial and coastal regions of the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans). The report underlines that ocean deoxygenation and climate change are strongly interlinked, and that the key contributors to both are the same: agriculture and burning of fossil fuels and that a key action is to address nutrient inputs to rivers and oceans from septic systems and wastewater treatment plants, fertiliser run off, livestock manure, and atmospheric deposition of nitrogen from the burning of fossil fuels.
“Ocean deoxygenation: Everyone’s problem. Causes, impacts, consequences and solutions”, D. Laffoley, J. Baxter and 67 scientist experts, IUCN, ISBN: 978-2-8317-2013-5, 2019
Scientists’ call for action on nitrogen
More than 150 scientists have signed a call for “urgent action on nitrogen pollution”, addressed to the United Nations. Currently, 80% of nitrogen used in agriculture is lost, that is more than 200 million tonnes of nitrogen per year, at a cost of 200 US$ billion, adding to nitrogen oxides generated by energy, industry and transport (combustion processes). Actions called for include more efficient use of fertilisers and manures, cutting food waste, reducing meat and dairy consumption and new technologies for nitrogen capture from transport and from fossil fuel burning. The initiative is led by CEH, Edinburgh, Scotland and the INMS (International Nitrogen Management System).
“Global action on nitrogen is essential to tackle the current environmental crisis”, INMS 23rd October 2019
Review of possible nutrient recovery technologies
A nineteen page review outlines a wide range of phosphorus and nitrogen recovery technologies for wastewater, providing some 200 references. P-recovery technologies addressed include: ion exchange / adsorption, electrodialysis, magnetic microsorbants, reactive filtration media (e.g. polonite, zeolites), urine separation, struvite precipitation, metal phosphate precipitation, electrochemical (sacrificial anode, dimensionally stable anode DSA), biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) and then land application of biosolids, algae harvesting. Nitrogen recovery technologies addressed include: ion exchange/adsorption of ammonium (e.g. using zeolites or clinoptilolites), electrochemical and microbial fuel cells, struvite precipitation, stripping, gas permeable membranes, conversion to livestock feed or protein by heterotrophic microorganisms. The authors underline that only a few of these processes result in a directly useable product (e.g. struvite, considered a “good fertiliser”), challenges of contaminants in the recovered product, and that all processes work better if nutrients are concentrated (e.g. by urine separation or EBPR). A table summarises ‘pros and cons’ of the different processes.
“Technologies for Recovering Nutrients from Wastewater: A Critical Review”, M. Perera et al., Environmental Engineering ScienceVol. 36, No. 5, 2019
ESPP members
Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews038
Download as PDF
Events
CRU Phosphates 2020
European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPC4)
Calls for papers
Call for papers ESPC4
Call for texts: phosphorus stewardship and climate change
Nitrogen regulations and “SafeManure”
Draft EU criteria for recycled manure products (Nitrates Directive)
Emission Ceilings Directive: ammonia
Germany tightens regulations on manure and fertiliser use
Netherlands crisis package to cut nitrogen emissions
Digestate and compost
Characteristics of digestate in Austria
European Compost Network promotes soil organic carbon
Ongoing discussion of “compostable” plastics
Platforms and networking
Proposals for Canada Nutrient Recovery and Reuse Framework
Scientific opinion: training for nutrient sustainability
Recycled fertilisers
Recovered struvite improves soil fertility in organic farming
ReFARM project will valorise carbon and nutrients from manure
Different qualities of recovered struvite
Wastewater grown algae tested as fertilisers
Paris: public tasting of urine-fertiliser grown bread
Science and research
LIFE pilot tests electrodialysis for nitrogen removal and recovery
Could urban agriculture feed the world
Conceptual framework for evaluation of organic fertilisers
Microplastics in soil shown to impact plants
Microplastics in soil shown to impact earthworms
Overview of national phosphorus flow studies (P-SFAs)
ESPP members
Stay informed
Events
CRU Phosphates 2020
Registration is now open for the 13th CRU Phosphates Conference, 8-10 March 2020 Paris. This is the world’s leading phosphate industry meeting, with over 400 industry participants from 40 countries expected, covering supply, market trends and industry processes and technologies for phosphate rock, fertilisers, animal feed and industrial phosphorus applications. The conference includes outlook presentations by executives of the world’s leading phosphates companies; supply, demand and market trends; new phosphate processing technologies and operating experience. See summary of the 12th CRU Phosphates Conference (Florida, 2019) in ESPP eNews n°33. 10% registration fee discount for ESPP members.CRU Phosphates 2020, 8-10 March Paris - https://events.crugroup.com/phosphates
European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPC4)
Registration is now open (on Eventbrite) for the 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference, Vienna, 15-17 June 2020. This 4th ESPC will centre in plenary on business models, company success stories and city and regional actions towards nutrient circularity. Parallel sessions will mix research with application (see below, call for papers). The third day (17th June) will be the 4th European phosphorus R&D day, showcasing R&D into phosphorus recycling and recycled products and new approaches.Registration: Eventbrite
Full details www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
See more upcoming events at www.phosphorusplatform.eu/upcoming-events
Calls for papers
Call for papers ESPC4
The call for abstracts and posters is now open (closes 31/12/2019) for the 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference, Vienna, 15-17 June 2020. Abstracts are invited for presentations at the six parallel sessions, for plenary success story mini-presentations, for posters or for stands. The parallel session themes are: economy (of phosphorus sustainability and nutrient recycling), enhanced efficiency fertilisers, sustainable phosphorus removal from waste streams, R&D cooperation and platforms, taking R&D developments through to the market and phosphorus sustainability perspectives. Proposed success story mini-presentations (3 minutes, plenary) should present your company, local authority (city, region …) or stakeholder successes in implementing phosphorus recycling or phosphorus management. Posters and stands can address any subject related to nutrient sustainability.Full details www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
Call for texts: phosphorus stewardship and climate change
ESPP (European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform) and the Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance (North America) are preparing a special SCOPE Newsletter edition on “Nutrients and Climate Change”. This will consist of selected short texts presenting expert perspectives on how climate change will impact nutrient emissions and eutrophication as well as actions to mitigate this. Proposed texts are invited from researchers, companies, stakeholders and any interested party. Around twenty texts will be selected for publication by an editorial committee chaired by Jessica Stubenrauch, Beatrice Garske (FNK Leipzig & University of Rostock), Anders Nättorp (FHNW Switzerland) and Jim Elser (University of Montana). The SCOPE Newsletter is circulated worldwide to 41 000 companies, stakeholders, regulators and media interested in nutrient management, with a detected opening rate of 12-14%, and is published on the ESPP website www.phosphorusplatform.eu Submit your text to be included!Send us your ideas for action for on nutrients and climate change to appear with the world’s leading experts.
Maximum 600 words. Deadline 31.01.2020 latest.
Call details and instructions here: https://phosphorusplatform.eu/callfortexts
Nitrogen regulations and “SafeManure”
Draft EU criteria for recycled manure products
The European Commission (JRC) has circulated for comment (deadline 16 December) first DRAFT proposed criteria for recycled manure products (“RENURE” – “Safemanure”). The criteria would define when nitrogen-containing recycled nutrient materials, recovered from manure, would NOT be treated as manure in Nitrates Directive Vulnerable Zones (that is, NOT subject to lower nitrogen application limits than for synthetic fertilisers).NOTE: this concerns the Nitrates Directive implementation (art. 2g), and is not related to the implementation of the EU Fertilising Products Directive, nor to the STRUBIAS discussions.
The main proposed RENURE criterion is that either total organic carbon/total nitrogen ≤ 300% or mineral-N/total-N ratio ≥ 90%. This criterion is based on sample testing and biogeochemical modelling of five different materials recovered from manure: scrubbing salts, “mineral concentrate”, liquid digestate, pelletised liquid digestate, pelletised solid digestate. ESPP raises questions about this criterion because it seems that a mixture of 90% raw manure + 10% urea would pass (whereas such a material, which is essentially “manure”, should be excluded, as is specified page 91).
The modelling suggests that use of the solid-fraction digestate products (which pass the proposed criterion) would lead in the long term to a reduction of 14-18% in crop NUE (nitrogen use efficiency), and so to probably a comparable level of increase in nitrogen soil leaching. The liquid fraction digestate as modelled also gives a lower NUE (and higher leaching), but not statistically significant.
ESPP regrets that other recycled materials from manure, for which full-scale recovery processes are today operational, are not included in this modelling (e.g. manure-recovered struvite, manure biochar), even if the nitrogen component of these is low.
There are also questions concerning analysis for the N-mineral criterion. Analysis may not be feasibly applicable to many recovered materials, because the analysis methods indicated (page 92: EN ISO 11732:2005, EN ISO 13395:1996, ISO/CD 23696 and ISO 10695:2000) are applicable to solutions in water, whereas the nitrogen in recovered materials may not be water soluble (e.g. struvite, solid materials containing organic nitrogen). Indeed, the JRC report notes (page 93) that “DG GROW has also requested the European Standardisation to develop a method for the determination of the organic N content.” The proposed criterion may thus, for many materials, rely on development of a future test method which today does not exist.
ESPP proposed in 2017, after consultation of experts and stakeholders, a simpler criterion: organic carbon (TOC) < 1% of dry matter. This TOC criterion is now validated by co-decision of Parliament and Council in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation (2019/1009) as the definition of a “Mineral Fertiliser”. ESPP regrets that this criterion has not been tested in JRC’s modelling.
The JRC report notes the significant presence of pharmaceuticals in manure and in processed manure products (such as digestates), e.g. tetracyclines, sulphonamides and fluoroquinolones at 0.01 to 23 mg/kg wet weight in manure in the EU (Spielmeyer 2018 is cited). JRC note (conclusions, page 3) that fixing limit values for veterinary drugs would have the benefit of inciting their removal in manure processing, but nonetheless conclude that fixing limits would not be appropriate, given the absence of evidence of risks to soil, plants or health.
The only contaminant limits proposed by JRC are: copper 300 mg/kgDM, mercury 1 mg/kgDM and zinc 800 mg/kgDM. This limit for mercury is the same as in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation FPR (for both organic and mineral fertilisers). For copper and zinc, however the proposed limits are lower than in the FPR (for mineral fertilisers, 800 and 1500 mg/kgDM Cu and Zn). ESPP notes that such differences in limits between regulations are liable to create market confusion. We suggest instead to specify that RENURE products must be certified under either applicable national or EU fertiliser regulations (so used by farmers under “Product” status and not “Waste” status). Use of RENURE products, under the Nitrates Directive, is more restrictive than general fertiliser regulation, so it could maybe be assumed that regulatory contaminant limits applicable to all fertilisers are adequate.
ESPP welcomes that the JRC report underlines the need for specific regional application and storage guidance for farmers, under Nitrates Directive Vulnerable Zone Management Plans, including addressing losses to air (page 4). This should include appropriate management of the phosphorus content of the RENURE product.
ESPP further notes that the JRC report does not address the important question of Nitrates Directive classification of products for which manure is only a small proportion of input material. At present, there is ambiguity: when a small amount of manure is taken in by an anaerobic digester then the whole output digestate may be classified as “processed manure” (and subject to Nitrates Directive limitations).
Comments are invited by JRC on the Safemanure interim draft report until 18 December. Comments can be submitted ONLY using the JRC excel form circulated to stakeholders. ESPP will be submitting comments. If you have comments, we can transmit them to JRC, if you send to us by 12 December latest, clearly specifying for each comment the relevant page and line number in the JRC report.
SAFEMANURE draft report “Developing criteria for safe use of processed manure in Nitrates Vulnerable Zones above the threshold established by the Nitrates Directive” (Interim Report), European Commission - Joint Research Centre (JRC), D. Huygens et al., September 2019. Online here: http://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/regulatory
Emission Ceilings Directive: ammonia
The European Commission has published its 2019 (for 2017) report on the National Emissions Ceilings Directive (NEC), which covers five emissions (nitrogen oxides, ammonia, sulphur dioxide, non-methane volatile organic compounds NMVOCs and fine particulates PM2.5) and implements the EU’s commitment to the Gothenburg Protocol to the UNECE Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution Convention (LRTAP). Ammonia emissions are largely related to livestock and manure management, and so actions taken to address these emissions strongly impact phosphorus reuse. Six Member States exceeded their ammonia emissions ceilings in 2017: Austria, Croatia, Germany, Ireland, The Netherlands and Spain. In total, the EU was below its ammonia emissions target, but to achieve the 2030 reduction commitment will require a total 16% reduction.“NEC Directive reporting status 2019”, European Environment Agency (EEA), 28th June 2019
Germany tightens regulations on manure and fertiliser use
Following the European Court of Justice ruling in 2018 that Germany had not respected the EU Nitrates Directive (see ESPP eNews n°24), Germany already issued a tightened Fertiliser Ordinance in 2017 (not considered in the 2018 judgement), and has now submitted proposals to Brussels to further tighten regulations on fertiliser and manure use. Proposed changes include: longer non-fertilisation periods for grassland, increased distance from surface water, tighter limits for use on slopes or on frozen ground and actions to reduce phosphorus losses to water bodies, including a complete ban on phosphorus fertilization from 1st December to 15th January.Germany has also published its National Air Pollution Control Programme, aiming to reduce atmospheric emissions, including of ammonia (see above, NEC Directive). This specifies that by 2025 liquid fertilising products must be injected and/or acidified (this presumably concerns manure, but also digestates, etc.). This alone represents over ¼ of the ammonia emissions reduction objective defined by the law
Nitrates Directive information thanks to Jana at the German Phosphorus Platform DPP
“Nationales Luftreinhalteprogramm des Bundesrepublik Deutschland” (German national air pollution control programme), 22nd May 2019
Netherlands crisis package to cut nitrogen emissions
Following the national High Court decision cancelling of part of The Netherlands nitrogen policy (ESPP eNews n°35) in May this year, the government has announced an emergency package of emission reduction measures. The High Court decision has blocked some 18 000 construction projects, including roads, airport extensions, wind farms and housing. The Dutch research institute EIB is reported to estimate that construction output will fall by 8%, losing tens of thousands of jobs, by 2021. The emergency package includes reducing national road speed limits to 100 km/h and cutting the protein levels in animal feeds.“Netherlands cuts speed limit to reduce nitrogen pollution” Reuters date
Digestate and compost
Characteristics of digestate in Austria
A study assesses literature data on some 564 samples of digestate from Austria, from 132 digesters taking agricultural crops or by-products and 27 plants taking wastes (food wastes, manure). These plants are estimated to take around 1 Mt/y ww (wet weight) input, producing 750 000 tww/y of digestate (more than might be expected, because some digesters add rainwater from buildings and silos into the digester). This is around half of the total estimated digestate production for Austria of 1.5 Mtww/y. The digestate showed an average dry matter content of around 8%. The authors note that nutrient content of many of the analysed digestates is too low for classification as “organic fertilisers” under Austrian regulation or under the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation: this is to be expected for the crop material digestates which make up most of the sample. A small number of digestates did show adequate nutrient content (e.g. phosphorus), possibly corresponding to digestates from manures. The contaminant and pathogen levels in the digestates are generally conform to both Austrian and EU Fertilising Product Regulation (FPR) requirements. The authors conclude that digestates cannot general be eligible for fertiliser PFC1 under the FPR, but are generally eligible for PFCs: organic soil improver, growing media, non-microbial biostimulant. ESPP suggests that these conclusions are misleading: firstly, this is possibly not applicable to manure digestates (higher nutrient contents) and secondly low-nutrient digestates (CMC3 or CMC4) can be PFC1 under the EU FPR, by adding nutrients (e.g. mineral nutrients CMC1). On the other hand, demonstrating that a digestate is a biostimulant may be challenging. Also, the authors conclude that it is important to establish legal End-of-Waste criteria for digestate. ESPP reminds that the achievement of FPR CE-Mark status (eligible digestate CMC, PFC criteria, labelling, conformity assessment) establishes European End-of-Waste status, and a regulatory process exists for site permitting of use of digestate from waste as fertiliser in Austria (described in the paper).“Legal requirements for digestate as fertilizer in Austria and the European Union compared to actual technical parameters”, B. Stürmer et al., Journal of Environmental Management 253 (2020) 109756 DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109756
European Compost Network promotes soil organic carbon
ECN (European Compost Network) and ISWA (International Solid Waste Association) have launched a “Manifesto: Save Organics in Soil”. The document underlines the importance of soil as a carbon sink, for supporting food production and other ecosystem services including biodiversity and nutrient and water cycle regulation. ECN indicate that Europe is, after Indonesia, the world’s biggest emitter of CO2 through soil organic carbon degradation, and that Europe is losing some 100 000 ha/y of land to urban sprawl and infrastructures. The EU currently has no policy goals nor coherent policy to reduce soil erosion, increase soil organic matter or reduce soil contamination, although there are elements of policy in e.g. the CAP (agriculture), waste, water and chemicals policies. ECN suggests that EU policy should protect existing carbon-rich soils (e.g. permanent grassland, wetlands), minimise organic carbon losses in all soils, develop the return of stabilised organic carbon to soils (e.g. composts and digestates) and encourage nutrient recycling. See also “Seven ways to save our soils”, The Soil Association UK, in SCOPE Newsletter n°120.“Manifesto: save organics in soils”, ECN, 2019
https://www.compostnetwork.info/s-o-s-soil-initiative-sign-online/
Ongoing discussion of “compostable” plastics
The presence of plastic fragments in composts or digestates can be a significant obstacle to nutrient and organic carbon recycling to soil. A problem being examined by the European Commission is how to regulate this appropriately, in order to ensure possible use of appropriately decomposable plastics only when they do bring benefits (e.g. biowaste bags have been shown to increase food waste separate collection rates and to reduce contamination), but avoid the introduction into composting or digestion of plastics which will not be effectively decomposed in the process.A proposal for decision criteria for defining actions, prepared by consultants EUNOMIA for DG Environment, was presented to a stakeholder meeting on 22nd October 2019. The consultants proposed priority “1” criteria for “the beneficial use of compostable plastic”. Some of these priority criteria concern local waste management conditions: effective waste sorting and treatment in place. Some concern the plastic’s uses: plastic contaminated with food waste (clean plastics should be recycled) or not adapted to recycling or reuse. Other priority criteria concern the plastic product itself: it should not combine compostable and non-compostable plastics, its waste sorting route should be clearly identifiable by the consumer, the term “biodegradable” should not be used, the product should meet EN standards. The consultants note that “compostable” criteria should address both the polymer and also additives in the plastic. ESPP notes that the quality of waste sorting and treatment cannot be guaranteed in all regions, and that it could therefore be argued that plastics should only labelled as “compostable” if they are fully decomposed in industrial composting conditions, in all widely used anaerobic digester conditions, and in household composting, but that they should also be biodegradable in the environment (soil, sediments). This study is ongoing.
ESPP also notes that there is often confusion between “compostable” or “biodegradable” and “biosourced”: in fact, bio-sourced polymers can be either biodegradable or not, and similarly for petro-sourced polymers. Biodegradable and compostable should mean chemical decomposition (to CO2), not disintegration into smaller plastic particles.
Outline of ongoing DG Environment study on ‘Relevance of biodegradable and compostable consumer plastic products and packaging in a circular economy’ here
Platforms and networking
Proposals for Canada Nutrient Recovery and Reuse Framework
A report by IISD (International Institute for Sustainable Development) proposes a Nutrient Recovery and Reuse (NRR) Framework for Canada and a Phosphorus Recovery and Reuse action plan. The report is based on outputs of the stakeholder Forum 8th march 2018 (80 participants). Existing initiatives identified include a fertiliser produced from sewage biosolids approved by the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (municipalities of Guelph, Saint Thomas, Elora in Ontario), Quebec policy banning incineration and disposal of organics to landfill by 2022 accompanied by 560 MCAD subsidy support for waste valorisation such as composting and anaerobic digestion, Lake Winnipeg Bioeconomy Project demonstration of non-point nutrient recycling through biomass harvesting, Lake Erie Action Plan incitement of phosphorus recycling technologies, neighbourhood manure management partnerships (Ontario), Canada strategic fertiliser project (mapping supply, demand and defining responsibilities for recycling). The NRR Framework proposed has the following pillars: information (e.g. phosphorus flow data, social costs), defining strategy, research coordination, establishing a Canadian Nutrient Network, supporting technologies and BMP (best management practices), market and funding mechanisms (including economic incentive policies).IISD “Nutrient Recovery and Reuse in Canada: Foundations for a national framework” 2018, 94 pages, funded by Ontario State, Everglades Foundation and Climate Change Canada
Scientific opinion: training for nutrient sustainability
A short opinion signed by some 40 scientists outlines why training should be put in place to for sustainability professionals to work with science, industry and governments, to equip them with the expertise necessary to develop and implement nutrient sustainability programmes, linking phosphorus, nitrogen and carbon. The scientists underline the need to incorporate resource planning across national and regional regulatory frameworks, in particular targeting the circular economy and phosphorus recovery. They consider that with the Critical Raw Materials policy, the EU can provide leadership. The scientists call to establish a coordinated programme to train, monitor and mobilise professionals in nutrient sustainability, underlining the importance of networks and of industrial internships.“New Training to Meet the Global Phosphorus Challenge”, K. Reitzel et al., Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8479−8481, DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.9b03519
Recycled fertilisers
Struvite improves soil fertility in organic farming
A one-season field trial in 2018 compared recovered struvite to manure on organically managed dairy grassland in Tingvoll, North West Norway (soil pH 5.7 – 6.2). The struvite was from the Hias IKS, Hedmark, Norway sewage works, which operated, for three months, a 10.000 p.e. prototype biological P-removal plant with sludge dewatering using a disc filter, and “P-stripping” (anaerobic conditions causing soluble phosphorus release). Struvite was precipitated from the stripping liquor and the final anaerobic digester output liquor. This Hias IKS prototype achieved dissolved phosphorus outflow levels of 0.17 mg PO4-P/L whereas the sewage works is currently operating phosphate precipitation to 0.4 mgP/l (95% P-removal). In a field trial with 4 replicate plots per treatment, the effect of a single spring application of struvite (40 kgP/ha) was compared to no struvite addition on plots already receiving five different treatments: digested dairy manure or raw dairy manure, at high (220 kgN/h) or low manure application rates (110 kgN/ha) rates, plus control (no manure). In the seven previous years, the fields had received the same manure applications. Results showed that struvite significantly improved clover-grass (ley) yields, especially in the control (no manure) and low manure plots. Importantly, struvite also significantly increased topsoil phosphorus content (measured in September) The authors conclude that struvite can significantly contribute to restoring soil phosphorus levels. This is especially relevant in organic farming systems with restricted access to animal manure. Even in organic dairy cow systems, soil P concentrations tend to decline over time, and some nutrients should be applied to balance those removed in farm products. An article in one of Norway’s national newspapers, “Nationen” summarises the study conclusions, underlining that struvite is today authorised as a fertiliser in many countries, including Norway, and that authorisation in Organic Farming has been recommended by the EU expert committee EGTOP and is pending inclusion of struvite in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation annexes (STRUBIAS).“Ta fosforet tilbake”, Nationen newspaper, 24 September 2019
“Effects of struvite application on soil and plants: a short‐term field study”, Norsøk report vol. 4, nr. 10, ISBN 978‐82‐8202‐091‐6, 2019, T. Rittl, A-K. Løoes et al., http://orgprints.org/36472/
ReFARM: valorising carbon and nutrients from manure
The project ReFARM of Wetsus and funded by EIT Climate-KIC aims to pilot a combination of anaerobic digestion with bio-crystallisation to treat dairy manure and separate nutrients for recycling. Manure is pre-treated with a screw-press into a thin and a thick fraction. The thick fraction has a low nutrient content and can (potentially) serve as a soil amendment to increase organic matter. The thin fraction, containing 80-90% of the phosphorus in dairy manure, will go to a 4.5 m3 pilot up-flow anaerobic sludge bed (UASB) reactor, from which methane and calcium phosphate are recovered. Calcium phosphate precipitation in the reactor will be biologically induced. The effluent of the UASB reactor contains high concentrations of nitrogen and can potentially to be treated with an electrochemical process to recover nitrogen as ammonium.ReFARM is funded by the EU’s European Institute for Innovation and Technology (EIT) under Climate-KIC. The project brings together three Dutch partners: WETSUS, Mulder Agro and Oosterhof Holman. Contact:
Different qualities of recovered struvite
The SUSFERT project (EU Horizon 2020, Bio-Based Industry Joint Undertaking BBI-JU) has published a short report on suitability of different recovered struvites for use as fertilisers. 14 struvite samples were analysed, coming from recovery from solid/liquid separated wastewaters, from UASB (up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket) effluent from potato processing and from municipal wastewater digestate (upstream of solid/liquid separation). Results show variable granule size and size distribution, with struvite precipitated upstream of solid/liquid separation (filtration or centrifuge) showing small granules, poorer quality, lower consistency and granules which are not spherical but instead long rhomboids. Fertiliser blending or marketing (distribution, application) however generally requires homogenous, largely spherical granules > 1mm. Reprocessing struvite which does not achieve these characteristics will be problematic, because granulation general takes place at temperatures >40°C at which struvite molecules will start to decompose releasing ammonia.In addition to recovered struvite as a fertiliser, the SUSFERT project is looking at bio-sourced and bio-degradable coatings for fertiliser coatings (lignosulphates from forestry by-products), probiotics to enhance plant uptake of phosphorus and of iron and siderophores (iron chelating molecules released by certain micro-organisms and which enable uptake of poorly-soluble iron compounds by plants).
SUSFERT SUStainable FERtilisers (Sustainable, multifunctional fertilisers for plant phosphorus and iron supply fitting into existing production processes and EU agricultural practice) www.susfert.eu
Deliverable 1.4 “Recommendations for struvite producers to make their product suitable for use as phosphorous source in fertilisers”, M. Spiller et al. 27/6/2019
Wastewater grown algae tested as fertilisers
Algae harvested from a pilot-scale synthetic municipal wastewater plant was tested as a fertiliser after drying and pressing, as directly harvested (paste) or after extrusion to slow-release pellets with other organic materials and the biosourced polymer polylactic acid (PLA). Results, as well as a literature review and discussion, are presented in an Iowa State University thesis 2018. The plant was a RAB (rotating algal biofilm) system. Fertiliser performance was compared for several crops (maize, French marigold, tomato, daisy) to commercial mineral and organic fertilisers in five month container growth trials. Results showed that the algal materials gave similar fertiliser effectiveness to commercial fertilisers. This confirms previous results from Coppens 2016 and Mulbry 2005 and 2006, using algae harvested from aquaculture and from digested manures.“The horticultural potential of wastewater-grown algae fertilizers”, J Gimondo, thesis 2018 Iowa State University https://lib.dr.iastate.edu/etd/16358
See also “Recycling of manure nutrients: use of algal biomass from dairy manure treatment as a slow release fertilizer”, W. Mulbry et al., Bioresource Technology 96 (2005) 451–458 DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2004.05.026 and “Biofertilizers from Algal Treatment of Dairy and Swine Manure Effluents: Characterization of Algal Biomass as a Slow Release Fertilizer”, W. Mulbry et al., Journal of Vegetable Science, Vol. 12(4) 2006
Paris: public tasting of urine-fertiliser grown bread
The Paris Region OCAPI project (Optimisation of Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus cycles In the city, see ESPP eNews n°22 and n°27) has organised public tasting of bread made from wheat grown with urine as fertiliser, with the participation of the regional Chamber of Agriculture. The urine is collected in separative urinals at festivals and in public places in Paris, and is stored for several months before application. The bread was considered a great success, with the public showing more interest in the address of the baker than in how it was grown, and the tasting was covered by press and TV. OCAPI is also working on the history of collection for recycling of sewage (“night soil”) in Paris, which continued into the nineteenth century; a mapping of toilets which are today not connected to sewerage, agronomic testing of urine compared to mineral fertiliser, analysis of contaminants (including pharmaceuticals), and design and installation of urine-separating toilets.OCAPI Newsletter n°5, Autumn 2019.
Science and research
LIFE tests electrodialysis nitrogen removal and recovery
The EU-funded LIFE-Newbies project (led by ESPP member, WETSUS) has started up a pilot plant in Girona Spain that will recover 1-2 kg NH3-N per day. In this pilot, the ammonia is first separated and concentrated from the wastewater using an electrodialysis cell. This electrodialysis cell consists of multiple compartments separated by ion exchange membranes. Then ammonia-nitrogen from the concentrated stream is recovered using a membrane contactor. This membrane contactor uses a gas permeable hydrophobic membrane (i.e. Trans-Membrane Chemi-Sorption/ammonia membrane stripping) to recover it as concentrated ammonium (NH4+) solution. Initial lab scale tests treating urine with a similar design showed an electrical energy input of ca. 4 kWh/kgN recovered, significantly lower than conventional ammonia recovery technologies. 74% of input ammonia-nitrogen is recovered as ammonia solution (up to 1.5 M (NH4)2SO4), which is suitable for use as fertilizer. The pilot will be evaluated using reject water, source separated urine and landfill leachate as wastewater inputs. This pilot aims to improve the overall performance of the technology through a reduced energy input, improved recovery and product concentration. The final intended product is an ammonia solution above 25 wt% and to provide pre-industrial demonstration scale.EU LIFE-Newbies project: http://life-newbies.eu/
Partners : WETSUS (NL), Catalan Institute of Water Research - IRCA (ES), W&F Technologies (NL), Evides Industriewater (NL).
Could urban agriculture feed the world
A paper from the US, Sweden and Australia provides data on the potential food production of urban agriculture (UA) compared to cities’ food needs, as well as an analysis framework. UA is taken to be food production within the urban area, either outdoors (gardens, urban farms, raised beds) or indoor systems. Collated data from several sources suggest that urban agriculture could product 10-70% of cities’ fruit and vegetable consumption, but <10% of calorific demand. In the past, UA has made significant contributions to food production: 55% of US fruit and vegetables in the 2nd world war Victory Gardens; up to 50% of calorific intake in Cuba by the year 2000 with a government programme of cultivating 10 m2 of urban land per person. The sustainability impacts (land use, water, labour, CO2) for lettuce production by outdoor or indoor urban agriculture in Minneapolis-Saint-Paul are compared to production in California (produces 70% of US lettuces). The California production has the highest land consumption, but lowest labour; indoor urban agriculture has the highest CO2 emissions (nearly one and a half times production and transport from California) whereas outdoor urban agriculture has the lowest CO2 emissions. It is noted that urban food production interacts with land prices in cities. The authors conclude that whether cities could and should be self-sufficient in food production is a simple question but with a complex answer.“Would a sustainable city be self-sufficient in food production”, G. Small, R. McDougall, G. Metson, Int. J. of Design & Nature and Ecodynamics. Vol. 14, No. 3 (2019) 178-194 1755-7445 (online) doi: 10.2495/DNE-V14-N3-178-194
Conceptual framework for evaluation of organic fertilisers
A 100-page report from Wageningen UR, The Netherlands, proposes an outline framework for evaluation of organic fertilisers, looking at characterisation of organic fertilisers, impacts on soil quality (in particular, nutrients and organic carbon), contaminants and risk assessment, economic value to farmers and to land owners. The work is based on literature, expert opinions, and an expert workshop on contaminants. The materials principally considered are manures and slurries, raw, digested and solid/liquid separated, and various composts. Conclusions note the importance of assessment of short- and long-term biodegradability of organic carbon in organic fertilisers, including in the soil; the need for studies on specific soils and crop rotations. A first wide listing of possible contaminants is proposed, but further work is needed to define risk priorities. A challenge is the current absence of methods to define the economic value of soil quality or of organic carbon content, resulting in a value attributed by farmers to the materials considered which is based only on nutrient content.“Development of a conceptual framework to evaluate organic fertilisers. Assessment on soil quality and agronomic, environmental and economic aspects”, O. Schoumans et al., Wageningen University & Research, October 2019, ISBN 978-94-6395-163-0
Microplastics in soil shown to impact plants
A German study has tested in pot trials the effects of six different microplastics, added to soil, on soil characteristics and on development of spring onion (Allium fistulosum) plants. Six different microplastics were added to sandy soil (from Berlin), one primary microplastic (polyamide microplastic beads 15-20 µm d = diameter) and five secondary microplastics: polyester wool, manually cut to average length 5000 µm, d = 8 µm) and high density polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene and polyethylene teephthalate (PET) milled to diameters mainly around 200 – 800 µm. Polyester was added to soil at 0.2% fresh weight, and the other microplastics at 2%. These loadings were considered by the authors to be “relevant for sites exposed to high human pressure” – but this seems to be based on Fuller, 2016, who found 7% microplastics in soil in around an industrial area in Sydney but stated “The microplastic concentrations were related to the vicinity of sample locations to the industrial area”. At the levels of microplastics tested, the authors found significant changes in soil physical parameters, such as increased soil bulk density or increased evapotranspiration (increased water availability). The microplastics also significantly impacted plant growth, but not in consistent directions. Most of the microplastics led to increased plant biomass, in some cases nearly doubled onion bulb dry mass. The authors suggest that this may in some cases result from nitrogen- or phosphorus-containing compounds released from the plastics (additives, unreacted polyamide monomers …) but this is only hypothesis.European Commission, Science for Environment Policy, issue 535, 19th November 2019, “Microplastics alter soil properties and plant performance, Germany” and “Microplastics Can Change Soil Properties and Affect Plant Performance”, A. de Souza Machado et al., Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6044−6052, DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.9b01339
Microplastics in soil shown to impact earthworms
A study from Cambridge, UK, has tested in 1.3 litre pot trials the effects of three different microplastics on rye grass and on earthworms (Aporrectodea rosea). The microplastics were bio-sourced, biologically degradable PLA (poly lactic acid), high density polyethylene HDPE (both average size 65 – 105 µm) and clothing fibres, and were mixed into soil at 0.1%, 0.1% or 0.01% dry weight. Results showed statistically lower rye grass seed germination in pots with PLA or textile fibres, compared to control (no microplastics). All microplastics decreased the MWD (aggregate mean weight diameter) of soil, and HDPE decreased soil pH. Impacts on rye grass growth varied, with shoot length was statistically lower with PLA, root biomass was higher with HDPE, shoot biomass was not significantly different, chlorophyll a/b ratio was significantly different for all microplastic containing pots. Impacts on earthworm growth were however coherent, with significant growth (weight increase) in control pots, but weight loss in pots with microplastic.“Effects of Microplastics in Soil Ecosystems: Above and Below Ground”, B. Boots et al., Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11496−11506, DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.9b03304
Overview of national phosphorus flow studies (P-SFAs)
A review compares information on phosphorus in waste management in 14 national phosphorus flow studies (also 2 others considered), covering Australia, Austria, China, Denmark, Finland, France, Japan, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, South Korea, Sweden, UK and USA. Unfortunately, these studies are not comparable (as some look at only one sector, for example, the UK study only considers wastewater, whereas others include phosphate mining), and manure is not taken into account (whereas it is the largest secondary phosphorus resource). The conclusions of the overview publication suggest very widely varying “waste sector recovery rates”, from over 67% in Finland, and around 50% in Denmark, France and the UK, to below 0.5% in the USA. The USA number is attributed to mining industry wastewater, despite the mining industry having a 91% material use efficiency, but this does not explain why China, which also has phosphate rock mining, is calculated to nearly 40% nor why Finland, which also has phosphate rock mining, is indicated to have zero phosphorus flow from industrial waste. It seems that the only conclusions which can be taken from this publication are that national phosphorus flow studies are often not comparable, and that numbers for “recycling rates” or “recovery rates” depend primarily on how system boundaries are fixed and what is defined to be recycling or recovery.“Determining the potential role of the waste sector in decoupling of phosphorus: A comprehensive review of national scale substance flow analyses”, S. Rahmana et al., Resources, Conservation & Recycling 144 (2019) 144–157, DOI: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.01.022
ESPP members
ESPP members

In this SCOPE newsletter:
Summary of the 3rd IWA
Resource Recovery Conference (IWARR 2019)
- Conference conclusions
- From recovery to market
- Workshop on implementation
- Circular City workshop
- Conference keynotes and context
- Sewage sludge challenges in Italy
- Baltic Bonus RETURN
- Operator resource recovery strategies
- EU funding of water resource recovery R&D
- Looking beyond Europe
- Phosphorus recovery technologies
Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP)
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews037
Download as PDF
Events
CRU Phosphates 2020
European biosolids conference
Calls for papers
Call for papers ESPC4
Call for texts: phosphorus stewardship and climate change
Call for consultants: EIP-AGRI
Study on EU “restrictions” for composts and digestates
DG ENVI study on contaminants in composts and digestates
ESPP new member
PhosAgro joins ESPP
Phosphorus recycling
Global compendium of P-recovery technologies
Communications
SPA blog on farm phosphorus traps
EU circularity rate
JRC: raw materials and Sustainable Development Goals
Business models for resource recovery in developing countries
FAO guidelines on estimating livestock nutrient flows and impacts
Science and research
Journal special issue and blog on phosphorus
EU Critical Raw Materials project on phosphate rock reserves
Clean Water Cluster Event
Iron phosphate for P-removal from sediments and runoff
New fertilisers
Events
CRU Phosphates 2020
Registration is now open for the 13th CRU Phosphates Conference, 8-10 March 2020 Paris. This is the world’s leading phosphate industry meeting, with over 400 industry participants from 40 countries expected, covering supply, market trends and industry processes and technologies for phosphate rock, fertilisers, animal feed and industrial phosphorus applications. The conference includes outlook presentations by executives of the world’s leading phosphates companies; supply, demand and market trends; new phosphate processing technologies and operating experience. See summary of the 12th CRU Phosphates Conference (Florida, 2019) in ESPP eNews n°33. 10% registration fee discount for ESPP members.
CRU Phosphates 2020, 8-10 March Paris - https://events.crugroup.com/phosphates
European biosolids conference
ESPP will moderate the resource recovery session at the AquaEnviro “European Biosolids & Organic Resources Conference”, Manchester (Old Trafford Stadium) UK, 19-20 November. This is Europe’s main conference on sewage sludge management with over 280 participants last year (2018). The water industry is focussed on maximising energy recovery from sewage sludges, whilst retaining the option of agricultural valorisation for treated biosolids. The use of thermal hydrolysis as a pre-treatment in so-called Advanced Anaerobic Digestion (AAD) is increasingly common, but the return liquors from these processes present a number of challenges, particularly in terms of ammonia load (operating experience from Severn Trent and Thames Water sites will be presented). Sessions include biosolids to land, ammonia management, biogas, resource recovery …
European Biosolids & Organic Resources Conference, Manchester UK, 21-22 November http://european-biosolids.com/
Save the date: 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference, Vienna, 15-17 June 2020
www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
See more upcoming events at www.phosphorusplatform.eu/upcoming-events
Calls for papers
Call for papers ESPC4
The call for abstracts and posters is now open (closes 31/12/2019) for the 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference, Vienna, 15-17 June 2020. Abstracts are invited for presentations at the six parallel sessions, for plenary success story mini-presentations, for posters or for stands. The parallel session themes are: economy (of phosphorus sustainability and nutrient recycling), enhanced efficiency fertilisers, sustainable phosphorus removal from waste streams, R&D cooperation and platforms, taking R&D developments through to the market and phosphorus sustainability perspectives. Proposed success story mini-presentations (3 minutes, plenary) should present your company, local authority (city, region …) or stakeholder successes in implementing phosphorus recycling or phosphorus management. Posters and stands can address any subject related to nutrient sustainability.
Full details www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
Call for texts: phosphorus stewardship and climate change
ESPP (European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform) and the Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance (North America) are preparing a special SCOPE Newsletter edition on “Nutrients and Climate Change”. This will consist of selected short texts presenting expert perspectives on how climate change will impact nutrient emissions and eutrophication as well as actions to mitigate this. Proposed texts are invited from researchers, companies, stakeholders and any interested party. Around twenty texts will be selected for publication by an editorial committee chaired by Jessica Stubenrauch, Beatrice Garske (FNK Leipzig & University of Rostock), Anders Nättorp (FHNW Switzerland) and Jim Elser (University of Montana). The SCOPE Newsletter is circulated worldwide to 41 000 companies, stakeholders, regulators and media interested in nutrient management, with a detected opening rate of 12-14%, and is published on the ESPP website www.phosphorusplatform.eu Submit your text to be included!
Send us your ideas for action for on nutrients and climate change to appear with the world’s leading experts.
Maximum 600 words. Deadline 31.01.2020 latest.
Call details and instructions here: https://phosphorusplatform.eu/callfortexts
Call for consultants: EIP-AGRI
The European Commission funded innovation platform “EIP-AGRI” has published a call for consultants/experts to coordinate (including drafting documents) or facilitate events on the following themes: resource management and sustainable soil management, farm resilience capacity and digitisation. Deadline for submission is 9th December 2019.
EIP call for coordinating experts / event facilitators: https://ec.europa.eu/eip/agriculture/en/news/call-interest-would-you-contribute-eip-agri-0
Study on EU “restrictions” for composts and digestates
DG ENVI study on contaminants in composts and digestates
A study commissioned by the European Commission (DG Environment) assesses risks related to contaminants in composts and digestates, and proposes possible “Risk Management” measures (restrictions using the EU Chemical Regulation REACH). ESPP submitted an Access to Information procedure for this document in June 2019, and has now been informed that it is published here (see ESPP eNews n°35).
It should be noted that although both compost and digestate are now exempt from REACH registration (see ESPP eNews n°34), EU-wide restrictions (effectively including bans) can nonetheless be implemented using REACH.
Four possible “Risk Reduction” measures are proposed: EU limits on contaminants in all composts and digestates; ban on use of sewage sludge and/or mechanically separated household organic waste MBT in composts and digestates; specific restrictions where composts or digestates are used as growing media; obligation for two-stage anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. The study appears to suggest that any restrictions for sewage sludge being used in compost or digestate should also be applied to all sewage sludge going to agricultural land.
Legal options discussed include restrictions on all composts and digestates (using REACH), modifications of the EU Fertilising Products Regulation annexes (would only impact CE-Mark composts and digestates), modification of the EU Sewage Sludge Directive or EU Waste Water Treatment Directive. It is ESPP’s understanding that a restriction under REACH could, for example, prevent the placing on the market in Europe (that is sale or use at no cost by any party other than the producer, other than under “waste” regulation) of any compost or digestate containing contaminants above specified limits and/or containing excluded input materials.
“European Commission. Digestate and compost as fertilisers: Risk assessment and risk management options. Final Report”, Ramboll – Peter Fisk – WOOD (referred to in the tender as the “AMEC” study), ref. 40039CL00313, 8th February 2019 https://etendering.ted.europa.eu/cft/cft-document.html?docId=57674
ESPP new member
PhosAgro joins ESPP
Russia-based leading phosphate fertiliser producer, PhosAgro, has become a member of ESPP. PhosAgro is the largest phosphate-based fertiliser producer and one of the leading animal feed phosphate producers in the European continent, and one of the world’s leading integrated phosphate rock and fertiliser producers. PhosAgro’s main products include phosphate rock, 39 grades of fertilizers, feed phosphates, ammonia, and sodium tripolyphosphate. These products are used by customers in more than 100 countries across the world. PhosAgro is the first fertiliser company not producing in the EU to become a member of ESPP, conform to ESPP’s statutes which specify that the association’s activities are related to Europe and admit as members any organisation with activities related to phosphorus sustainability. PhosAgro’s 2025 strategy prioritise sustainable development and high standards in social, environmental and corporate governance performance. PhosAgro’s low-cadmium phosphate-based fertilizers stand out for their high efficiency and their environmental safety. PhosAgro is the first Russian company selected by the UN Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) to implement a global soil protection initiative.
PhosAgro website www.phosagro.ru
Phosphorus recycling
Global compendium of P-recovery technologies
The Global Water Research Consortium has produced a 40-page report summarising technologies currently available worldwide for phosphorus recovery from municipal sewage, summarising how the different technologies integrate into sewage works operation and sludge processing systems. It describes each process, how it functions, the technology readiness level, compatibility with German phosphorus recovery legislation requirements, limitations of application regarding sewage works type and sludge and other information relevant to implementation. Processes considered include P-recovery of dissolved phosphate from liquors by struvite precipitation, HAP (hydroxyapatite) precipitation, calcium silicate hydrate adsorption; release of further phosphorus from sludge to increase recovery potential from liquors (lysis: Cambi, Pondus; bio-acidification: Ostara Wasstrip, Veolia Phosforce). A total of over 20 such technologies are listed. Processes recovering phosphorus directly from sewage sludge considered are: Budenheim Extraphos, pyrolysis, EuPhoRe, Kubota, Mephrec/P.KON. Considered processes taking sewage sludge incineration ash as input material are: Glatt SeraPlant, Ecophos, Remondis Tetraphos, Phos4Life/ZAR Zurich, EasyMining Ash2Phos/CleanMap, Metawater alkali leaching Japan, AshDec.
Global Water Research Consortium http://globalwaterresearchcoalition.net ““Global Compendium on Phosphorus Recovery from Sewage/Sludge/Ash”, Technical Report, March 2019 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331982837_Global_Compendium_on_Phosphorus_Recovery_from_SewageSludgeAsh
Communications
SPA blog on farm phosphorus traps
The Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance, North America, has published another of its online thematic blog series, summarising the potential of phosphorus traps for removing dissolved phosphorus in run-off from fields or subcatchments with legacy phosphorus losses, that is sites where phosphorus losses will remain elevated “for decades” because of accumulated phosphorus in soils. Traps are buried tanks containing materials which adsorb soluble phosphorus from collected runoff. Identified criteria for installation are indicated as: convergence of tile drainage or surface water at a site with vertical height above outflow (hydraulic push through adsorbent), at least 0.2 mgPsolube/l, design to cope with peak flow rates (at many sites, 90% of P is lost in 5% of flow events) and so sufficient space (e.g. 40 tons of adsorbent for 4000 l/minute for a poultry farm). Adsorbent materials are often iron-containing by-products (such as steel slag) but these will not be recyclable, but research into regeneration is underway.
SPA blog “A tool for trapping dissolved phosphorus”, C. Penn, 10/2019 https://phosphorusalliance.org/2019/09/05/chad-penn/ and “Review. A Review of Phosphorus Removal Structures: How to Assess and Compare Their Performance”, C. Penn et al. Water 2017, 9, 583; http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/w9080583
EU circularity rate
An update from Eurostat indicates that the “circularity rate” in the EU reached 11.7% in 2016, slowly progressing up from 8.4% in 2004. The “circularity rate” covers all materials fed into the economy, and is much lower that the “recycling rate” (around 55% in the EU) which considers only wastes. The circularity rate varies from 1.3% in Greece to 29% in The Netherlands, not only because of recycling but also because of higher imports of materials (including fossil fuels) or higher rates of materials extraction (mining), both of which lead to lower circularity rate.
“What goes around comes around – EU circularity rate”, Eurostat, 18th September 2019 https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/products-eurostat-news/-/DDN-20190918-2
JRC: raw materials and Sustainable Development Goals
A European Commission (JRC) Science for Policy publication looks at how raw materials use interacts with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), noting that raw materials are necessary for sustainability objectives (e.g. for production of energy-saving technologies) but that their extraction has significant impacts. The role of forestry is underlined, providing raw materials, as well as ecosystem and climate services, on condition of sustainable forest management. The role of phosphate and potash, in SDG2 (“Zero Hunger”) is noted, by their contribution to agricultural productivity. The importance of EU Raw Materials policies, and also policies for the Circular Economy and minerals conflicts are underlined, as is the need for monitoring.
“Future supply of raw materials must not repeat the sustainability problems of the past”, European Commission (JRC), Mancini et al., 2nd October 2019 https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/en/news/future-supply-raw-materials-must-not-repeat-sustainability-problems-past
Business models for resource recovery in developing countries
An 800 page report from the IWMI (International Water Management Institute) presents business models for energy, nutrient and water reuse in low- and middle-income countries. The report underlines the potential to combine closing nutrient recycling loops, develop a circular economy, recover waste and water treatment costs and develop viable businesses, whilst ensuring the key public service of sanitation. Decentralised solutions may help address the non-availability of funding necessary to establish or upgrade large scale installations. Examples presented adding “night soil” (faeces) in composting of municipal solid waste to improve the nutrient value of the product, using low-cost technology and enabling sale to farmers (Sri Lanka), composting livestock waste (Mexico), public toilet faeces to nutrient-rich compost (Rwanda), faecal sludge use on farm (India), provision of sanitation and processing faeces and urine to organic fertiliser for agriculture (Burkina Faso).
“Resource recovery from waste. Business models for energy, nutrient and water reuse in low- and middle-income countries”, M. Otoo & P. Drechsel, ed., Routledge, ISBN 978-1-315-78086-3, 2018 http://www.iwmi.cgiar.org/Publications/Books/PDF/resource-recovery-from-waste.pdf
FAO guidelines on estimating livestock nutrient flows and impacts
The UN Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) has published LEAP guidelines (Livestock Environmental Assessment and Performance Partnership) on how to assess and account nitrogen and phosphorus flows and life cycle assessment (LCA) for livestock production and supply chains. FAO underlines the importance of these nutrients for the sustainability of agriculture, citing planetary boundaries and that phosphorus is a non-renewable, non-substitutable, finite resource. The aim is to enable identification opportunities to improve nutrient management, improve nutrient efficiency and reduce impacts. ESPP participated in the document development process, underlining the importance of evaluating recycling flows, and the final document does clearly address not only inputs, outputs and losses but also specifically nutrient recycling.
“Nutrient flow and associated environmental impacts in livestock supply chains. Guidelines for assessment”, Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations 2018, 196 pages, ISBN 978-92-5-130901-8 http://www.fao.org/partnerships/leap/publications/guidelines/en/
Science and research
Journal special issue and blog on phosphorus
The Journal of Environmental Quality has published (open access) a special issue on phosphorus with 23 papers, mainly on phosphorus in agriculture and catchment management. The papers are mostly reviews and opinion summaries, rather than new research. A summary (Johnston & Poulton) of 175 years of long-term field experiments at Rothamsted, UK, and at other sites shows the clear link between plant available phosphorus in soil (soil P higher than the critical level related to soil phosphorus buffering capacity) and crop yield, with high fertiliser efficiency when soil P is near the critical level and inputs are slightly higher than offtakes (90 – 55% P-use efficiency). Other papers show the challenges of phosphorus loss mitigation strategies: no single solution or measure fits all, uncertainty of results, time delays. The situation in the Chesapeake Bay is illustrative (Kleinman, Fanelli et al.), despite the management plan, dissolved P is increasing in some tributaries and challenges include legacy P, artificial drainage and livestock density. Several papers present data on P behavior in agricultural catchments, showing that agriculture increases labile P in soils compared to natural vegetation (Neidhardt, Acthen et al.), that agricultural soil P losses occur in both drains and surface runoff (Macrae, Ali et al.) and that high P losses occur with drought and with rainfall events because of resuspension of legacy P in sediments (Bieroza, Bergström et al.). A review of studies (Nash, McDowell et al.) shows that recent fertiliser application can contribute 30 – 80% of P-runoff from grassland, but that this can be reduced to <10% by good management practices. A series of blogs are published to promote the content of this science special issue to a wider audience.
Journal of Environmental Quality special issue on phosphorus, JEQ Volume 48 Issue 5, September-October 2019 https://dl.sciencesocieties.org/publications/jeq/tocs/48/5#h1-SPECIAL%20SECTION:%20CELEBRATING%20THE%20350TH%20ANNIVERSARY%20OF%20DISCOVERING%20PHOSPHORUS%E2%80%94FOR%20BETTER%20OR%20WORSE
Blogs on phosphorus: “The discovery and general uses of phosphorus”, “Why is phosphorus needed on farms”, “What are sources of phosphorus for crops”, “What are the challenges regarding phosphorus use”, “Ten things we can do to manage phosphorus better” https://soilsmatter.wordpress.com/author/soilsmatter2011/ and web story https://www.soils.org/discover-soils/story/reduce-reuse-recycle-the-future-of-phosphorus
EU Critical Raw Materials project on phosphate rock reserves
The EU-funded Expert Network on Critical Raw Materials (SCRREEN) has published a “Report on the Future Use of Critical Raw Materials”. This includes a useful breakdown of use of phosphate rock (2016, worldwide, provided by IFA, International Fertilizer Association), indicating that >80% goes to fertilisers, 7% to animal feeds, <5% to detergents and <1% to human food additives (5-6% other industrial uses). The report underlines that unlike for example fossil fuels, phosphorus cannot be replaced in agriculture because it is essential for plants and animals (although the report does misguidedly add “with current scientific understanding”). The report indicates that world demand for phosphate rock is likely to grow considerably, with increasing world population and in parts of the world increasing animal products in diets, leading to conclude a possible “inelastic supply gap at market in the decade of 2020-2030” and that “current phosphate rock reserves will be depleted in approximately 70 to 140 years”. No mention is made of the environmental impacts of phosphorus use (eutrophication).
SCRREEN (Solutions for CRitical Raw materials – a European Expert Network, Horizon 2020, 2016-2020) “Report on the Future Use of Critical Raw Materials”, L. Tercero Espinoza et al., http://scrreen.eu/results/ and deliverable D2.3 http://scrreen.eu/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/SCRREEN-D2.3-Report-on-the-future-use-of-critical-raw-materials-2.pdf
Clean Water Cluster Event
The Horizon 2020 cluster event, Girona, 22nd October 2019, brought together 12 R&D projects in the field of clean water with themes including phosphorus removal, groundwater nitrates and antimicrobial resistance.
Stefan Peiffer, University of Bayreuth, presented the recently started P-TRAP project (https://h2020-p-trap.eu/) that targets diffuse phosphorus input to surface waters. The project will focus on immobilization of phosphorus in artificially drained agricultural areas as well as long-term stabilization of phosphorus in lake sediments, using iron-containing by-products from drinking water treatment. Also, vivianite and phosphorus-containing Fe(III)oxides recovered from phosphorus “traps” in agricultural runoff will be evaluated as a fertilizer in collaboration with Spanish company Fertiberia.
Sara Johansson, University of Girona, presented her work on phosphorus and potassium recovery from digested sludge liquors developed within the recently finished TreatRec project (https://treatrec.eu/). Published results show that anammox as a nitrogen removal step before struvite precipitation enables the formation of potassium struvite (magnesium potassium phosphate (MgKPO4*6H2O). Granular partial nitritation-anammox sludge can also function as a biological crystallizer and form hydroxyapatite.
Philipp Kehrein, Delft University, presented his work in the Super-W project (https://www.superw.ugent.be/) to identify bottlenecks hindering implementation of treatment and recovery technologies in wastewater treatment plants. His recommendation is that WWTPs increase efforts in value chain development for recovered resources e.g. work with market actors for recovered products.
Daniela Buzica and Anna Marczak, European Commission DG Environment, participated via video link and presented current development in EU water policy. Water and sludge reuse are two of the topics that are being considered in the evaluation of the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive.
“Clean Water”, Horizon 2020 MSCA-ITN cluster event for Horizon 2020 Marie Skłodowska-Curie (MSC) Innovative Training Networks (ITN) projects, Girona, Spain, 22nd October 2019. Jointly organised by the Research Executive Agency (REA) and the Catalan Institute for Water Research (ICRA) https://ec.europa.eu/info/horizon-2020-msca-itn-cluster-event-clean-water_en
Iron phosphate for P-removal from sediments and runoff
WETSUS Netherlands and other partners have received a subsidy from the Dutch scientific organisation NOW (Idea Generator Call) for research into stimulating iron phosphate precipitation, as vivianite (iron II phosphate) from freshwater sediments and waters with high phosphorus loadings. The objective is to remove phosphorus contributing to eutrophication in a potentially recoverable form, because vivianite is magnetic, and because it is easier to separate phosphorus from iron II than from iron III phosphate (so potentially enabling recovery as phosphate salts).
“Subsidy for vivianite research”, WETSUS News September 2019 https://www.wetsus.nl › home › wetsus-news › wetsus-news-september-2019
New fertilisers
Weeks & Hetiarachchi (in the JEQ special issue indicated above) provide a review of new fertiliser technologies, and of their results in use. New fertiliser approaches presented are (1) controlled release fertilisers, using coatings, pH modifiers, scaffolds (loading onto materials such as layered double hydroxides LDH, nano-particles, graphene oxides), organic and organo-mineral matrices and inherent slow-release chemicals (2) “blockers”, intended to inhibit fixation of P onto anions in soils (i.e. calcium, iron, aluminium in soils), including maleic-itaconic polymers and humic substances (from decomposition of organic materials) and (3) inducers, intended to stimulate uptake by crops of poorly available soil P, including oxide nano-particles of anatase (titanium), magnetite (Fe2O), zinc and copper. The authors conclude that in many cases field results do not reflect positive claims from pot trials, mechanisms are complex (impacts on soil chemistry, crop P uptake, soil microbes) and that considerable more work is needed to identify economically and environmentally viable products. The paper does not consider that use of microbes as biostimulants to improve P uptake.
“A Review of the Latest in Phosphorus Fertilizer Technology: Possibilities and Pragmatism”, J. Weeks & G. Hettiarachchi, J. Environ. Qual. (JEAQ) 48:1300–1313 (2019) http://dx.doi.org/10.2134/jeq2019.02.0067
ESPP members

Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP).
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews036
Download as PDF
Events
Waste water phosphorus removal tomorrow: ambitions and reality
CRU Phosphates 2020
Calls for papers
Call for papers ESPC4
Call for texts: phosphorus stewardship and climate change
Policy
EU consultation on Circular Bio-Based Europe Partnership
EU call for expert consultants on fertilising product standards
ESPP input to Horizon Europe programme
EU Critical Raw Materials list update work underway
“STRUBIAS” final report published
Call for experts on nutrient recycling in processed manures
Phosphorus sustainability in action
Italmatch LIFE Trialkyl project successful
Finland gypsum soil treatment project
Research
9th International Phosphorus Workshop (IPW9)
120 days/year of phosphorus needs in food waste
Phosphorus and other metals from sunscreens
PolFerAsh P-recovery process
JRC-led study brings together environmental footprints
New phosphorus materials
Organic fertilisers from sewage sludge
Functionalised cow dung biochar
RECOVER resource recovery processes development Norway
ESPP members
Stay informed
Events
Waste water phosphorus removal tomorrow: ambitions and reality
9th October, Liège, near Brussels. In the context of the current revision of EU water policy (Water Framework Directive, Waste Water Treatment Directive), and with participation of the European Commission (DG ENVI, DG RTI), this workshop will enable dialogue between the water industry, experts and policy makers (EU, national) on perspectives for phosphorus removal: low discharge consents, flexible permitting / emissions trading, P-removal from small sewage works. Register now: https://www.eventbrite.co.uk/e/waste-water-phosphorus-removal-tomorrow-ambitions-and-reality-tickets-60192633788In partnership with / supported by: IWA (the International Water Association), Eureau, CIWEM (Chartered Institution of Water and Environmental Management), Université de Liège and ECSM’19 (European Conference on Sludge Management), Liège 6-8 October 2019 https://events.uliege.be/ecsm2019/ for information on the phosphorus removal workshop, contact

CRU Phosphates 2020
Registration is now open for the 13th CRU Phosphates Conference, 8-10 March 2020 Paris. This is the world’s leading phosphate industry meeting, with over 400 industry participants from 40 countries expected, covering supply, market trends and industry processes and technologies for phosphate rock, fertilisers, animal feed and industrial phosphorus applications. See summary of the 12th CRU Phosphates Conference (Florida, 2019) in ESPP eNews n°33. Early bird registration rate to 31st October 2019.CRU Phosphates 2020, 8-10 March Paris - https://events.crugroup.com/phosphates
See more upcoming events at www.phosphorusplatform.eu/upcoming-events
Calls for papers
Call for papers ESPC4
The call for abstracts and posters is now open (closes 31/12/2019) for the 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference, Vienna, 15-17 June 2020. Abstracts are invited for presentations for the six parallel sessions, for plenary success story mini-presentations, for posters or for stands. The parallel session themes are: economy (of phosphorus sustainability and nutrient recycling), enhanced efficiency fertilisers, sustainable phosphorus removal from waste streams, R&D cooperation and platforms, taking R&D developments through to the market and phosphorus sustainability perspectives. Proposed success story mini-presentations (3 minutes, plenary) should present your company, local authority (city, region …) or stakeholder successes in implementing phosphorus recycling or phosphorus management. Posters and stands can address any subject related to nutrient sustainability.Full details www.phosphorusplatform.eu/espc4
Call for texts: phosphorus stewardship and climate change
ESPP (European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform) and the Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance (North America) are preparing a special SCOPE Newsletter edition on “Nutrients and Climate Change”. This will consist of selected short texts presenting expert perspectives on how climate change will impact nutrient emissions and eutrophication as well as actions to mitigate this. Proposed texts are invited from researchers, companies, stakeholders and any interested party. Around twenty texts will be selected for publication by an editorial committee chaired by Jessica Stubenrauch, Beatrice Garske (FNK Leipzig & University of Rostock), Anders Nättorp (FHNW Switzerland) and Jim Elser (University of Montana). The SCOPE Newsletter is circulated worldwide to 41 000 companies, stakeholders, regulators and media interested in nutrient management, with a detected opening rate of 12-14%, and is published on the ESPP website www.phosphorusplatform.eu Submit your text to be included!Send us your ideas for action for on nutrients and climate change to appear with the world’s leading experts.
Maximum 600 words. Deadline 31.01.2020 latest.
Call details and instructions here: https://phosphorusplatform.eu/callfortexts
Policy
EU consultation on Circular Bio-Based Europe Partnership
The European Commission has opened, until 6 November 2019, a public consultation on twelve proposed “Partnerships” under Horizon Europe, including the proposed “Circular Bio-Based Europe Partnership”. These Partnerships aim to extend and widen the “Joint Initiatives” approach of Horizon2020 and to bring together companies, other stakeholders and EU R&D funding to work towards a defined common goal, in particular to accelerate societal and market uptake. The proposed partnerships range from narrow sectors (three cover aviation, railways and automated road transport) to wide themes (e.g. “Innovative SMEs”). For each of the proposed Partnerships, an “Inception Impact Assessment” is published (here for Circular Bio-Based), that is the document already submitted to public consultation in August 2019, see ESPP eNews n°35). Comments are requested on this document, on the societal, economic and science impacts of the proposed Partnerships, and on how each Partnership proposal fits with other Horizon Europe or other public policy tools.EU public consultation “European Partnership for a circular bio-based Europe (Horizon Europe programme)”, open to 6th November 2019 https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/initiatives/ares-2019-4972449/public-consultation_en
EU call for expert consultants on fertilising product standards
A call is opened for experts to assist the European Commission in assessing the compliance of proposed European harmonised standards with the new EU Fertilising Products Regulation (2019/1009). These “Harmonised Standards (HAS) Consultants” will assess to what extent documents drafted by the European standardisation organisation CEN comply with the European Commission standardisation request and address requirements set by EU legislation, and will provide advice to the relevant CEN committees. HAS Consultants are already widely used in other industry standardisation sectors, but this is the first time for fertilising products. The European Commission has delegated the recruitment and contracting of HAS Consultants to EY (Ernst & Young) for all sectors. The consultants will work closely with the European Commission, and have a formalised and decisive role in the EU standard development process. Applicant consultants should specify their price per day of work and available time, and their contracts are for one year with possible renewal. Inclusion in the validated pool of consultants does not guarantee assignment of work. Applicants are required to provide evidence of expertise on, and work experience with, harmonised and/or international standards and in fertilising products (see detail in call documents, below).Full details of requirements, template contract and downloadable copy of the application form (which must be then completed online) are available here: https://www.ey.com/be/en/services/specialty-services/ey-harmonized-standards-consultant
ESPP input to Horizon Europe programme
The European Commission published in July the proposed programme content (“Orientations”, 142 pages) for Horizon Europe, the EU’s 100 billion € R&D funding 2021-2028. ESPP welcomed the accent on Critical Raw Materials and on the Circular Economy, the Mission on “Soil health and food” and the proposed Partnerships on Circular Bio-Based Europe (see consultation to 6/11/19), on Water and on Raw Materials. In Cluster 6, ESPP welcomed the links made between environment, diets, resources, nutrients and water; the accent on circularity in the food system; and the proposal to develop a “comprehensive EU policy to balance nutrient cycles”. Amongst ESPP proposals are to include crop productivity and plant nutrients in the Mission “Soil health and food”; linking to the food and beverage industry and to agri-food circularity. ESPP underlined that the circular and bio-based economy is key to future prosperity, and that resources efficiency and recycling are key to competitivity.ESPP input to EU public consultation on Horizon Europe: http://www.phosphorusplatform.eu/R&D
EU Critical Raw Materials list update work underway
The European Commission is currently carrying out (re) assessments of the 27 materials currently included in the EU Critical Raw Materials list (CRM), and also of a number of other materials for possible consideration to add to the list. The current (third) CRM list (2017) includes both “Phosphate rock” (in effect covering phosphorus in different forms in fertilisers, animal feed, chemicals and other uses) and “Phosphorus” (referring to elemental phosphorus P4, often known as white phosphorus, produced from phosphate rock in specific furnaces and essential for a wide range of organic phosphorus chemicals and electronics-grade phosphoric acid). The (re)assessment studies (Criticality Assessment excel files and backup information Factsheets) are being led by the European Commission’s Joint Research Centre (JRC) and aims to be completed by end 2019 / early 2020. For several materials including “Phosphorus”, a more detailed MSA (Materials System Analysis) is underway, over a longer timeline. Materials not on the 3rd EU CRM List and currently being assessed include Potassium. ESPP and DPP (German Phosphorus Platform) made input to and participated in an Expert Workshop on 12th September, however content and draft documents are subject to a Non Disclosure Agreement (NDA) so cannot be shared. If you wish to access documents and engage in this CRM update process, you must register as an expert and sign the NDA by contacting the emails indicated below. ESPP and DPP have input both factual information and data sources regarding different uses of phosphate rock and P4, and have emphasised the development of phosphorus recycling.EU Critical Raw Materials webpage https://ec.europa.eu/growth/sectors/raw-materials/specific-interest/critical_en
Emails to contact to participate in the EU CRM (re)assessment process: and
“STRUBIAS” final report published
The European Commission (JRC) has published the final ‘STRUBIAS’ report, proposing draft European criteria (under the EU Fertilising Products Regulation, 2009/1009 = FPR) for recovered struvite / precipitated phosphate salts, for ash-based materials and for biochars / pyrolysis / gasification materials. The draft criteria are presented as proposed “Recovery Rules”, pages 9-19 of the JRC report. The European Commission (DG GROW) will now prepare draft annexes to the FPR (“CMC” specifications) for each of these three categories of materials. These draft annexes must then be validated by the EU Fertilisers Working Group (hopefully before end 2019), which consists of Member States plus stakeholders (ESPP and Fertilizers Europe are members). This should not pose problems, because these parties were all consulted already during the JRC STRUBIAS process, which is ran 2016-2016. Before becoming applicable, these additions to the FPR Annex II (CMCs) must finally be published in the Official Journal. Key aspects of the proposed criteria, and modifications made since the final STRUBIAS meeting in September 2018, are indicated below. Please note that this is simplified (for precise wording see the document pages 9-19) and that it is a first analysis (ESPP will prepare detailed comments in coming weeks, any input is welcome).Recovered phosphate salts: recovery from “manure” has been deleted and replaced by references to Animal By-Products having reached certain End Points (does this mean manure must be first sanitised?); recovery from animal feed industry and biofuel wastewaters is added; recovery from municipal sewage remains included; minimum phosphate level of 16% P2O5 (DM) and maximum organic carbon 3% (DM) are not modified; “derivatives” of recovered phosphate salts are included, that is fertilising products produced by chemical processing of these salts. It has been added that recovered phosphate salts must not only be REACH registered, but that the Registration must have Annexes VI-VIII and CSR.
For ash materials (called “Thermal oxidation materials and derivates”): in the input materials, sewage sludge is explicitly included, vegetable materials from the food industry and from virgin pulp & paper industries are added, specifications for animal by-products are modified (an End Point must have been reached – as above, does this mean that non-sanitised manure is excluded?); minimum combustion temperature is maintained at 800°C, or 450°C for some low-risk input materials; limits of 6 mg/kg DM PAH and 20 ng WHO tox.eq./ kgDM for PCDD/F are not modified (applicable to the ash itself, not to the final ‘derivative’); ash ‘derivatives’ are included (see above).
For “Pyrolysis and gasification materials” (inc. biochars): in the input materials, sewage sludge is excluded (despite the STRUBIAS group proposal to include this, however “JRC recommends undertaking more scientific research to … show … not present an unacceptable risk … and are sufficiently effective …”, pages 57-60), but food industry, virgin pulp & paper and biofuel residues are added; a minimum processing temperature of 180°C is added and the H/C-org < 0.7 condition is maintained; PAH and PCDD/F limits are maintained (same as for ash, above).
“Technical proposals for selected new fertilising materials under the Fertilising Products Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2019/1009). Process and quality criteria, and assessment of environmental and market impacts for precipitated phosphate salts & derivates, thermal oxidation materials & derivates and pyrolysis & gasification materials”, Huygens et al., European Commission JRC, 24/9/2019, ISBN 978-92-76-09888-1 https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/en/publication/eur-scientific-and-technical-research-reports/technical-proposals-selected-new-fertilising-materials-under-fertilising-products-regulation and http://dx.doi.org/10.2760/186684
Call for experts on nutrient recycling in processed manures
The European Commission is calling for candidates, stakeholders and experts to provide input to the SAFEMANURE draft report. This European Commission (DG ENVI, JRC) project aims to define criteria for allowing certain nitrogen fertilisers derived (wholly or partly) from manure to be not treated as ‘processed manure” under the Nitrates Directive (see ESPP eNews n°23). Actions engaged include: literature search, biogeochemical modelling, pot tests. Provisional planning is indicated to be draft report probably late 2019, expert consultative meeting early 2020.Organisations interested should send contact details of up to two experts to (subject line: SAFEMANURE interest list)
Phosphorus sustainability in action
Italmatch LIFE Trialkyl project successful
ESPP participated at the final meeting 25th June 2019 of the EU LIFE Trialkyl project, at Federchimica’s Auditorium, Milan, opened by Nicoletta Fascetti Leon, from Italian Ministry for the Environment Land and Sea. This LIFE project is led by phosphorus chemicals specialist Italmatch, with the support of SC Sviluppo Chimica, Italy, and RISE Research Institute, Sweden. The Trialkyl project has successfully developed and demonstrated a new and more sustainable production route for high quality trialkyl phosphites (trimethylphosphite TMPi), an organophosphorus chemical used in a wide range of industry applications including fire safety, crop protection, plastics, childcare products and pharmaceuticals. Current production technologies use tertiary amines as intermediates, and these are classified as hazardous, so that process wastewater has to be chemically neutralised and treated. Within the LIFE Trialkyl project, a new one-stage reactor process has been developed based on PCl3 (the standard chemical ‘vector’ for elemental phosphorus in the chemical industry) and alcohols, with sophisticated parameter control, leading to zero water usage and so zero wastewater, 20-30% less energy consumption, and a large reduction in the use of solvents. After successful laboratory scale testing, a pilot plant was set up and demonstrated in Italmatch’s Arese plant (near Milan).LIFE-Trialkyl www.life-trialkyl.eu/en - see also ESPP eNews n°13

Picture Trialkyl project
Finland gypsum soil treatment project
The Finnish Ministry of the Environment has launched a research project to promote the spreading of gypsum to reduce soil phosphorus losses from fields, stating that the objective is to enable the inclusion of gypsum in HELCOM’s Baltic Sea action plans. Field testing in Finland during the last 10 years, including over 4 000 hectares of fields in the SAVE project, has shown that gypsum application can reduce total phosphorus losses from fields by 50% and also reduce organic carbon losses. The quality of gypsum used is important (should not contain contaminants). The gypsum used has been from Yara’s site in Siilinjärvi situated in Eastern Finland, where 1 million tonnes gypsum is generated annually in phosphoric acid production. Around 4 tonnes of gypsum per hectare are used, at a treatment cost of c. 220 €/ha, that is a cost of 60 – 70 € per kg P loss reduction, considered to be significantly less than costs of other currently available measures.SAVE summary “Gypsum amendment of fields as a water protection measure in agriculture”, 10 pages, February 2019 https://blogs.helsinki.fi/save-kipsihanke/files/2019/02/SAVE-Infopackage-of-Gypsum-Amendment.pdf
“Finland aims to improve water quality in the Baltic Sea by applying gypsum to fields”, Finnish Environment Ministry, 11/9/2019 https://valtioneuvosto.fi/en/article/-/asset_publisher/ymparistoministerion-tutkimushanke-selvittaa-kipsin-kayttoa-pelloilla-itameren-rantavaltioissa
Research
9th International Phosphorus Workshop (IPW9)
This conference in Zurich, July 2019, brought together over 200 participants from 31 countries worldwide, with over 80 plenary and parallel session presentations and more than 100 posters. It discussed the questions: “Putting phosphorus first? How to address current and future challenges?”. The conference built on the identification of research needs related to phosphorus in soil and in agriculture from previous IPW conferences, starting with IPW1 in Ireland in 1995. Key points raised include: awareness, phosphorus flows and cycles, data, P-recycling, regulation, market, importance of long-term field trials, impacts of dietary choices and livestock production, soil – fertilisation links, need for improved agronomic fertilisation recommendations. The conference and its conclusions are summarised in ESPP’s SCOPE Newsletter n°131.ESPP SCOPE Newsletters https://phosphorusplatform.eu/scopenewsletter
120 days/year of phosphorus needs in food waste
A study by experts at Nestlé and at WRAP UK assesses “nutrition days” lost in UK food waste, for 25 nutrients, vitamins and food values, and looks at different areas of environmental impacts. The study is based on detailed data on UK food waste (WRAP), with a total of around 5.4 million tonnes/year of avoidable or possibly avoidable, edible food waste (UK) compared to dietary needs (UK RNI: Reference Nutrient Intake, that is 0.55 gP/person/day for phosphorus). Phosphorus shows more wasted nutrition-days than for any other nutrient (120 phosphorus nutrition days wasted per capita per year) and is fourth of all food values assessed (after vitamin B12, vitamin C, thiamin). Considering all food values together, some 42 daily diets per person (nutritional value) were discarded annually in UK food waste. The authors note that losses are particularly significant for food values which are under-consumed in the UK, such as calcium, food folate and dietary fibre. This is one of the first scientific publications to look at nutrient losses in food waste, rather than simply tonnages of waste and calories. A previous paper looking at US food waste (Spiker et al., 2017, with US Department of Agriculture participation) found similar results (using US Recommended Daily Allowance RDA, that is 0.7 gP/person/day for phosphorus), with the highest losses being again for vitamin B12, thiamine and phosphorus (92 nutrition-days, and a loss of 0.45 gP/capita/day). This new paper also looks at how environmental impacts are distributed, noting that the principal environmental impacts come from agricultural production (higher than food processing, distribution, etc.) and that meat and fish losses in food waste have the highest environmental impacts, but that fresh vegetables are also significant.“Nutrition in the bin: a nutritional and environmental assessment of food wasted in the UK”, K. Cooper, T. Quested, et al., Nestlé Research Centre, Lausanne, Switzerland, and WRAP United Kingdom, Frontiers in Nutrition, 5, 19, 2018, , https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2018.00019
“Wasted food, wasted nutrients: nutrient loss from wasted food in the United States and comparison to gaps in dietary intake”, M. Spiker et al., J Acad Nutr Diet (2017) 117(7):1031–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2017.03.015

Phosphorus and other metals from sunscreens
New research assesses nutrient and toxic metal releases from sunscreens and estimates the possible significance for coastal eutrophication and aquatic toxicity. Release tests were carried out on one widely used sunscreen product (SPF50, milk spray, not named, selected from ConsumerReports recommendations), assessing release into seawater under UV exposure comparable to a Mediterranean beach. The sunscreen contained phosphorus at over 300 ppm, and also ppm or ppb levels of metals including (highest levels first) titanium, lead, manganese, copper molybdenum, nickel, cadmium, aluminium and cobalt. The Mediterranean received over 330 million tourists in 2016. The authors estimate release of different elements into seawater using conservative estimates of number of bathers, use of sunscreen, part washed off in water, coastal water renewal rate, etc. suggesting that sunscreen could increase dissolved phosphate and silicon concentrations in coastal waters by 0.2% and 0.6%, and also significantly increase concentrations of titanium (nearly 20%), aluminium (4%) and lead (0.25%), posing possible toxicity risks.“Sunscreens as a New Source of Metals and Nutrients to Coastal Waters”, A. Rodríguez-Romero et al., Environ. Sci. Technol.2019, 53, 17, 10177-10187 https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b02739
PolFerAsh P-recovery process
Results are presented of lab-scale testing of gasification of dried sewage sludge (150 mm diameter, fixed-bed gasifier, 800 – 1 000 °C) followed by leaching of the solid gasifier residue (by phosphoric or nitric acids), the Cracow University of Technology patented PolFerAsh process. 50 – 60 % of the sludge energy potential (after drying) was converted to syngas. The sewage sludge used was from a sewage works operating chemical P-removal and contained 6% phosphorus (P) and 6.7% iron (Fe). Use of dilute phosphoric or nitric acid enabled extraction of 70 – 85 % of the phosphorus in the gasifier residue, with better results (higher P, lower Fe) with phosphoric acid. Chromium, zinc and nickel were also significantly extracted and could pose quality issues for use of the leachate. The leachate showed concentrations of up to 360 mg H3PO4/l and could be used for fertiliser production or directly in liquid fertilisers.“Sewage sludge as a fuel and raw material for phosphorus recovery: Combined process of gasification and P extraction”, K. Gorazda et al., Waste Management 73 (2018) 404–415, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.10.032
JRC-led study brings together environmental footprints
A study led by the European Commission Joint Research Centre (JRC), based on a workshop of 23 global experts (at which ESPP participated), systematises existing environmental footprints and proposes a footprint family framework. This is graphically summarised in the diagram shown. The aim is to provide a tool for environmental sustainability assessment, particularly targeting coherence with Planetary Boundaries, the United National Sustainability Goals (SDGs) and the Water – Energy – Food – Ecosystem (WEFE) nexus. The authors note that an increasing number of papers are being published on environmental footprints addressing mostly only one question, with over 6 700 such papers identified, but only 28 were found integrating multiple footprints. Phosphorus and nitrogen footprints are amongst the pressures and impacts considered (P, N, carbon/greenhouse gas, land use, water, ozone, atmospheric particulates, chemicals, biodiversity, raw materials). The authors conclude that environmental footprint indicators can be used to identify the extent to which different processes or societies contribute to exceeding of planetary boundaries, to identify potential measures to address this, and to quantify and communicate changes needed.“Environmental footprint family to address local to planetary sustainability and deliver on the SDGs”, D. Vanham et al., Science of the Total Environment 693 (2019) 133642, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133642
New phosphorus materials
Phosphorus can be generated as single atom thickness sheets (2D black phosphorus or “phosphorene”), similar to the graphene form of carbon. This material, first demonstrated in 2014, offers potentially valuable properties, including high strength, electrical conductivity and electron transfer, modulable light energy adsorption (transforming light energy into chemical energy) and biocompatibility. It is today being researched for potential applications in electronics, energy storage, artificial photosynthesis, photosensors and biomedical systems. Possible energy storage applications include in lithium ion, magnesium ion or lithium sulphur batteries (LIB, MIB, LSB) or in ultracapacitors. 2D blue phosphorus, with a honeycomb structure, demonstrated in 2016, offers more varied electronic properties. A challenge, however, is that 2D black carbon is stable in air for only a few days, probably as a result of water condensation. It can be stabilised by encapsulation, functionalisation or doping (e.g. with diazonium or tellurium) or by use in a liquid phase (in water or in a solvent). 2D black phosphorus is biocompatible and in vivo biodegradable, and shows lower cytotoxicity than graphene. Potential biomedical applications include biosensors (to detect colours, electrical fields, gases …), cancer imaging and cancer phototherapy, drug delivery.“2D Black Phosphorus: from Preparation to Applications for Electrochemical Energy Storage”, S. Wu et al., Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700491, https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201700491
“Black Phosphorus and its Biomedical Applications”, J. Choi et al., Theranostics 2018, Vol. 8, Issue 4, 1005-1026. doi: https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.22573
Organic fertilisers from sewage sludge
Kominiko et al., Cracow University of Technology, Poland, have published further work on production of granulated organo-mineral fertilisers using digested, dried municipal sewage sludge, combined with poultry litter ash, biomass combustion ash (flax straw) and mineral fertilisers, using sulphuric and nitric acid as binders. This follows a previous study summarised in ESPP eNews n°13. The new study includes nutrient and heavy metal data for (digested) sewage sludge from eleven Polish municipal sewage works, concluding that cadmium, chromium, lead, mercury and nickel were above limits for organic fertilisers (as per the Polish Fertilising Products Regulation) at several or most of the sewage works. The fertiliser granulation tests were carried out with batches of up to 2 kg dry weight. Digested sludge from the Żywiec municipal sewage works was used (works operating biological and occasional chemical P-removal), combining e.g. 40% sludge, 10% ashes, 40% mineral fertiliser and 10% of acid. The phytotoxicity tests showed that the sludge-combined fertilisers resulted in longer stalk growth and lower root growth of rapeseed in comparison with control sample“Potentiality of sewage sludge-based organo-mineral fertilizer production in Poland considering nutrient value, heavy metal content and phytotoxicity for rapeseed crops”, H. Kominko, K. Gorazda, Z. Wzorek, Journal of Environmental Management 248 (2019) 109283 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109283
Functionalised cow dung biochar
In lab scale tests, cow dung was dried and pyrolysed at different temperatures 450 – 750°C, with or without prior reaction with magnesium. These biochar materials were then tested for phosphorus adsorption from potassium phosphate solution, and the resulting P-loaded biochars were tested as fertiliser in 60-day pot trials with lettuce. The biochars showed P adsorption capacities up to 260 mgP/g. The addition of biochar significantly improved lettuce seed germination, early and late stage growth, with the Mg-modified biochar giving the best results, probably as a combined effect of phosphorus fertilisation and liming (pH of the Mg-modified biochar was >11). The authors note that a challenge would be scale up of the pyrolysis process to generate a consistent and stable product.“Cow dung-derived engineered biochar for reclaiming phosphate from aqueous solution and its validation as slow-release fertilizer in soil-crop system”, Q. Chen, J. Cleaner Production, Volume 172, pp. 2009-2018, 2018 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.224
RECOVER resource recovery processes development Norway
The 2.8 M€ R&D project RECOVER (Research Council of Norway, 2015-2020) is developing new processes to recover phosphorus and nitrogen, as well as energy, from wastewater. The project involves three Norwegian research institutes (NTNU, NMBU and SINTEF) with industrial partners (Cambi, Doscon, Kemira, Krüger Kaldnes, Norconsult and Salsnes Filter) and several municipal wastewater treatment plants (IVAR, HIAS).. Research is addressing process, control and monitoring solutions, in particular for biological phosphorus removal, phosphorus and nitrogen recovery, sensors for biological treatment systems, LCA and sustainability analysis.RECOVER https://www.ntnu.no/recover/doktorgradsarbeider and https://www.ntnutechzone.no/en/2017/02/recover-resource-recovery-from-wastewater/ and https://www.researchgate.net/project/RECOVER-Nutrient-recovery-from-wastewater
See also: “Sustainable Sewage Sludge Management: From Current Practices to Emerging Nutrient Recovery Technologies”, S. Shaddel et al., Sustainability 2019, 11(12), 3435; https://doi.org/10.3390/su11123435

ESPP members

Stay informed
SCOPE newsletter: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/SCOPEnewslettereNews newsletter: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNewshome
If you do not already receive SCOPE and eNews (same emailing list), subscribe at www.phosphorusplatform.eu/subscribe
LinkedIn group: www.linkedin.com/groups/4783093 (or search for European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform)
Twitter: @phosphorusfacts
Slideshare presentations: www.slideshare.net/NutrientPlatform
Contributions (600 words) are invited from researchers, companies, stakeholders on “Nutrients and Climate Change” for publication in a SCOPE Newsletter Special Issue (41 000 distribution). Submit your text to be included! Deadline 29th February 2020. Instructions here.
Summary of the 9th International Phosphorus Workshop (IPW9)
ETH Zurich, 8 – 12 July 2019:
- Site visits
- Holistic view
- Phosphorus excess or phosphorus insufficiency?
- Fertiliser innovation
- Animal feeds
- Long-term field trials
- Phosphorus management policies
- Phosphorus recycling
- Conclusions
Newsletter about nutrient stewardship - European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP).
Please subscribe www.phosphorusplatform.eu/Subscribe
Link to www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNews035
Download as PDF
Events and conferences
Waste water phosphorus removal tomorrow: ambitions and reality
Call for papers ESPC4
Policy
Horizon Europe public consultation
EU Circular Bio-Economy public consultation
EU public consultation: CAP agriculture policy and soil
Netherlands nitrogen policy cancelled by Council of State
EU publishes regulation on sewage sludge spreading information
EU tender for risk assessment of contaminants in fertilisers
Preparation of a “Guidance” for German P-recovery regulation
Assessment of EU detergent phosphate ban
Netherlands “Circular Agriculture” vision
Cooperation and perspectives
Fertilizer Focus magazine features organic fertilisers perspectives
The future of water
Global alliance for “regenerative farming”
Canada Nutrient Platform development
Dutch Nutrient Platform members meet-up, March 2019
Research
H2020 calls on Critical Raw Materials
Horizon Europe “Missions” and cluster themes defined
Sweden: sewage and manure nutrient recycling geo-distribution challenges
Cost-effective phosphorus management on arable farms
Biochar and compost tested as fertilising products
Struvite recovery uses less “emergy” than mineral fertiliser production
Nitrification inhibitor impacts struvite plant availability
Different phytases show varying benefits for poultry
ESPP members
Stay informed and unsubscribe
Events and conferences
Waste water phosphorus removal tomorrow: ambitions and reality
9th October, Liège, near Brussels. In the context of the current revision of EU water policy (Water Framework Directive, Waste Water Treatment Directive), and with participation of the European Commission (DG ENVI, DG RTI), this workshop will enable dialogue between the water industry, experts and policy makers (EU, national) on perspectives for phosphorus removal: low discharge consents, flexible permitting / emissions trading, P-removal from small sewage works. Registration now open here.In partnership with / supported by: IWA (the International Water Association), Eureau, CIWEM (Chartered Institution of Water and Environmental Management), Université de Liège and ECSM’19 (European Conference on Sludge Management), Liège 6-8 October 2019 https://events.uliege.be/ecsm2019/ for information on the phosphorus removal workshop, contact

Call for papers ESPC4
The call for abstracts and posters is now open (closes 31/12/2019) for the 4th European Sustainable Phosphorus Conference (ESPC4), Vienna, 15-17 June 2020. Abstracts are invited for presentations for the six parallel sessions, for plenary success story mini-presentations, for posters or for stands. The parallel session themes are: economy (of phosphorus sustainability and nutrient recycling), enhanced efficiency fertilisers, sustainable phosphorus removal from waste streams, R&D cooperation and platforms, taking R&D developments through to the market and phosphorus sustainability perspectives. Proposed success story mini-presentations (3 minutes, plenary) should present company, local authority (city, region …) or stakeholder successes in implementing phosphorus recycling or phosphorus management. Posters and stands can address any subject related to nutrient sustainability.Full details and more information about ESPC4 www.phosphorusplatform.eu/ESPC4

See more upcoming events at www.phosphorusplatform.eu/upcoming-events
Policy
Horizon Europe public consultation
The European Commission has launched a public consultation on Horizon Europe, open to 8th September 2019, including inviting comments on the proposed “Orientations” document which will define the content of Horizon Europe (thematic funding, Missions, Partnerships …). The consultation aims to define the general research and innovation challenges to be addressed by Horizon Europe, citing the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and questioning priorities (Europe to be Protective, Fair, Sustainable, Competitive or Influential?) and opens the possibility for detailed comments on the thematic objectives, targeted impacts and R&I orientations which will define the content of future R&D calls (‘Second Pillar’).Public consultation open to 8th September 2019 (Horizon Europe Co-design 2021-2024 consultation) introduction https://ec.europa.eu/info/news/have-your-say-future-objectives-eu-funded-research-and-innovation-2019-jun-28_en
Orientations document for comment (Orientations towards the first Strategic Plan implementing the research and innovation framework programme Horizon Europe) https://ec.europa.eu/research/pdf/horizon-europe/ec_rtd_orientations-towards-the-strategic-planning.pdf
Online survey and submission form https://ec.europa.eu/eusurvey/runner/HorizonEurope_Codesign_2021-2024

EU Circular Bio-Economy public consultation
The European Commission has launched a public consultation open to 27th August 2019 on a proposed “Partnership for a Circular bio-based Europe”, envisaged under the Horizon Europe “European Partnerships” tool. The partnerships objectives will be to support innovation for value creation from waste and biomass, including renewable products and nutrients, and will build on the “Bio Based Industries Joint Technology Initiative” (BBI) of Horizon 2020. The proposed roadmap identifies as challenges to address: the multi-sectoral, fragmented nature of the bio-based sector, the complex policy environment, the high risk and high capital expenditure of large biorefineries and uncertainties around feedstock materials availability and costs. It underlines the need to understand resource variability and flows, deploy demonstration biorefineries and reduce policy fragmentation. Citizen and stakeholder input on the proposed roadmap is requested through the public consultation.Public consultation open to 27th August 2019 https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/initiatives/ares-2019-4972449

EU public consultation: CAP agriculture policy and soil
The European Commission has launched a public consultation open to 27th August 2019 on a planned evaluation of how EU agriculture policy (CAP) impacts soil, citing in particular soil erosion, compaction, organic matter, biodiversity, pollution and salinisation. The evaluation will consider interactions between CAP and other EU policies. This will input to the 2021 EU report on performance of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP).Public consultation open to 27th August 2019 https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/initiatives/ares-2019-3760776_en
Netherlands nitrogen policy cancelled by Council of State
The Netherlands Council of State (29th May 2019) has effectively cancelled part of The Netherlands nitrogen policy, concerning nitrogen emissions near to Natura 2000 areas, and has also invalidated a significant number of permits accorded to livestock farms and also infrastructure projects. The Council of State judgement transposes the European Court of Justice decision of 7th November 2018, which was a preliminary ruling on interpretation of the EU Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC), following an action brought be environmental NGOs. This ECJ judgement states that “grazing of cattle or application of fertiliser” (in the vicinity of a Natura 2000 site) may be classified as a “project” (under the EU Project Assessment Directive 2011/92/EU), and thus that national legislation authorising such activities must be subject to an “appropriate assessment”, before permitting, which shows “that there is no reasonable scientific doubt as to the lack of adverse effects” on the integrity of the Natura 2000 site. The Netherlands “PAS” (Nitrogen Action Programme) did not respect these criteria, and so permits accorded under this programme could be cancelled. Media coverage suggests that over 200 court cases are already underway in the Netherlands concerning PAS permits, for livestock farms, but also for road and airport projects, and that their existing permits may now be cancelled. The Ministry of Agriculture, Nature and Food Quality (LNV) is currently assessing the court decisions and possible consequences, and is looking at possible legally secure solutions in dialogue with stakeholders.“Dutch nitrogen policy in violation of European nature legislation”, 29 may 2019 www.tellerreport.com/life/2019-05-29---judge--dutch-nitrogen-policy-in-violation-of-european-nature-legislation-.Hyh8XHn6V.html and also: www.nos.nl/artikel/2289778-tientallen-projecten-dreigen-te-sneuvelen-door-stikstof-uitspraak-raad-van-state.html
Netherlands Ministry (LNV) letter to Parliament, 29 May 2019 (in Dutch): www.rijksoverheid.nl/binaries/rijksoverheid/documenten/kamerstukken/2019/05/29/eerste-reactie-op-uitspraak-raad-van-state-inzake-het-programma-aanpak-stikstof/Eerste_reactie_op_uitspraak_Raad_van_State_inzake_het_Programma_Aanpak_Stikstof.pdf
European Court of Justice, decision of 7 November 2018, cases C-293/17 and C-294/17 – search by case number on http://curia.europa.eu
EU publishes regulation on sewage sludge spreading information
The new EU Regulation updating environmental reporting obligations has been published, as presented in ESPP eNews n°s 25 and 27. Current EU legislation (art. 10 of the EU Sludge Directive 86/278) already obliges Member States to maintain a register of data on quantities of sewage sludge produced, quantities used in agriculture, treatments, identification of farms and fields where the sludge is used. The new regulation additionally requires that this information be made available to the public “in a consolidated form”.EU Regulation 2018/1010, 5th June 2019, “on the alignment of reporting obligations in the field of legislation related to the environment …” https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32019R1010
EU tender for risk assessment of contaminants in fertilisers
The European Commission (DG ENVI) has opened a tender (closing 26/8/19, estimated budget 400 000 €) “Contaminants in fertilisers: Assessment of the Risks from their Presence and of the Socio-economic impacts of a Possible Restriction under Reach”. Tasks include to assess contaminants in fertilisers, to prepare a “pre-regulatory Management Option Analysis (pre-RMOA) and a pre-Annex XV dossier”, to screen data in REACH Registrations and in literature and to assess “alternatives to fertilisers”, including market and cost aspects. It is not clearly stated but it seems this study concerns contaminants in both organic and inorganic fertilisers (the “Tender Specifications” refer to “fertilising products placed on the market”, and to organic contaminants). Compost and digestate are however not covered, because the Commission already has a service contract report (see below). The Tender Specifications refer to possible future amendments to modify contaminant limits in the EU Fertilising Products Regulation or, in order to cover also national fertilisers, in Annex XVII of REACH. The study is very wide, in that analysis of “alternatives to fertilisers” is specified to include “a move to organic farming, limiting the fertilising doses, with an assessment of the potential consequences (reduction in supply of certain crops, reduction of competitiveness of the sector, increase of imports of crops, etc).” and also “the possible reactions of farmers to the unavailability of a specific fertiliser the possibility to use risk management measures for agricultural fields (such as vegetative edge strips, deep placement, etc.), instead of a ban.” Concerning compost and digestate, the Tender Specifications refer to a previous service contract report to the European Commission: “Digestate and compost as fertilisers. Risk assessment and risk management option” (Amec). It is indicated that this report will be transmitted to the contractor selected for the new fertiliser study. To our understanding, this Amec report is not published. ESPP has requested to receive a copy.EU Commission tender, open to 26th August 2019, ENV/2019/OP/0001, 2019/S 132-323039 “Contaminants in fertilisers: Assessment of the Risks from their Presence and of the Socio-economic Impacts of a Possible Restriction under Reach” https://etendering.ted.europa.eu/cft/cft-display.html?cftId=5131 and Tender Specifications https://etendering.ted.europa.eu/cft/cft-document.html?docId=56624 NOTE: thank you to Fertilizers Europe for alerting ESPP to this information

Preparation of a “Guidance” for German P-recovery regulation
In Germany, the new Sewage Sludge Ordinance (AbfKlärV) came into force in October 2017, making obligatory phosphorus (P) recovery from sewage sludge from 2029. Sewage plant operators thus need to decide which recovery method to choose. However, various aspects of the legal framework are not easy to interpret. Therefore a “Guidance” document (Vollzugshilfe) for the AbfKlärV is currently being prepared by the German authorities. The Environment Ministries of the federal states have set up an ad-hoc group of the waste working group “Bund Länderarbeitsgemeinschaft Abfall” (LAGA) to prepare this Guidance. The Guidance will not be legally binding, but aims to enable a uniform implementation in the federal states. In June 2019, stakeholder organisations were given the opportunity to comment on a first draft and provide input. With its members, the German Phosphorus Platform (DPP) submitted detailed comments. DPP called in particular to clarify the calculation of the specified P-recovery level based on concentrations: the sludge mass may be lower after the P-recovery operation and this should not impact the recovery rate calculation. Furthermore, DPP called for a clear definition of the legal areas of wastewater and waste so that users know exactly to which legal area a P-recovery technology belongs. In Germany, phosphorus recovery is only mandatory in the AbfKlärV (waste legislation, applicable to sewage sludge). However, there are also processes that recover P during wastewater treatment. Publication of the Guidance is expected in spring 2020.Summary of German P-recovery legislation, see SCOPE Newsletter n°129
German Phosphorus Platform www.deutsche-phosphor-plattform.de

Assessment of EU detergent phosphate ban
The European Commission (COM) has published an assessment of the 2004 EU Detergents Regulation (648/2004), which banned phosphates in domestic laundry and domestic dishwasher detergents (in 2013 and 2017). The ban does not concern industrial and institutional detergents. The assessment concludes that there is no evidence of any environmental benefit from the phosphates ban, because the ban only entered into force recently, because the contribution of detergents to eutrophication was already “relatively small” compared to agriculture before the ban, and because many sewage works in any case remove phosphorus so that detergent P was not reaching the environment. The political nature of the detergent phosphates discussion is demonstrated by the fact that the European Commission website title states the contrary to the assessment conclusions, saying that it “shows environment protection”. COM estimates that the ban has resulted in 55 000 tonnesP/year less being used in detergents. The total cost of Regulation implementation (including other aspects, such as labelling) is estimated to be 0.7 – 1.8 bn€/year (around 0.5% of detergent industry turnover). Overall, the COM assessment considers that the impact of the Regulation has been positive.“Review of the detergents regulation shows improved consumer and environment protection”, European Commission, 10th July 2019 ec.europa.eu/growth/content/review-detergents-regulation-shows-improved-consumer-and-environment-protection_en and “Evaluation of Regulation (EC) No 648/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 31 March 2004 on detergents”, SWD(2019) 298 final = summary and SWD(2019) 299 final = full assessment 10th July 2019
Netherlands “Circular Agriculture” vision
The Netherlands Minister of Agriculture, Carola Schouten, presented in 2018 a vision for “The Netherlands as a leader in circular agriculture”, and plan to implement this vision was transmitted to the Netherlands Parliament in June 2019. The Ministry document indicates that Dutch farming, horticulture and fisheries are constantly innovating, making the Netherlands a global leader in these sectors. However, current production methods are not without cost. The Netherlands faces serious social and ecological challenges and needs to prevent depletion of soil, freshwater supplies and raw materials, halt the decline in biodiversity and fulfil commitments to the Paris climate agreement. Carola Schouten sees circular agriculture as the logical and conclusive answer to these issues. This means closing cycles of minerals and other resources as far as possible, strengthening the focus on biodiversity and respecting the Earth’s natural limits, preventing waste and ensuring that farmers are paid a fair price for their work. The government’s goal is for cycles of raw materials and resources to be closed at the lowest possible level, either nationally or internationally, by 2030. The Minister hopes that the Netherland’s vision on circular agriculture will become a source of inspiration at European level.Netherlands vision for circular agriculture: “Agriculture, nature and food: valuable and connected”, English version www.government.nl/ministries/ministry-of-agriculture-nature-and-food-quality/documents/policy-notes/2018/11/19/vision-ministry-of-agriculture-nature-and-food-quality---english

Cooperation and perspectives
Fertilizer Focus magazine features organic fertilisers perspectives
The July-August edition of the trade magazine Fertilizer Focus summarises the first Summit of the Organic Fertilisers Industry in Europe (SOFIE, organised by ESPP) and a discussion of the organic-based fertilisers market by ECOFI. It is underlined that most fertilisers used in Certified Organic Farming are organic-based (based on natural materials containing organic carbon), but that most organic-based fertilisers are not Organic Farming Certified. Both articles state that sales of organic-based fertilisers in Europe are estimated to be around 2.5 bn€ (source: Allied Market Research 2016). ECOFI underline the complementarity between mineral and organic fertilisers (including with organo-mineral products), as was also emphasised by Fertilizers Europe at SOFIE. ECOFI indicate that EU organic-based fertiliser producers are increasingly developing high-value export markets, and the SOFIE conference article highlights a number of companies innovating in this market: ILSA, Veolia, Fertikal, 4R Group, Biolan, Soilfood, OvinAlp. The SOFIE conference conclusions are summarised, including recommendations for clarifying new products, data on agronomic performance and on industry, importance of ensuring consistent quality and tailor-made, added-value products for continuing development.Fertilizer Focus (Argus Media) www.argusmedia.com/en/fertilizer/fertilizer-focus
This article, and also full summary of SOFIE conference in ESPP SCOPE Newsletter n°130, at www.phosphorusplatform.eu/SOFIE2019
The future of water
A discussion paper from IDB (Inter-American Development Bank) discusses disruptive technologies susceptible to restructure water and wastewater management in coming decades. Ideas presented include “one water” (integration of waste-, storm- and drinking water infrastructures) enabled with advanced processing technologies (e.g. membranes), to facilitate water reuse and address challenges of drought and floods; energy and resource recovery (especially biogas from sewage sludge and phosphorus recycling; decentralisation facilitated by distant digital sensing and control; cost reduction of desalination (to address water supply), LED UV for advanced oxidation and disinfection. The importance of regulation to enable technology uptake is underlined.“The future of water”, essays by G. Daigger, N. Voutchkov, U. Lall, W. Sarni, IDB (Inter-American Development Bank) Discussion Paper n° IDB-DP-657, April 2019 (75 pages) http://water.columbia.edu/files/2019/04/FINAL_The_Future_of_Water_28March2019.pdf

Global alliance for “regenerative farming”
The three year project “Farming for Generations” has been launched by eight leading global agri-food companies: Danone (leader), Connectera, Corteva Agriscience, DSM, FutureCow, MSD Animal Health, Neogen and Yara, with Wageningen UR. The project will work with 25 dairy farms in Europe, the USA and Russia to identify and test new approaches and best practices, and develop an applied toolbox for dairy farmers. The project states that “food systems need to be changed to be fit for the future” and “sustainable diets” need to be defined to provide nutrition to the world population whilst respecting environmental limits. “Regenerative (dairy) farming” is indicated as aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, protect soil and biodiversity, provide quality feed for cows, ensure that animals have a healthy and stress-free life and empower farmers.“Global alliance Farming for Generations launches to transform dairy farming towards regenerative agriculture” 26 June 2019 www.yara.com/news-and-media/news/archive/2019/global-alliance-farming-for-generations/ and www.connecterra.io/about-us/press-media/press-release-farming-for-generations
Canada Nutrient Platform development
Discussions are underway, between academics, government staff and stakeholders, to establish a Canadian Nutrient Recovery and Reuse (CNRR) Platform. This follows the 8th March 2018 National (Canadian) Nutrient Recovery and Reuse (NNRR) Forum held in Toronto and hosted by the International Institute of Sustainable Development (IISD) Inc., which brought together more than 80 participants from government and academic sectors. The Platform intends to work collaboratively with the European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform (ESPP) and the USA based Sustainable Phosphorus Alliance (SPA). The development of the CNRR Platform was a key recommendation in IISD's report from the Toronto Forum, titled “Nutrient Recovery and Reuse in Canada, Foundations for a national framework”. This proposes to base the CNRR Platform around stakeholder communication strategies / programs, public policy, industry practices and technology improvements and development, and market based incentive development and to focus initially on phosphorus recovery and reuse from urban and rural point and non-point sources. Work is currently underway to develop a multi-year funding proposal to build and lead the CNRR platform and allow it to transform to a self-sustaining platform.Toronto 8 March 2018 Canada Nutrient Reuse an Recovery Forum, including presentations and report: www.iisd.org/event/national-nutrient-reuse-and-recovery-forum
Dutch Nutrient Platform members meet-up, March 2019
Bringing supply and demand together, that was the aim of the first Nutrient Platform member meeting in 2019. The members Meststoffen NL, Agro America and Avebe joined forces to facilitate this meeting. Curious about what the meeting looked like? Watch the video here (in Dutch). The program started with a presentation from Wageningen UR about circularity in agriculture and the Next Level Manure Valuation project. The new SusPhos company showed how they are actively working on recovering phosphate from ash and Van Iperen shared their insights from the fertilizer side about the use of recovered nutrients. After these introductions it was time for real matchmaking. During three different round table discussions, the participants looked at products from waste water streams, animal waste streams and organic waste streams. Agro America, BMC, SusPhos, IRS (Royal Cosun / SuikerUnie) and the water boards presented their products to the Nutrient Platform members and to the producers and distributors of Meststoffen NL. For some members this immediately resulted in follow-up agreements. The discussions provided the secretariat of the Nutrient Platform with new action points and suggestions to facilitate the use of recovered nutrients.Netherlands Nutrient Platform www.nutrientplatform.org/ and meeting video: www.youtube.com/watch?v=uXUAwWUcJ2A

Research
H2020 calls on Critical Raw Materials
Two calls are open for Horizon Europe R&D funding on circular economy and Critical Raw Materials, both 2-stage with first deadline 6 February 2020. The first call looks for innovative pilots and scale-up of (non-energy, non-agriculture) circular and Critical Raw Materials production technologies TRL 6-7, including market uptake and link to the EC Raw Materials Information System RMIS. Actions can include: processing of primary or secondary raw materials, recycling from end-of-life products. The second call is for expert network(s) to cover all EU Critical Raw Materials (current list and/or under evaluation and/or future lists).Call: “Raw materials innovation for the circular economy: sustainable processing, reuse, recycling and recovery schemes” CE-SC5-07-2020 https://ec.europa.eu/info/funding-tenders/opportunities/portal/screen/opportunities/topic-details/ce-sc5-08-2020
Call: “Raw materials policy support actions for the circular economy - Expert network on Critical Raw Materials” CE-SC5-08-2020 https://ec.europa.eu/info/funding-tenders/opportunities/portal/screen/opportunities/topic-details/ce-sc5-08-2020
Horizon Europe “Missions” and cluster themes defined
The EU institutions have agreed the key aspects of Horizon Europe, the EU’s 9th research and innovation funding programme, which will follow on from Horizon 2020 and run from 2021 to 2028 with an expected budget of around 100 billion € EU funding. Horizon Europe will be structured in four “Pillars”: I - Excellent Science (inc. Marie-Curie networks), II - “Global Challenges and European Industrial Competitiveness”, III - Innovative Europe (inc. SMEs = now EIC) and IV - Widening participation & ERA. Pillar II will have seven “Clusters”: Health; Culture and inclusive society; Civil security; Digital & space; Climate, energy, mobility; Food, bioeconomy, natural resources, agriculture & environment and JRC. The 6th cluster “Food, bioeconomy, natural resources, agriculture & environment” is of strong relevance to phosphorus sustainability. Also, five “Missions” have been decided, which will be horizontal across all pillars with objectives to “boost the impact of EU-funded research and innovation by mobilising investment and EU wide efforts around measurable and time-bound goals around issues that affect citizens’ daily lives”. The five “Missions” are: (1) Adaptation to Climate Change including Societal Transformation; 2 - Cancer; 3 - Healthy Oceans, Seas, Coastal and Inland Waters; 4 - Climate-Neutral and Smart Cities; 5 - Soil Health and Food. Nutrients are central to the 5th mission, and also relevant to the 2nd mission.Horizon Europe “Missions” announced (4/7/19)
https://ec.europa.eu/info/news/commission-launches-work-major-research-and-innovation-missions-cancer-climate-oceans-and-soil-2019-jul-04_en
“Political agreement” on Horizon Europe (reached between Council, Parliament and the Commission), April 2019: statement http://europa.eu/rapid/press-release_STATEMENT-19-2163_en.htm and full document as adopted by Parliament (17/4/2019) www.europarl.europa.eu/doceo/document/TA-8-2019-0396_EN.html
European Commission proposal published FP9 regulation proposal published (7/6/18)
http://europa.eu/rapid/press-release_IP-18-4041_en.htm
and https://ec.europa.eu/info/designing-next-research-and-innovation-framework-programme/what-shapes-next-framework-programme_en

Sweden: sewage and manure nutrient recycling geo-distribution challenges
Currently Sweden supplies 81% of its crop nitrogen (N) need from mineral fertilisers, 38% of phosphorus (P) and 33% of potassium (K). Livestock manure and human excreta also supply 55% + 20% of N, 65% + 16% of P and 151% + 16% of K, showing significant (localised) nutrient supply surpluses. A study assesses to what extent nutrients in livestock manure and human excreta could supply crop needs. Figures of 11 gN, 1.5 gP and 3.6 gK per person per day for nutrients in human excreta* and for nutrients in different animal manures were combined with municipality human and livestock population data. Crop needs were estimated based on agricultural district data, nutrient needs for different crops and soil data. The study concludes that human excreta and animal manure could cover 75% of crop N needs and 81% of P needs, with a 67% K** excess. However, necessary movement of manures and human excreta from livestock density and high human population areas to crop production areas would generate 24 000 km/year of truck movements (estimated cost 200 M€/year), based on wet weight of manure (solid or slurry), urine and faeces, assuming 100% nutrient collection and availability from both human and livestock excreta (so effectively assuming 100% separative collection of human urine and faeces) but discounting N losses in storage.“Enhancing nutrient recycling from excreta to meet crop nutrient needs in Sweden – a spatial analysis”, U. Akram, N-H. Quttineh, U. Wennergren, K. Tonderski, G. Metson, Scientific Reports volume 9, Article number: 10264 (2019), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46706-7
* calculated from Supplementary Table 2. ** the figure for K is corrected, the number in the study abstract was missing 16%
Cost-effective phosphorus management on arable farms
The final report of the UK Sustainable Arable LINK study (AHDB) concludes that phosphorus (P) management in arable farming should become “crop focused” rather than targeting only soil P status, with grain P content a much more reliable management tool than soil P analysis. Results are based on field trial data from twelve site-seasons (9 sites) and from soil P data over seven years in the UK. Field tramline trials confirmed that crop yields were significantly affected by soil P status in soils with low P, but showed that new P applications in soils with low or variable P status, generally increased crop yield, but were not necessarily cost-effective (cost of fertiliser), whereas crop yield was significantly impacted by long-term soil phosphorus. Grain P content showed to be a good indicator of crop responsiveness to P (i.e. of whether or not P fertiliser application was necessary) and was more reliable (but more expensive) than soil Olsen P analysis. Routine soil Olsen P results were so variable as to be very unreliable unless several analyses were taken nearby, probably because of inherent variability of P fixation within soil. Annual grain P analysis is recommended to both calculate P offtake with harvest and to predict future P fertiliser requirements. For a given soil P status, soil P rundown was significantly faster where soil P status had been recently built up to Index 2 (compared to soils where it had been maintained at Index 2 for some time). Whereas current agronomic recommendation is to maintain soil P at Index 2, it was cost effective for some crop rotations to maintain soil P at Index 1 only (for other rotations, Index 2 should be maintained). The report underlines that initial take-up of P fertilisers by arable crops was only 4% and overall <8%, showing “massive scope for improvement”, whereas the cost of P fertilisers used in the UK is over 100 M€ per year. Nonetheless, around one quarter of cereal crops in the UK are P-deficient and would benefit from increased P fertilization. A table of revised default values for P-removal from soil by different crops is proposed. The report proposes the establishment of a farm “Phosphorus Efficiency Network” and recommends further R&D into: testing products and practices for P efficiency, improving P monitoring (analysis, standards, benchmarks …) and dissemination of best practice and science.“Final Project Report. Cost-effective Phosphorus Management on UK Arable Farms” (includes the report on “Work-Package 3: Improving the efficiency of fresh P applications”), R. Sylvester-Bradley et al., March 2019, 66 pages, AHDB (UK Agriculture and Horticulture Development Board) project report n° 570 https://cereals.ahdb.org.uk/media/1487193/pr570-final-project-report-wp3.pdf

Biochar and compost tested as fertilising products
The results of the EU-funded FERTIPLUS (7th FP) project are now published in “Agronomy”. Biochar (from oak tree biomass) and composts from olive mill by-products, green waste and biowaste (municipal solid organic wastes) and from sheep manure were tested at 20 – 100 tonnes/ha in one to three year field trials in four crop systems: olive groves in Spain, greenhouse tomatoes in Spain, arable rotation in Belgium and vineyards in Italy. The biochar alone had no fertiliser effect (because of its very low nutrient content) but both biochar and composts, and the two together, showed in most trials to increase soil organic carbon, water retention and nutrient availability and to improve soil pH. They showed no negative impacts on crop yield and in some cases led to improved crop qualities. The conclusion is that biochar and compost can contribute to support and maintain soil fertility.“Agronomic Evaluation of Biochar, Compost and Biochar-Blended Compost across Different Cropping Systems: Perspective from the European Project FERTIPLUS”, M. Sánchez-Monedero et al., Agronomy 2019, 9, 225; http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9050225
Struvite recovery uses less “emergy” than mineral fertiliser production
A desk study presents “emergy” accounting for struvite recovery from municipal wastewater (based on data from Ostara 2013 for Crystal Green struvite) and compares to mineral fertiliser production (DAP, based on data from Mosaic and from Agrium, both 2013).“Emergy” is stated to be the “available energy required directly and indirectly to make a product”. The paper concludes that, taking into account variability of data for DAP production and also for struvite (e.g. possible economies from scale-up, with or without WASSTRIP), the “emergy” for recovered struvite is in all scenarios significantly lower than for DAP.“Nutrient Recovery from Municipal Wastewater for Sustainable Food Production Systems: An Alternative to Traditional Fertilizers”, Env. Eng. Science 2019 http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/ees.2019.0053
Nitrification inhibitor impacts struvite plant availability
Struvite recovered from dairy wastewater (Phos-Paques) was assessed in 65-day pot trials with rye grass, comparing to conventional magnesium and phosphate fertilisers (Epsom Salts - magnesium sulphate, TSP - triple super phosphate), with and without addition of the nitrification inhibitor DCD (dicyandiamide). Soil was nutrient poor, sandy, pH 5.5. In these conditions, struvite was as effective or better than the conventional fertilisers for rye grass shoot growth and for phosphorus and magnesium uptake, with no significant impact of whether the struvite was fresh, air dried, or heat dried (40°C). The magnesium uptake could be positive to redress declining magnesium in many crops over recent decades (e.g. cereals). The nitrification inhibitor slowed short-term phosphorus uptake from struvite in some of the tests, probably because it inhibited struvite breakdown because of struvite’s ammonium content. This could in some circumstances be significant where crops need rapid early phosphorus supply for growth.“Plant availability of magnesium and phosphorus from struvite with concurrent nitrification inhibitor application”, C. Watson, J. Clemens, F. Wichern, within the Interreg Food Pro.tec project, Soil Use Management 2019, 00:1-8 https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12527
Different phytases show varying benefits for poultry
Tests carried out for DuPont looked at effects on phosphate uptake by chickens with two different phytase enzymes, and also at digestion of protein and sodium and overall growth. A total of 1152 broilers were fed controlled diets for 16 days. The two phytases were produced by different bacteria: E. coli and Buttiauxella sp. Increasing phytase doses (or increasing phosphate food additive MCP mono calcium phosphate) resulted in improved feed intake and weight gain, but effects were greater for the Buttiauxella phytase. This phytase, but not the E. coli phytase, showed to improve protein digestibility. The authors conclude that “non phosphate” effects of phytases are not necessarily correlated to effects on phosphorus uptake, and can vary between different phytases.“Comparative effects of two phytases versus increasing the inorganic phosphorus content of the diet, on nutrient and amino acid digestibility in boilers”, Y. Dersjant-Li, C. Kwakernaak, Animal Feed Science and Technology 253 (2019) 166–180, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2019.05.018
ESPP members
Up to date list of members: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/members
Stay informed
SCOPE newsletter: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/SCOPEnewslettereNews newsletter: www.phosphorusplatform.eu/eNewshome
If you do not already receive SCOPE and eNews (same emailing list), subscribe at www.phosphorusplatform.eu/subscribe
LinkedIn group: www.linkedin.com/groups/4783093 (or search for European Sustainable Phosphorus Platform)
Twitter: @phosphorusfacts
Slideshare presentations: www.slideshare.net/NutrientPlatform

